
In the metal carbonyl of general formula $M{{(CO)}_{x}}$ where M = metal and X=4, the metal is bonded to:
(A) Carbon and Oxygen
(B) Carbon
(C) Oxygen
(D) CO triple bond
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: To understand the bonding between metal and ligand that can tell us who is donating electron pairs to the metal atom, we need to explore the structure of metal carbonyl. The most important point over here is ligands are neutral molecule CO and over all complex compounds don't have any charge which explains that oxidation number of metal will be zero in $M{{(CO)}_{4}}$ type compounds.
Complete answer:
Metal carbonyl: when CO d0nate its lone pair to metals such as nickel, cobalt, or iron surrounded by carbonyl (CO) groups. Some common metal carbonyls include: $Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}$, $Fe{{(CO)}_{5}}$Vetc.
Structure of CO:
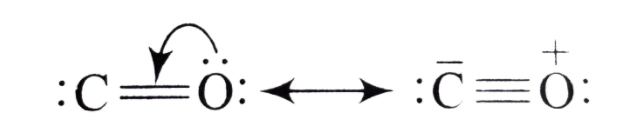
As you can in the structure of CO, oxygen is donating its lone pair to the vacant orbital of carbon and that’s why it is having formal negative charge and oxygen is having formal positive. So clearly Carbon is having two lone pairs and formal negative, which makes it the usual donor.
Structure of $M{{(CO)}_{4}}$: CO is a strong field ligand, over here compound formed will be low spin complex, so structure of the compound will be tetrahedral where carbon will donate the lone pair to the metal atom. So over here Carbon will form the bond with metal.
Correct answer is Option (B).
Additional Information: An important aspect of CO binding is called "back-donation". In back-donation, not only does the ligand donate electrons to the metal, but the metal also donates to the ligand.
Note: Spectrochemical series is the important series that help us to decide the strength of ligands. According to that generally the ligands where the donor atom has the high electronegativity is a weak field ligand and generally the ligands like cyanide ion, CO etc. where the donor atom is carbon are strong field ligands.
Complete answer:
Metal carbonyl: when CO d0nate its lone pair to metals such as nickel, cobalt, or iron surrounded by carbonyl (CO) groups. Some common metal carbonyls include: $Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}$, $Fe{{(CO)}_{5}}$Vetc.
Structure of CO:

As you can in the structure of CO, oxygen is donating its lone pair to the vacant orbital of carbon and that’s why it is having formal negative charge and oxygen is having formal positive. So clearly Carbon is having two lone pairs and formal negative, which makes it the usual donor.
Structure of $M{{(CO)}_{4}}$: CO is a strong field ligand, over here compound formed will be low spin complex, so structure of the compound will be tetrahedral where carbon will donate the lone pair to the metal atom. So over here Carbon will form the bond with metal.
Correct answer is Option (B).
Additional Information: An important aspect of CO binding is called "back-donation". In back-donation, not only does the ligand donate electrons to the metal, but the metal also donates to the ligand.
Note: Spectrochemical series is the important series that help us to decide the strength of ligands. According to that generally the ligands where the donor atom has the high electronegativity is a weak field ligand and generally the ligands like cyanide ion, CO etc. where the donor atom is carbon are strong field ligands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




