
In trapezium ABCD, \[M \in \overline {AD} ,N \in \overline {BC} \] are the points such \[\dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{{BN}}{{NC}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]. The diagonal \[\overline {AC} \] intersects \[\overline {MN} \] at\[O\]. Then find the value of \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{AC}}\].
Answer
620.1k+ views
Hint: A trapezium is a 2D shape which falls under the category of quadrilaterals. A trapezium has two parallel sides and two non-parallel sides. Using this information first draw the diagram with the given data and solve the problem accordingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given trapezium ABCD, \[\overline {AB} \parallel \overline {CD} \], \[M\] and \[N\]are the points on the traversals \[\overleftrightarrow {AD}\] and \[\overleftrightarrow {BC}\] respectively as shown in the below diagram.
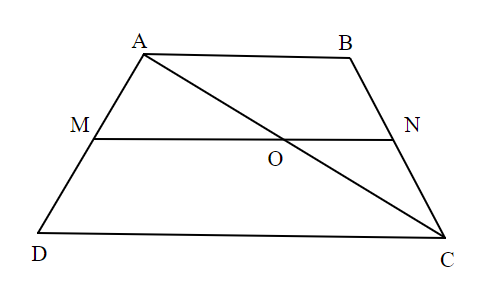
Also, given \[\dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{{BN}}{{NC}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
So, clearly from the diagram, \[\overline {MN} \parallel \overline {AB} \] and \[\overline {AB} \parallel \overline {CD} \].
Given that diagonal \[\overline {AC} \] intersects \[\overline {MN} \] at \[O\].
In \[\Delta ADC\], \[\overline {MO} \parallel \overline {DC} \] such that \[M \in \overline {AD} {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}O \in \overline {AC} \].
We know that by the Triangle Proportionality theorem, if a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides of the triangle, then the lines divide these two sides proportionally.
By using this property in \[\Delta ADC\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}}\]
But we have \[\dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
So, \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
We have to find \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{AC}}\]. From the diagram, \[OC = AO + OC\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{AO + OC}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{{2 + 3}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{5} \\
\]
Thus, \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{5}\].
Note: The length of the mid-segment is equal to half of the sum of parallel bases in a trapezium. In this problem we have used both the properties of triangles as well as the properties of trapezium.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given trapezium ABCD, \[\overline {AB} \parallel \overline {CD} \], \[M\] and \[N\]are the points on the traversals \[\overleftrightarrow {AD}\] and \[\overleftrightarrow {BC}\] respectively as shown in the below diagram.

Also, given \[\dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{{BN}}{{NC}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
So, clearly from the diagram, \[\overline {MN} \parallel \overline {AB} \] and \[\overline {AB} \parallel \overline {CD} \].
Given that diagonal \[\overline {AC} \] intersects \[\overline {MN} \] at \[O\].
In \[\Delta ADC\], \[\overline {MO} \parallel \overline {DC} \] such that \[M \in \overline {AD} {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}O \in \overline {AC} \].
We know that by the Triangle Proportionality theorem, if a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides of the triangle, then the lines divide these two sides proportionally.
By using this property in \[\Delta ADC\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}}\]
But we have \[\dfrac{{AM}}{{MD}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
So, \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
We have to find \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{AC}}\]. From the diagram, \[OC = AO + OC\]
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{{AO}}{{AO + OC}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{{2 + 3}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{5} \\
\]
Thus, \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{OC}} = \dfrac{2}{5}\].
Note: The length of the mid-segment is equal to half of the sum of parallel bases in a trapezium. In this problem we have used both the properties of triangles as well as the properties of trapezium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




