
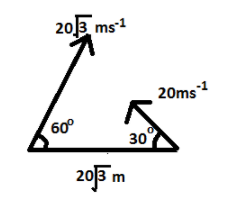
In the figure shown, the two projectiles are fired simultaneously. The minimum distance between them during their flight is

Answer
518.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are first going to look for the figure and write all the information given the velocities, distance and the acceleration. Then, the relative motion is assessed and the relative acceleration and the velocities are calculated after which the minimum distance is calculated.
Formula used:
The minimum distance is given by the formula
\[{d_{\min }} = d\cos \theta \]
Where, \[d\]is the distance between the projectiles and \[\theta \]is the angle difference between them.
Complete answer:
Let us see the figure as given in the question, we see that the velocities of the two projectiles are
$ {v_1} = 20\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\
{v_2} = 20m{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
The velocity of the projectiles with respect to the horizontal axes are:
$ {v_{1x}} = - 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\
{v_{2y}} = 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
The distance between the two projectiles at the time of firing is
\[d = 20\sqrt 3 m\]
The acceleration of the two projectiles are
$ {a_1} = g \\
{a_2} = g \\ $
Thus, the relative acceleration of the two projectiles is
\[{a_{12}} = 0\]
Thus we see that the relative motion of the projectiles is uniform.
The relative velocity of the two projectiles can be calculated as
\[{v_{21}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {20\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2}} \]
Now, the minimum distance is given by the formula
\[{d_{\min }} = d\cos {60^ \circ }\]
Putting the value of the initial distance between the projectiles, we get
\[{d_{\min }} = 20\sqrt 3 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 10\sqrt 3 \,m\]
Note: Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. The two projectiles fired simultaneously have the zero relative acceleration which makes it the uniform relative motion.
Formula used:
The minimum distance is given by the formula
\[{d_{\min }} = d\cos \theta \]
Where, \[d\]is the distance between the projectiles and \[\theta \]is the angle difference between them.
Complete answer:
Let us see the figure as given in the question, we see that the velocities of the two projectiles are
$ {v_1} = 20\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\
{v_2} = 20m{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
The velocity of the projectiles with respect to the horizontal axes are:
$ {v_{1x}} = - 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\
{v_{2y}} = 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}} \\ $
The distance between the two projectiles at the time of firing is
\[d = 20\sqrt 3 m\]
The acceleration of the two projectiles are
$ {a_1} = g \\
{a_2} = g \\ $
Thus, the relative acceleration of the two projectiles is
\[{a_{12}} = 0\]
Thus we see that the relative motion of the projectiles is uniform.
The relative velocity of the two projectiles can be calculated as
\[{v_{21}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {20} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {20\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2}} \]
Now, the minimum distance is given by the formula
\[{d_{\min }} = d\cos {60^ \circ }\]
Putting the value of the initial distance between the projectiles, we get
\[{d_{\min }} = 20\sqrt 3 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 10\sqrt 3 \,m\]
Note: Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. The two projectiles fired simultaneously have the zero relative acceleration which makes it the uniform relative motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




