
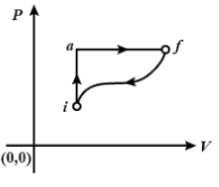
In the diagram shown \[{{\text{Q}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 80\;{\text{cal}}\] and \[{{\text{W}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 50\;{\text{cal}}\]. If W\[ = - 30\;{\text{cal\;}}\] for the curved path \[{\text{fi}}\], the value of Q for the path \[{\text{fi}}\] , will be:
A.\[60{\text{ cal}}\]
B.\[30{\text{ cal}}\]
C.\[ - 30\;{\text{cal}}\]
D.\[ - 60{\text{cal}}\]

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of the first law of thermodynamics. According to this law, the change in internal energy of a system depends on the net heat transfer into the system and the network done by the system.
The formula used:
\[\Delta {\text{U }} = {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{Q }} - {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{W}}\]
where \[\Delta {\text{U}}\] is the change in internal energy of the system, \[\Delta {\text{Q }}\]is heat transfer and \[\Delta {\text{W}}\]is work done on the system
Complete step by step answer:
The equation of the first law of thermodynamics is
\[\Delta {\text{U }} = {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{Q }} - {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{W}}\].
The values of the conditions along the path \[{\text{iaf}}\]as
\[{{\text{Q}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 80{\text{ cal, }}{{\text{W}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 50{\text{ cal}}\].
The question requires us to find us the value of conditions for the path \[{\text{fi}}\], \[{{\text{W}}_{{\text{fi}}}} = - 30{\text{ cal\;}},\,\,{{\text{Q}}_{{\text{fi}}}} = ?\].
Along the path \[fi\;\],\[\Delta {\text{U}} = {\text{Q}} - {\text{W}} = 80 - 50 = 30{\text{cal}}\]
\[\Delta {\text{U}}\;{\text{for fi}} = - 30{\text{cal}}\]
Using these values in the equation of first law we get
\[{\text{Q}} = {\text{W}} + \Delta {\text{U}} = - 30 - 30 = - 60{\text{cal}}\].
\[{\text{Q}}\] for path \[{\text{fi}}\]= \[ - 60{\text{cal}}\].
Hence, the final answer is D.
Note:
We can confuse between different types of reactions. Make sure to remember the difference between isobaric, isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic processes. An isobaric process is one where the pressure of the system (often a gas) stays constant.
An isochoric process is defined as the thermodynamic process where the volume of the system stays constant.
An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is exchanged between the system and the surrounding. The limitation of this first law of thermodynamics is that it fails to explain why heat flows from hot end to cold end when a metallic rod is heated at one end, not in another case and vice-versa. This means that the first law only quantifies the energy transfer that takes place during this process. It is the second law of thermodynamics which provides the criterion for the feasibility of the various processes.
The formula used:
\[\Delta {\text{U }} = {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{Q }} - {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{W}}\]
where \[\Delta {\text{U}}\] is the change in internal energy of the system, \[\Delta {\text{Q }}\]is heat transfer and \[\Delta {\text{W}}\]is work done on the system
Complete step by step answer:
The equation of the first law of thermodynamics is
\[\Delta {\text{U }} = {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{Q }} - {\text{ }}\Delta {\text{W}}\].
The values of the conditions along the path \[{\text{iaf}}\]as
\[{{\text{Q}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 80{\text{ cal, }}{{\text{W}}_{{\text{iaf}}}} = 50{\text{ cal}}\].
The question requires us to find us the value of conditions for the path \[{\text{fi}}\], \[{{\text{W}}_{{\text{fi}}}} = - 30{\text{ cal\;}},\,\,{{\text{Q}}_{{\text{fi}}}} = ?\].
Along the path \[fi\;\],\[\Delta {\text{U}} = {\text{Q}} - {\text{W}} = 80 - 50 = 30{\text{cal}}\]
\[\Delta {\text{U}}\;{\text{for fi}} = - 30{\text{cal}}\]
Using these values in the equation of first law we get
\[{\text{Q}} = {\text{W}} + \Delta {\text{U}} = - 30 - 30 = - 60{\text{cal}}\].
\[{\text{Q}}\] for path \[{\text{fi}}\]= \[ - 60{\text{cal}}\].
Hence, the final answer is D.
Note:
We can confuse between different types of reactions. Make sure to remember the difference between isobaric, isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic processes. An isobaric process is one where the pressure of the system (often a gas) stays constant.
An isochoric process is defined as the thermodynamic process where the volume of the system stays constant.
An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is exchanged between the system and the surrounding. The limitation of this first law of thermodynamics is that it fails to explain why heat flows from hot end to cold end when a metallic rod is heated at one end, not in another case and vice-versa. This means that the first law only quantifies the energy transfer that takes place during this process. It is the second law of thermodynamics which provides the criterion for the feasibility of the various processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




