
In the following reaction, the major product is:
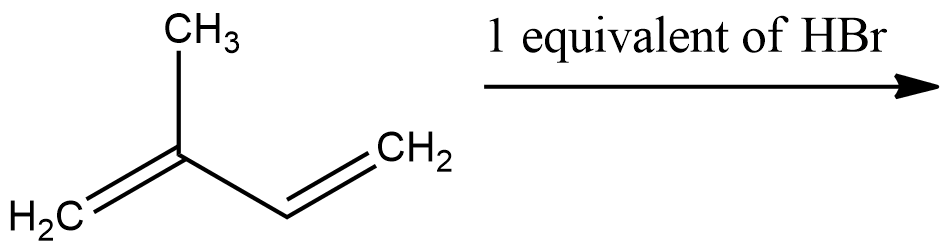
(A)
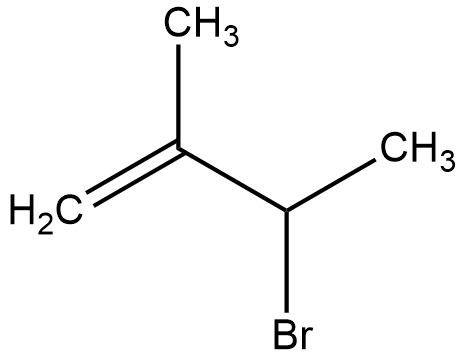
(B)
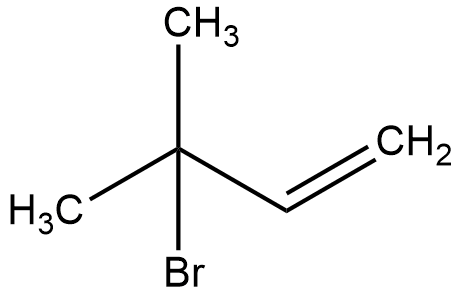
(C)

(D)
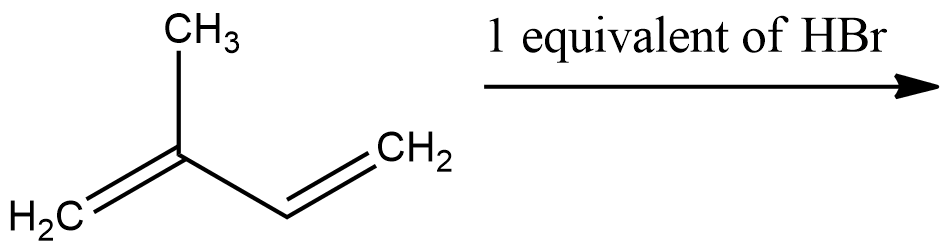




Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Think about the additional reaction of hydrogen bromide to alkenes. Think about the Markovnikoff’s rule which is applicable to additional reactions of asymmetric unsaturated compounds. Try to find out the mechanism in which this reaction will take place and think about the stability of the intermediate form and then complete the reaction.
Complete answer:
- The given reactant is 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene. It is an asymmetric alkene.
- According to the reaction, 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene is treated with one equivalent of HBr and we need to find out the major product.
- This an example of an additional reaction to asymmetric alkenes which will obey Markovnikoff’s rule.
- According to Markovnikoff’s rule, in an addition to asymmetric alkene, the major product formed will have the nucleophile or electronegative atom attached to that carbon atom which has less number of hydrogen atoms. So, protons will attack on carbon atoms having more number of hydrogen atoms.
- Now, in the given compound, there are two double bonds and only one equivalent of HBr is given. So, in the product only one double bond will be saturated and the other will remain unsaturated.
- This reaction will proceed by formation of carbocation intermediate. HBr will split to form ${{H}^{+}}$ and $B{{r}^{-}}$. Now, bromide ion will be the nucleophile which will attack the carbocation formed and form the product.
- The possibilities are shown as follows:
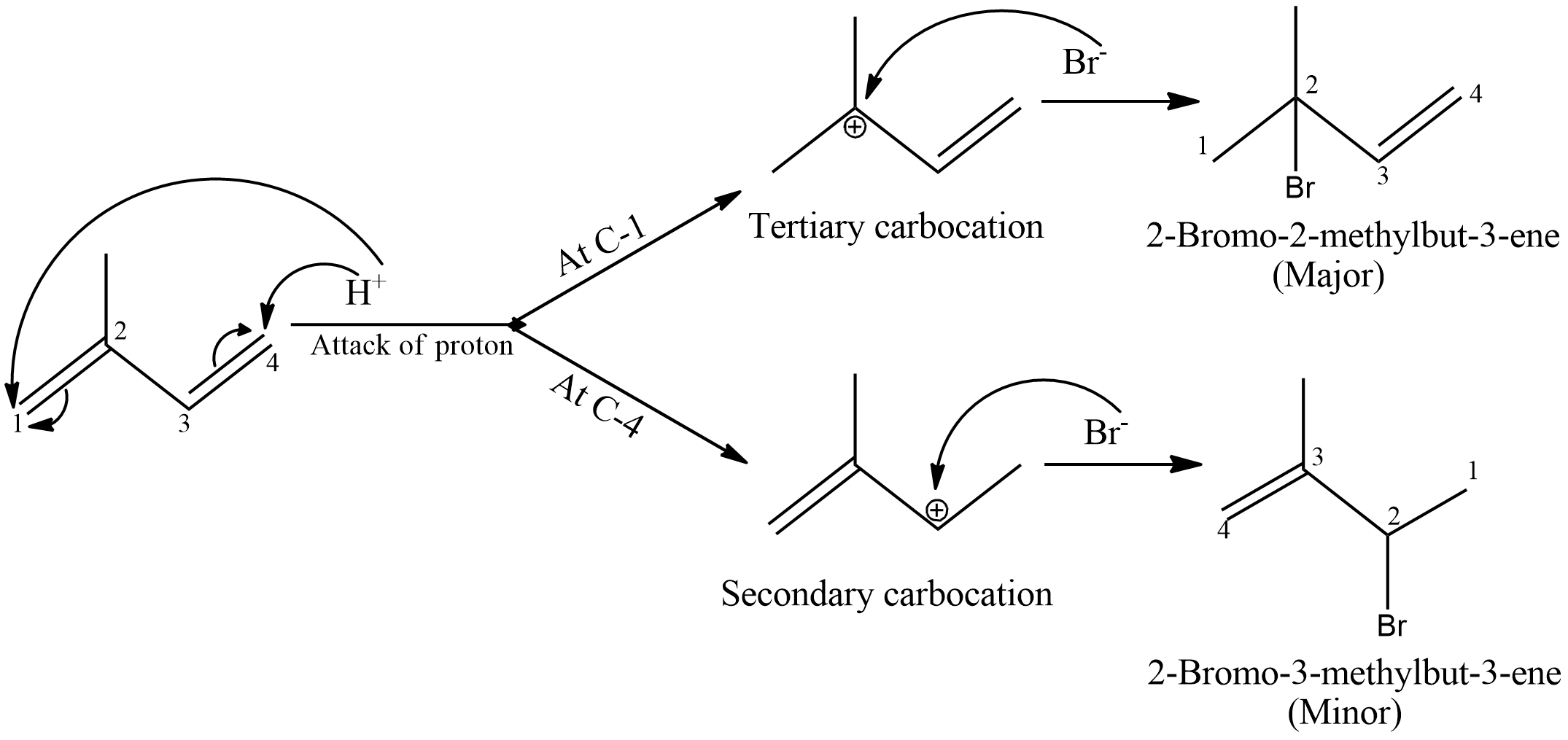
- Proton attack will happen only on C-1 and C-4 because of Markovnikoff’s rule.
- We know tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation due to hyperconjugation effects. Therefore, even the secondary carbocation will try to show hydrogen shift and get converted to tertiary carbocation.
- Therefore, 2-Bromo-2-methylbut-3-ene will be formed as the major product in this reaction.
Therefore, the answer is option (B).
Note:
Remember the major product formed will be dependent on the stability of the intermediates formed during the reaction. Try to write the mechanism in such a problem to get the answer. Remember Markovnikoff’s rule is applicable to addition of asymmetric alkenes. In case, peroxide is present in the reaction then, Anti-Markovnikov's rule will be applicable.
Complete answer:
- The given reactant is 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene. It is an asymmetric alkene.
- According to the reaction, 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene is treated with one equivalent of HBr and we need to find out the major product.
- This an example of an additional reaction to asymmetric alkenes which will obey Markovnikoff’s rule.
- According to Markovnikoff’s rule, in an addition to asymmetric alkene, the major product formed will have the nucleophile or electronegative atom attached to that carbon atom which has less number of hydrogen atoms. So, protons will attack on carbon atoms having more number of hydrogen atoms.
- Now, in the given compound, there are two double bonds and only one equivalent of HBr is given. So, in the product only one double bond will be saturated and the other will remain unsaturated.
- This reaction will proceed by formation of carbocation intermediate. HBr will split to form ${{H}^{+}}$ and $B{{r}^{-}}$. Now, bromide ion will be the nucleophile which will attack the carbocation formed and form the product.
- The possibilities are shown as follows:

- Proton attack will happen only on C-1 and C-4 because of Markovnikoff’s rule.
- We know tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation due to hyperconjugation effects. Therefore, even the secondary carbocation will try to show hydrogen shift and get converted to tertiary carbocation.
- Therefore, 2-Bromo-2-methylbut-3-ene will be formed as the major product in this reaction.
Therefore, the answer is option (B).
Note:
Remember the major product formed will be dependent on the stability of the intermediates formed during the reaction. Try to write the mechanism in such a problem to get the answer. Remember Markovnikoff’s rule is applicable to addition of asymmetric alkenes. In case, peroxide is present in the reaction then, Anti-Markovnikov's rule will be applicable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




