
In the following reaction, identify $X$.
\[\text{Methyl}\,\text{magnesium}\,\text{bromide}\,+X\to \text{2-}\,\text{methyl}\,\text{propan}\,\text{2-ol}\]
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: A formation of a new C-C bond can be seen in the product formed. Also, the methyl magnesium bromide compound, the electropositive nature of magnesium makes the adjacent alkyl group to become partially negative. Thus, involving a nucleophilic substitution in the given reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, the reactant methyl magnesium bromide is in the form of R-Mg-X which is a Grignard reagent, where R is the methyl group and X is the bromide group.
It is formed by the reaction of the magnesium metal with the methyl bromide in presence of diethyl ether. They have a highly polarized C-Mg bond, making it highly reactive in nature.
\[C{{H}_{3}}-Br+Mg\,\,\xrightarrow{ether}\,\,\overset{-}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}}}\,-\overset{+}{\mathop{Mg}}\,-Br\]
Then, in the product side of the given reaction it is seen that a new carbon-carbon single bond is formed with the formation of alcohol, that is, $\text{2-}\,\text{methyl}\,\text{propan}\,\text{2-ol}$.
We can obtain this by the reaction of the Grignard reagent with a carbonyl compound such as acetone. The reaction involves the attack on the carbonyl carbon of the acetone by the nucleophilic carbon of Grignard reagent which is highly polarized. Thus, breaking the $C=O$ bond and forming magnesium tert- butoxide as the intermediate.
On acid work-up, that is ${{H}_{2}}O/{{H}^{+}}$ , the hydrolysis of the intermediate alkoxide species takes place. It gets protonated at the $O-MgBr$ bond. Thus, giving us the corresponding alcohol, that is, $\text{2-}\,\text{methyl}\,\text{propan}\,\text{2-ol}$.
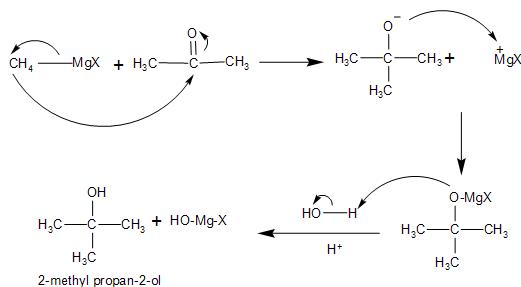
Therefore, the compound $X$ in the given reaction is acetone.
Note: The Grignard reagent being used with a polarized C-Mg bond. It makes it act as a good nucleophile and strong base. So, measures must be taken to keep the water molecules away from it as it may react with water, getting protonated and forming alkanes. So, in order to prevent this, we have used diethyl ether in the reaction as it is a good solvent, which helps in stabilising the magnesium ion.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, the reactant methyl magnesium bromide is in the form of R-Mg-X which is a Grignard reagent, where R is the methyl group and X is the bromide group.
It is formed by the reaction of the magnesium metal with the methyl bromide in presence of diethyl ether. They have a highly polarized C-Mg bond, making it highly reactive in nature.
\[C{{H}_{3}}-Br+Mg\,\,\xrightarrow{ether}\,\,\overset{-}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}}}\,-\overset{+}{\mathop{Mg}}\,-Br\]
Then, in the product side of the given reaction it is seen that a new carbon-carbon single bond is formed with the formation of alcohol, that is, $\text{2-}\,\text{methyl}\,\text{propan}\,\text{2-ol}$.
We can obtain this by the reaction of the Grignard reagent with a carbonyl compound such as acetone. The reaction involves the attack on the carbonyl carbon of the acetone by the nucleophilic carbon of Grignard reagent which is highly polarized. Thus, breaking the $C=O$ bond and forming magnesium tert- butoxide as the intermediate.
On acid work-up, that is ${{H}_{2}}O/{{H}^{+}}$ , the hydrolysis of the intermediate alkoxide species takes place. It gets protonated at the $O-MgBr$ bond. Thus, giving us the corresponding alcohol, that is, $\text{2-}\,\text{methyl}\,\text{propan}\,\text{2-ol}$.

Therefore, the compound $X$ in the given reaction is acetone.
Note: The Grignard reagent being used with a polarized C-Mg bond. It makes it act as a good nucleophile and strong base. So, measures must be taken to keep the water molecules away from it as it may react with water, getting protonated and forming alkanes. So, in order to prevent this, we have used diethyl ether in the reaction as it is a good solvent, which helps in stabilising the magnesium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




