
In gymnosperm, the pollination is
(a) Anemophilous-micropylar
(b) Anemophilous-stigmatic
(c) Entomophilous-micropylar
(d) None of the above
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: There is some abiotic factor that is responsible for bringing about the pollination in the naked seeded plants. It is completed because of exposed ovules.
Complete answer:
Pollination occurs only by the wind in gymnosperms i.e anemophilous pollination. Also, the pollen grains are transferred directly to the ovule as the ovules are exposed directly to the surface. Therefore, pollination is not stigmatic but micropylar. The transfer of pollen to the female organs of seed plants is called pollination. Immature seeds (ovules) are located within carpels in flowering plants (angiosperms, or "covered seeds"). In non-flowering seed plants, ovules are uncovered to which the pollen is transferred, making these "naked seeds" (gymnosperms). Pollen grains are blown by the wind to land on the female cones during pollination. Examples of living gymnosperms are conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The conifers are the most common and abundant group of "gymnosperms" existing today.
Additional Information:
-The micropyle is a small opening on the surface of the ovule.
-Angiosperms have many types of pollination methods that involve many different agents to transfer pollen, including insects (entomophily), birds (ornithophily), bats (chirpily), wind (anemophily), and water (hydrophily).
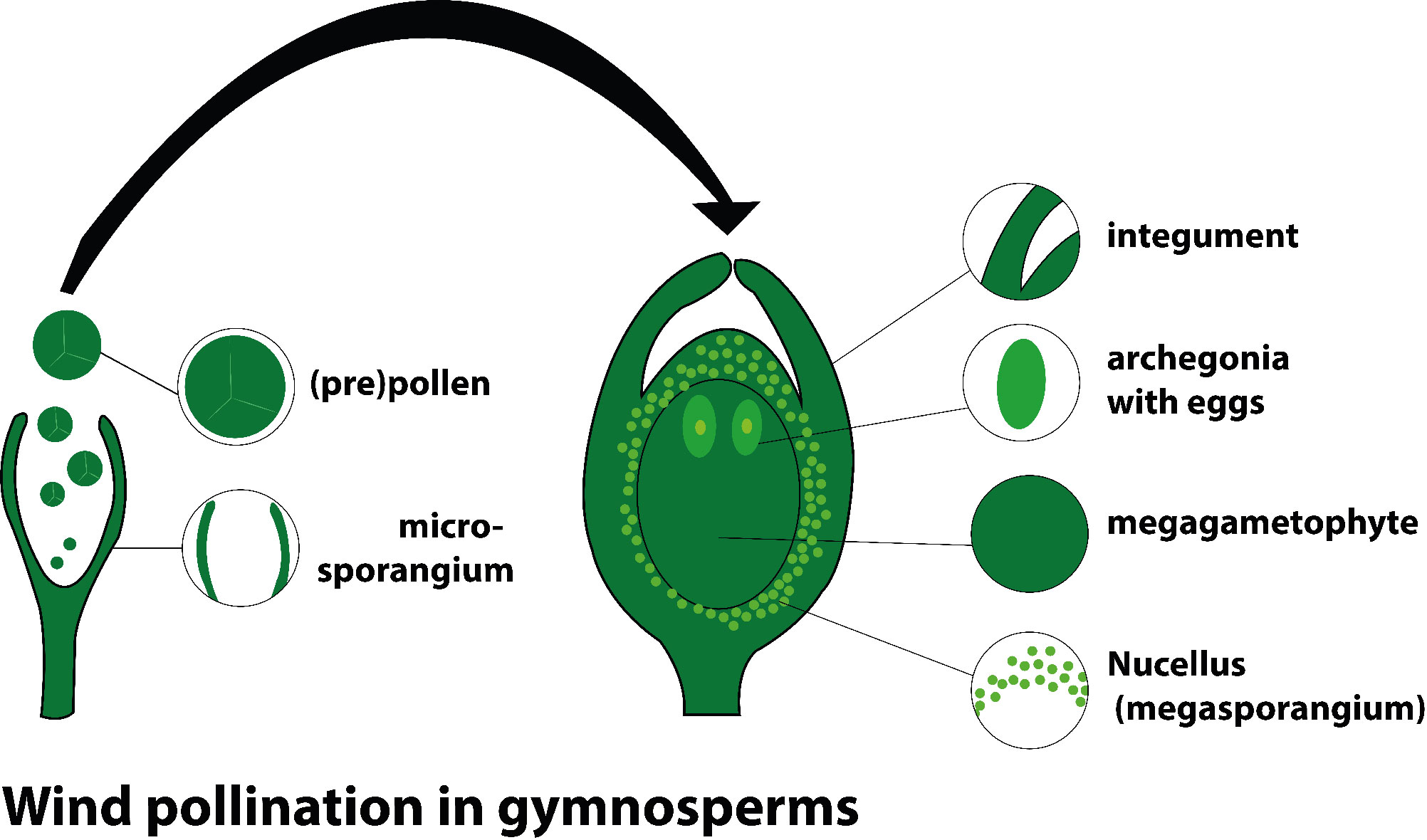
So, the correct answer is, 'Anemophilous- micropylar'.
Note:
-Animals are attracted usually by a conspicuous floral display, with color and scent playing important roles. Bees are attracted by yellow and blue flowers, hummingbirds are attracted by red flowers, butterflies are attracted by pink flowers, and moths and bats are attracted by white flowers that stand out at night.
-Animal-based pollination is associated with a food reward to assure a continuing relationship.
Complete answer:
Pollination occurs only by the wind in gymnosperms i.e anemophilous pollination. Also, the pollen grains are transferred directly to the ovule as the ovules are exposed directly to the surface. Therefore, pollination is not stigmatic but micropylar. The transfer of pollen to the female organs of seed plants is called pollination. Immature seeds (ovules) are located within carpels in flowering plants (angiosperms, or "covered seeds"). In non-flowering seed plants, ovules are uncovered to which the pollen is transferred, making these "naked seeds" (gymnosperms). Pollen grains are blown by the wind to land on the female cones during pollination. Examples of living gymnosperms are conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The conifers are the most common and abundant group of "gymnosperms" existing today.
Additional Information:
-The micropyle is a small opening on the surface of the ovule.
-Angiosperms have many types of pollination methods that involve many different agents to transfer pollen, including insects (entomophily), birds (ornithophily), bats (chirpily), wind (anemophily), and water (hydrophily).

So, the correct answer is, 'Anemophilous- micropylar'.
Note:
-Animals are attracted usually by a conspicuous floral display, with color and scent playing important roles. Bees are attracted by yellow and blue flowers, hummingbirds are attracted by red flowers, butterflies are attracted by pink flowers, and moths and bats are attracted by white flowers that stand out at night.
-Animal-based pollination is associated with a food reward to assure a continuing relationship.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




