
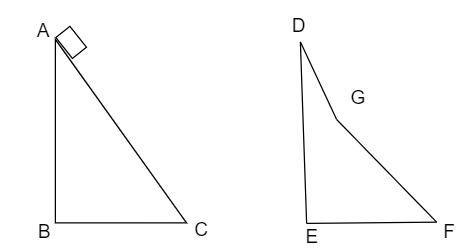
In the figure $\left( A \right)$ and $\left( B \right)$ $AC,\,DG,\,$ and $GF$ are fixed inclined planes, $BC = EF = x$ and $AB = DE = y$. A small block of mass $M$ is released from the point $A$ . It slides down $AC$ and reaches $C$ with a speed ${v_c}$ . The same block is released from rest from the point $D$ . It slides down $DGF$ and reaches the point $F$ with speed ${v_F}$ . The coefficient of kinetic frictions between the block and both the surfaces $AC$ and $DGF$ are $\mu $ . Calculate ${v_c}$ and ${v_F}$ .

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint Analyse the diagram given in the question, and derive the equation of the motion of the block from that. Use the potential energy and the kinetic energy in it. The simplification of the above equation provides the value of the velocity of the block.
Useful formula
(1) The formula of the potential energy is given by
$P = mgh$
Where $P$ is the potential energy, $m$ is the mass of the block, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
(2) The formula of the kinetic energy is given by
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
$K$ is the kinetic energy, $v$ is the velocity of motion.
Complete step by step solution
It is given that the
$AC,\,DG,\,$ and $GF$ are fixed inclined planes
$BC = EF = x$
$AB = DE = y$
The speed at which the $AC$ reaches $C$ is ${v_c}$ .
The speed at which the block slides down $AC$ and reaches $C$ is ${v_c}$
The coefficient of the kinetic friction is considered as $\mu $
It is known that the potential energy of the block is converted into the kinetic energy while moving.
$P - K = {f_2}{s_1} + {f_2}{s_2}$
Substituting the formula in it,
$mgy - \dfrac{1}{2}mv_F^2 = \mu mg\cos \beta {S_1} - \mu mg\cos \alpha {S_2}$
By simplifying the above equation, we get
${v_F} = \sqrt {2g\left( {y - \mu x} \right)} $
Note The friction affects the motion of the body when it rolls or slides down the surface. This is because the surface with the diffraction is rough and this reduces the velocity . This sliding motion is due to the acceleration due to gravity and not due to the external force applied on it.
Useful formula
(1) The formula of the potential energy is given by
$P = mgh$
Where $P$ is the potential energy, $m$ is the mass of the block, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
(2) The formula of the kinetic energy is given by
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
$K$ is the kinetic energy, $v$ is the velocity of motion.
Complete step by step solution
It is given that the
$AC,\,DG,\,$ and $GF$ are fixed inclined planes
$BC = EF = x$
$AB = DE = y$
The speed at which the $AC$ reaches $C$ is ${v_c}$ .
The speed at which the block slides down $AC$ and reaches $C$ is ${v_c}$
The coefficient of the kinetic friction is considered as $\mu $
It is known that the potential energy of the block is converted into the kinetic energy while moving.
$P - K = {f_2}{s_1} + {f_2}{s_2}$
Substituting the formula in it,
$mgy - \dfrac{1}{2}mv_F^2 = \mu mg\cos \beta {S_1} - \mu mg\cos \alpha {S_2}$
By simplifying the above equation, we get
${v_F} = \sqrt {2g\left( {y - \mu x} \right)} $
Note The friction affects the motion of the body when it rolls or slides down the surface. This is because the surface with the diffraction is rough and this reduces the velocity . This sliding motion is due to the acceleration due to gravity and not due to the external force applied on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




