
In this diol:
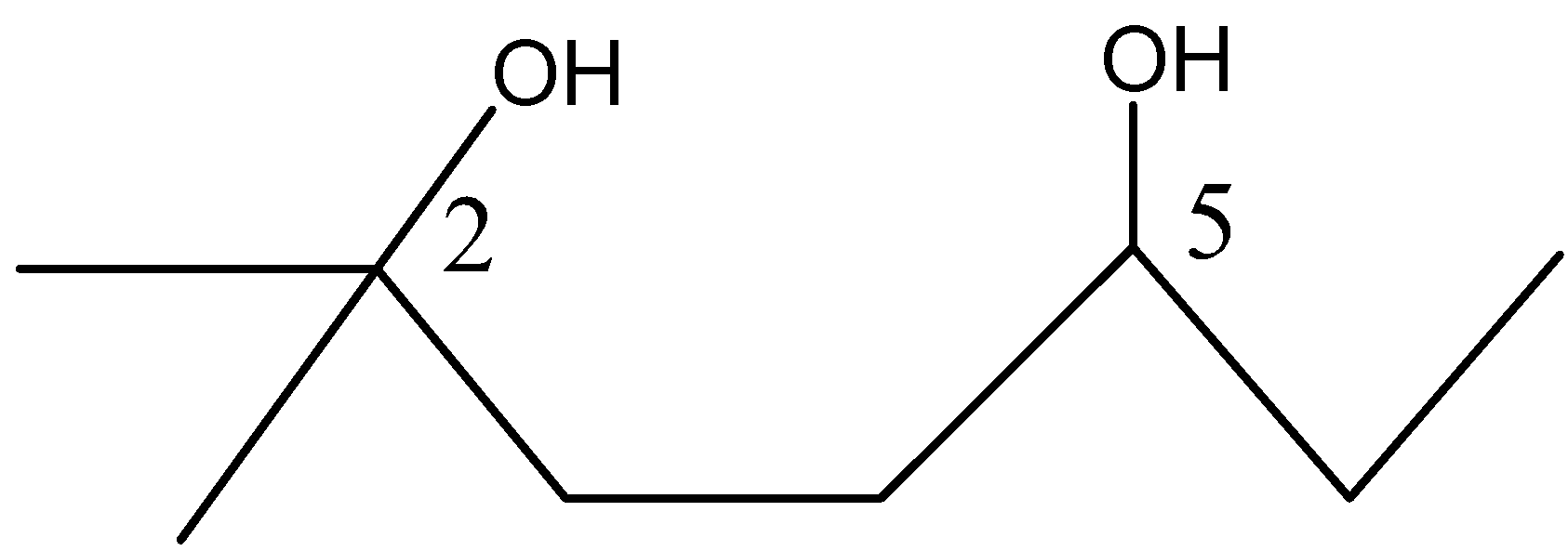
A) $O{{H}^{-}}$ of ${{C}_{2}}$ is more basic than that of at ${{C}_{5}}$
B) $O{{H}^{-}}$ of ${{C}_{2}}$ is more acidic than at ${{C}_{5}}$
C) Both have same basicity
D) Both have same acidic strength

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The answer here is based upon the basicity of the alcohols that is the decreasing order of the alcohols is tertiary > secondary > primary. This fact leads you to the required answer.
Complete Solution :
In the classes of organic chemistry, we have come across the concepts that deals with the acidity, basicity and neutrality of the given solutions.
Now, let us see the trends in which the basicity or acidity depends for which we must know their definitions.
- Acidity is the tendency of a substance to act as a proton donor that is the chemical that gives or donates the protons in water that acts as medium which can further form salts.
- Basicity on the other hand is the measure of the acceptance of protons, that is the tendency of accepting a proton from water to neutralise an acid.
Therefore based on these definitions we can say that option B) and D) are ruled out as there is presence of $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion that has a tendency to accept protons.
- Now, according to the trends of basicity of alcohols that is tertiary > secondary > primary, the tertiary carbocation formed after the removal water molecules when $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion accepts a proton will be more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than primary.
The reaction is as follows:
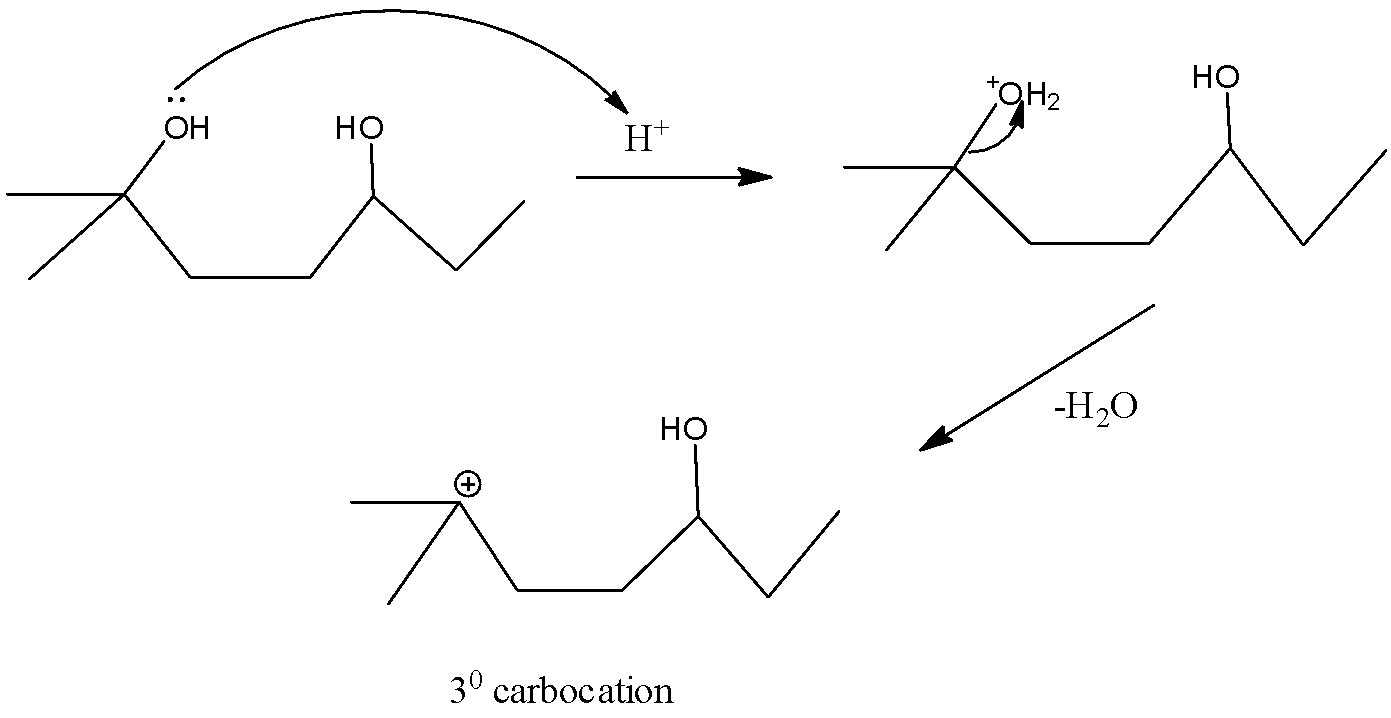
Thus, tertiary carbocation will be formed by the removal of water molecules from the carbon at position 2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) $O{{H}^{-}}$ of ${{C}_{2}}$ is more basic than that of at ${{C}_{5}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that tertiary alcohols are more reactive due to the inductive effect and tertiary carbocations are more stable because they can distribute its positive charge to the three methyl groups.
Complete Solution :
In the classes of organic chemistry, we have come across the concepts that deals with the acidity, basicity and neutrality of the given solutions.
Now, let us see the trends in which the basicity or acidity depends for which we must know their definitions.
- Acidity is the tendency of a substance to act as a proton donor that is the chemical that gives or donates the protons in water that acts as medium which can further form salts.
- Basicity on the other hand is the measure of the acceptance of protons, that is the tendency of accepting a proton from water to neutralise an acid.
Therefore based on these definitions we can say that option B) and D) are ruled out as there is presence of $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion that has a tendency to accept protons.
- Now, according to the trends of basicity of alcohols that is tertiary > secondary > primary, the tertiary carbocation formed after the removal water molecules when $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion accepts a proton will be more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than primary.
The reaction is as follows:

Thus, tertiary carbocation will be formed by the removal of water molecules from the carbon at position 2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) $O{{H}^{-}}$ of ${{C}_{2}}$ is more basic than that of at ${{C}_{5}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that tertiary alcohols are more reactive due to the inductive effect and tertiary carbocations are more stable because they can distribute its positive charge to the three methyl groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




