
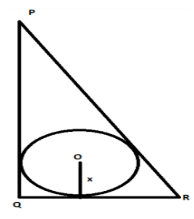
In $\Delta PQR,PQ=24$cm, $QR=7$cm and $\angle PQR={{90}^{\circ }}$. Find the radius (in cm) of the inscribed circle.

Answer
621.9k+ views
Hint: If two tangents are drawn from a point to a circle, then the length of those two tangents from that particular point to the circle will be equal. In this question, $PQ,QR$ and $PR$ are the tangents to the circle.
In this question, we are given a right angle triangle having sides $PQ=24$cm, $QR=7$cm and $\angle
PQR={{90}^{\circ }}$. We can calculate the length of side $PR$ by using Pythagoras theorem.
Consider a triangle $ABC$ having $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$.
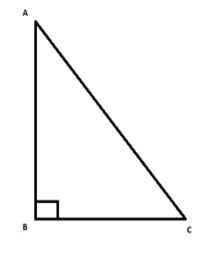
Using Pythagoras theorem the relation between the base, perpendicular and the hypotenuse of the
triangle is given by,
$AC=\sqrt{{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}}.....................\left( 1 \right)$
Using Pythagoras theorem from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ in the triangle $PQR$, we get,
$PR=\sqrt{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}}$
In the question, it is given $PQ=24$cm, $QR=7$cm.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{{{\left( 24 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{576+49} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{625} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=25 \\
\end{align}$
Since the circle is inscribed in the triangle $PQR$, sides $PQ,QR,PR$ will act as a tangent to the
circle. Let us name the point of contact of circle with the tangent $PQ$ as $A$, tangent $QR$ as $B$
and tangent $PR$ as $C$. Let us join the point $A,B,C$ to the center of the circle $O$ . Also, let us
consider the radius of the circle equal to $x$.
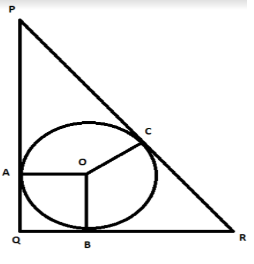
Since $OA,OB,OC$ are the radius, their lengths are equal to $x$.
It can be seen from the figure that in quadrilateral $AOQB$, two adjacent sides ($OA,OB$) are equal
(since they are the radius of the circle) and all the angles are right angles. This means, $AOQB$ is a
square. So, $AQ=x$ and $BQ=x$.
There is a property of tangent which states that, if two tangents are drawn from a point to a circle,
then the length of those two tangents from that particular point to the circle will be equal. Using this
property in the above triangle,
$\Rightarrow PA=PC,QA=QB,RB=RC............\left( 2 \right)$
We have obtained $AQ=x$. Also $PQ=24$. Since $PAQ$ is a straight line, we can say,
$\begin{align}
& PA=PQ-QA \\
& \Rightarrow PA=24-x \\
\end{align}$
From $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $PA=PC$.
$\Rightarrow PC=24-x............\left( 3 \right)$
Also, we have obtained $BQ=x$. Also $QR=7$. Since $QBR$ is a straight line, we can say,
$\begin{align}
& RB=QR-QB \\
& \Rightarrow RB=7-x \\
\end{align}$
From $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $RB=RC$.
\[\Rightarrow RC=7-x............\left( 4 \right)\]
Since $PCR$ is a straight line, we can write,
$PR=PC+RC$
Using Pythagoras theorem, we obtained $PR=25$cm. Also, from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and
equation $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $PC=24-x$ and \[RC=7-x\]. Substituting in the above equation,
we get,
$\begin{align}
& 25=24-x+7-x \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the radius of the inscribed circle is $3$.
Note: There is an alternative method to find the radius of the inscribed circle. The radius of the
inscribed circle of a triangle is given by the formula, $r=\dfrac{K}{s}$ where $K$ is the area of the
triangle and $s$ is the half of the perimeter of the triangle.
In this question, we are given a right angle triangle having sides $PQ=24$cm, $QR=7$cm and $\angle
PQR={{90}^{\circ }}$. We can calculate the length of side $PR$ by using Pythagoras theorem.
Consider a triangle $ABC$ having $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$.

Using Pythagoras theorem the relation between the base, perpendicular and the hypotenuse of the
triangle is given by,
$AC=\sqrt{{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}}.....................\left( 1 \right)$
Using Pythagoras theorem from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ in the triangle $PQR$, we get,
$PR=\sqrt{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}}$
In the question, it is given $PQ=24$cm, $QR=7$cm.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{{{\left( 24 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{576+49} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=\sqrt{625} \\
& \Rightarrow PR=25 \\
\end{align}$
Since the circle is inscribed in the triangle $PQR$, sides $PQ,QR,PR$ will act as a tangent to the
circle. Let us name the point of contact of circle with the tangent $PQ$ as $A$, tangent $QR$ as $B$
and tangent $PR$ as $C$. Let us join the point $A,B,C$ to the center of the circle $O$ . Also, let us
consider the radius of the circle equal to $x$.

Since $OA,OB,OC$ are the radius, their lengths are equal to $x$.
It can be seen from the figure that in quadrilateral $AOQB$, two adjacent sides ($OA,OB$) are equal
(since they are the radius of the circle) and all the angles are right angles. This means, $AOQB$ is a
square. So, $AQ=x$ and $BQ=x$.
There is a property of tangent which states that, if two tangents are drawn from a point to a circle,
then the length of those two tangents from that particular point to the circle will be equal. Using this
property in the above triangle,
$\Rightarrow PA=PC,QA=QB,RB=RC............\left( 2 \right)$
We have obtained $AQ=x$. Also $PQ=24$. Since $PAQ$ is a straight line, we can say,
$\begin{align}
& PA=PQ-QA \\
& \Rightarrow PA=24-x \\
\end{align}$
From $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $PA=PC$.
$\Rightarrow PC=24-x............\left( 3 \right)$
Also, we have obtained $BQ=x$. Also $QR=7$. Since $QBR$ is a straight line, we can say,
$\begin{align}
& RB=QR-QB \\
& \Rightarrow RB=7-x \\
\end{align}$
From $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $RB=RC$.
\[\Rightarrow RC=7-x............\left( 4 \right)\]
Since $PCR$ is a straight line, we can write,
$PR=PC+RC$
Using Pythagoras theorem, we obtained $PR=25$cm. Also, from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ and
equation $\left( 2 \right)$, we have $PC=24-x$ and \[RC=7-x\]. Substituting in the above equation,
we get,
$\begin{align}
& 25=24-x+7-x \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=6 \\
& \Rightarrow x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the radius of the inscribed circle is $3$.
Note: There is an alternative method to find the radius of the inscribed circle. The radius of the
inscribed circle of a triangle is given by the formula, $r=\dfrac{K}{s}$ where $K$ is the area of the
triangle and $s$ is the half of the perimeter of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




