
In Rosenmund reactions, presence of \[BaS{O_4}\]acts as _______ for \[Pd\].
(A): promoter
(B): moderator
(C): inhibitor
(D): poison
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: A Rosenmund reaction can be referred to as a hydrogenation process which involves a reaction between molecular hydrogen and acyl chloride in the presence of palladium (catalyst) on barium sulphate (\[BaS{O_4}\]). The mechanism of this reaction mainly explains how acyl chlorides get selectively reduced to aldehydes. This reaction is named after Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund who reported this reaction for the first time in 1918.
Complete step by step answer:
A Rosenmund reaction or Rosenmund Reduction, an organic chemical reaction, converts an acid chloride into an aldehyde by passing the hydrogen gas over \[Pd\] (palladium) on \[BaS{O_4}\]. Actually, \[BaS{O_4}\] decreases the activity of \[Pd\] (or partially deactivate \[Pd\]) owing to its very low surface area. Thereby, it also declines the reducing power of \[Pd\]to prevent the over-reduction of acid. Hence, \[BaS{O_4}\] acts as a poison for \[Pd\]. If reducing power of \[Pd\ ] is not reduced, it can further reduce aldehyde to alcohols which can ultimately produce esters by reacting with remaining acyl chloride. The Rosenmund reaction can be written as stated below:
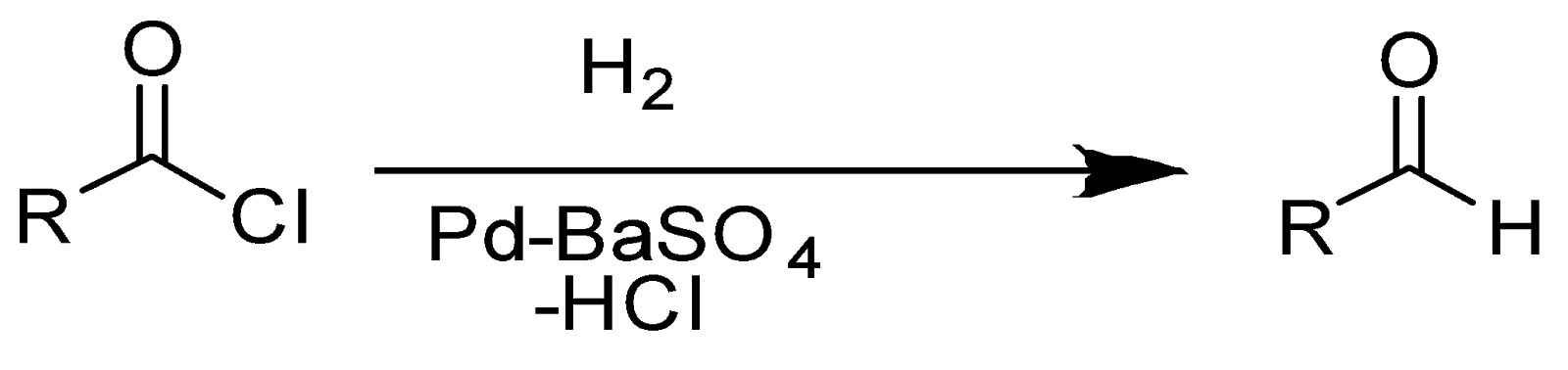
An example of Rosenmund reaction is: reaction of benzoyl chloride (which is an acid chloride) with molecular hydrogen as well as \[Pd\]/\[BaS{O_4}\](which is a poisoned catalyst) producing benzaldehyde.
Thus, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: For certain highly reactive acyl chlorides, the Rosenmund catalyst (\[Pd\]-\[BaS{O_4}\]) has to be mixed with more poisons such as thioquinanthrene or thiourea to prevent further reduction or hydrogenation. Apart from this, Formaldehyde cannot be synthesized through this method as formyl chloride being unstable at room temperature. Application of Rosenmund reaction is formation of saturated fatty aldehyde.
Complete step by step answer:
A Rosenmund reaction or Rosenmund Reduction, an organic chemical reaction, converts an acid chloride into an aldehyde by passing the hydrogen gas over \[Pd\] (palladium) on \[BaS{O_4}\]. Actually, \[BaS{O_4}\] decreases the activity of \[Pd\] (or partially deactivate \[Pd\]) owing to its very low surface area. Thereby, it also declines the reducing power of \[Pd\]to prevent the over-reduction of acid. Hence, \[BaS{O_4}\] acts as a poison for \[Pd\]. If reducing power of \[Pd\ ] is not reduced, it can further reduce aldehyde to alcohols which can ultimately produce esters by reacting with remaining acyl chloride. The Rosenmund reaction can be written as stated below:

An example of Rosenmund reaction is: reaction of benzoyl chloride (which is an acid chloride) with molecular hydrogen as well as \[Pd\]/\[BaS{O_4}\](which is a poisoned catalyst) producing benzaldehyde.
Thus, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: For certain highly reactive acyl chlorides, the Rosenmund catalyst (\[Pd\]-\[BaS{O_4}\]) has to be mixed with more poisons such as thioquinanthrene or thiourea to prevent further reduction or hydrogenation. Apart from this, Formaldehyde cannot be synthesized through this method as formyl chloride being unstable at room temperature. Application of Rosenmund reaction is formation of saturated fatty aldehyde.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




