
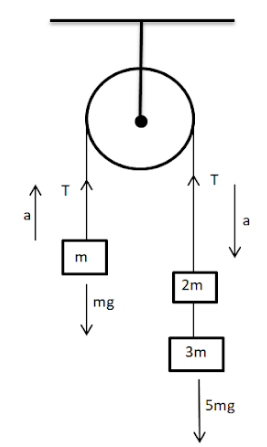
In the figure given below, with what acceleration does the block of mass $m$ will move? (Pulley and strings are massless and frictionless).

Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint:All that is required is the balancing of the forces. The net external force is equal to the sum of the forces acting on the object. Also keep in mind the tension force which comes along whenever strings/ropes are into play.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, $F=ma$ where $F$ is the net external force, m is the mass of the body and $a$ is the acceleration with which the body moves. According to Newton’s third law of motion,to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction force.We know that all physical objects that are in contact can exert forces on each other.Tension is the force exerted by a rope,string,chain etc.Tension is a pulling force transmitted along the axis.
For an object with mass m, the net external force acting on it is the sum of all the forces acting on the object. And according to the second law, net external force is equal to ma.
Let $T$ be the tension in the string going over the pulley. Therefore $ma=T+(-mg)$.......[$mg$ is in the opposite direction to that of the external force,hence a negative sign.]
$T-mg=ma$
$\Rightarrow T=ma+mg$--equation $1$
Let us consider the right hand masses as a single unit of mass $5$m ($3$m+$2$m). For an object with mass $5m$, the net external force acting on it is the sum of all the forces acting on the object. Net external force is equal to 5ma. (According to second law)
Therefore $5$ma=$5$mg+(-T )......[ T is in the opposite direction to that of the external force.]
$5mg-T=5ma$
$\Rightarrow 5mg-5ma=T$--equation 2
Substituting value of $T$ from equation 1 in equation 2, we get
$5mg-5ma=ma+mg$
$\Rightarrow 5mg-mg=ma+5ma$
$\Rightarrow 4mg=6ma$
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{4g}{6}$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2g}{3}$
Hence the acceleration of the block of mass $m$ is $\dfrac{2g}{3}$.
Note:Two or more physical objects that are in contact, exert forces on each other.Based on the objects in contact we give these contact forces different names. If one of these objects in contact happens to be a string, rope, cable or spring, we call the force as tension.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, $F=ma$ where $F$ is the net external force, m is the mass of the body and $a$ is the acceleration with which the body moves. According to Newton’s third law of motion,to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction force.We know that all physical objects that are in contact can exert forces on each other.Tension is the force exerted by a rope,string,chain etc.Tension is a pulling force transmitted along the axis.

For an object with mass m, the net external force acting on it is the sum of all the forces acting on the object. And according to the second law, net external force is equal to ma.
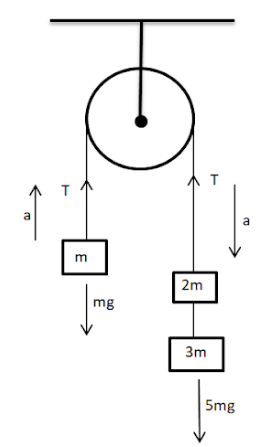
Let $T$ be the tension in the string going over the pulley. Therefore $ma=T+(-mg)$.......[$mg$ is in the opposite direction to that of the external force,hence a negative sign.]
$T-mg=ma$
$\Rightarrow T=ma+mg$--equation $1$
Let us consider the right hand masses as a single unit of mass $5$m ($3$m+$2$m). For an object with mass $5m$, the net external force acting on it is the sum of all the forces acting on the object. Net external force is equal to 5ma. (According to second law)
Therefore $5$ma=$5$mg+(-T )......[ T is in the opposite direction to that of the external force.]
$5mg-T=5ma$
$\Rightarrow 5mg-5ma=T$--equation 2
Substituting value of $T$ from equation 1 in equation 2, we get
$5mg-5ma=ma+mg$
$\Rightarrow 5mg-mg=ma+5ma$
$\Rightarrow 4mg=6ma$
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{4g}{6}$
$\therefore a=\dfrac{2g}{3}$
Hence the acceleration of the block of mass $m$ is $\dfrac{2g}{3}$.
Note:Two or more physical objects that are in contact, exert forces on each other.Based on the objects in contact we give these contact forces different names. If one of these objects in contact happens to be a string, rope, cable or spring, we call the force as tension.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




