
In the following species, the one which is likely to be the intermediate during the benzoin condensation of benzaldehyde is:
[A]
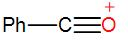
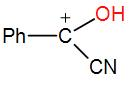
[B]
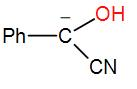
[C]
[D]
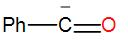
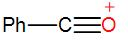


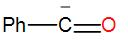
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Benzoin condensation is an addition reaction. Here, we use cyanide as a nucleophile which attacks the other aldehyde and gives us the required product. Therefore, the intermediate formed will have a cyanide group .
Complete step by step answer:
We know that benzoin condensation is an addition reaction between two aldehydes. The most common application of benzoin condensation is conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoin. The conversion is-
\[PhCHO\xrightarrow{C{{N}^{-}},{{H}_{2}}O/EtOH}PhCHCPh\]
As we can see in the above reaction, benzaldehyde in presence of cyanide undergoes benzoin condensation to give us benzoin as the final product.
Let us discuss the mechanism of the reaction of conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoin in order to find out which intermediate is likely to be formed.
In this reaction, we use a cyanide nucleophile in the first step. The cyanide anion undergoes nucleophilic addition with the aldehyde (which is benzaldehyde in this case) and forms an intermediate. (We know that an aldehyde is a compound with a –CHO functional group.) Rearranging the intermediate results in the reversal of polarity of the carbonyl group and to this another carbonyl group attacks and undergoes a nucleophilic addition once again. Then the cyanide group is eliminated through proton transfer and forms the benzoin product. We can write the reaction mechanism as-
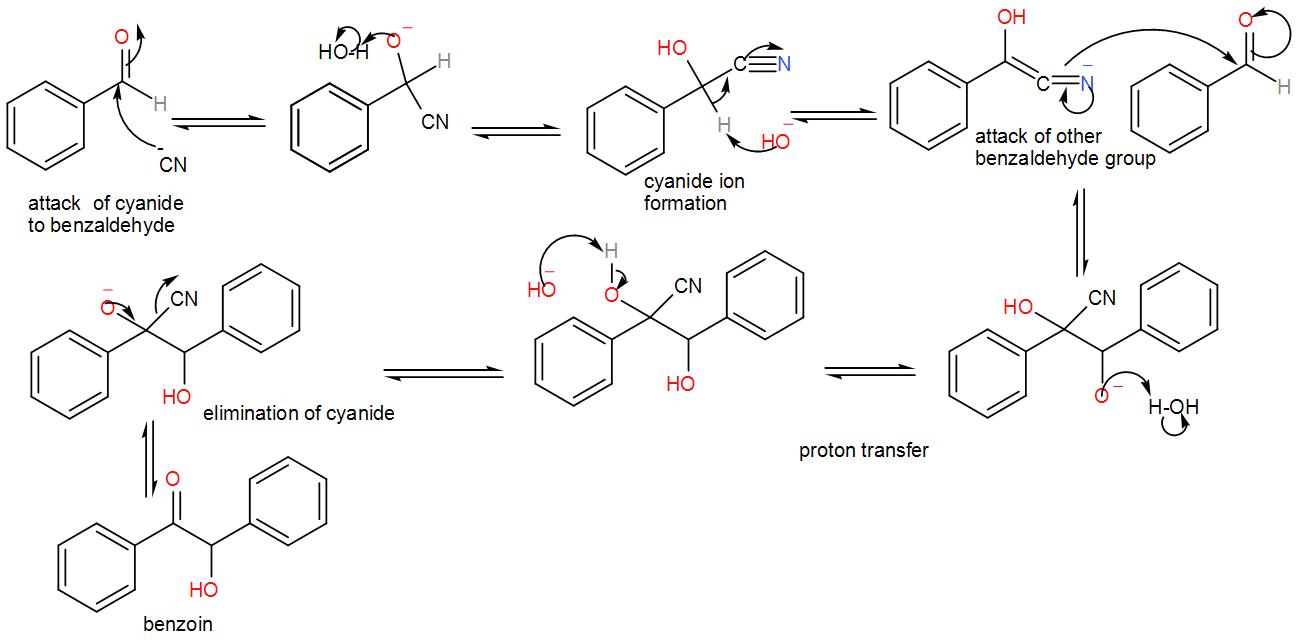
Here, as we can see from the above reaction and the discussion, the intermediate attacks on the other carbonyl group. Therefore, the intermediate is –
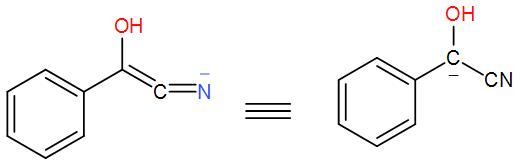
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
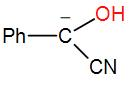
Note: In this reaction, one aldehyde donated proton and the other accepts the proton as benzaldehyde is both proton acceptor and a proton donor. Therefore, it could accept as well as donate protons here. There are some aldehydes which can only donate protons or accept protons.
Also, this reaction is reversible which means we can determine the distribution of products by the relative stability of the reactant and the product.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that benzoin condensation is an addition reaction between two aldehydes. The most common application of benzoin condensation is conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoin. The conversion is-
\[PhCHO\xrightarrow{C{{N}^{-}},{{H}_{2}}O/EtOH}PhCHCPh\]
As we can see in the above reaction, benzaldehyde in presence of cyanide undergoes benzoin condensation to give us benzoin as the final product.
Let us discuss the mechanism of the reaction of conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoin in order to find out which intermediate is likely to be formed.
In this reaction, we use a cyanide nucleophile in the first step. The cyanide anion undergoes nucleophilic addition with the aldehyde (which is benzaldehyde in this case) and forms an intermediate. (We know that an aldehyde is a compound with a –CHO functional group.) Rearranging the intermediate results in the reversal of polarity of the carbonyl group and to this another carbonyl group attacks and undergoes a nucleophilic addition once again. Then the cyanide group is eliminated through proton transfer and forms the benzoin product. We can write the reaction mechanism as-

Here, as we can see from the above reaction and the discussion, the intermediate attacks on the other carbonyl group. Therefore, the intermediate is –
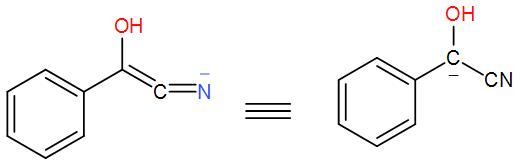
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.

Note: In this reaction, one aldehyde donated proton and the other accepts the proton as benzaldehyde is both proton acceptor and a proton donor. Therefore, it could accept as well as donate protons here. There are some aldehydes which can only donate protons or accept protons.
Also, this reaction is reversible which means we can determine the distribution of products by the relative stability of the reactant and the product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




