
In a dihybrid cross, the recombination frequency is usually:
A. More than 50%
B. Less than 50%
C. Zero
D. Up to 100%
Answer
388.5k+ views
Hint: To receive the F2 generation, the F1 generation must be self-sterilised. The phenotype ratio must be 9:3:3:1. The recombination frequency must not be greater than 50% and calculations must be done in such a way to get the desired result.
Complete Step-By-Step Answer :
During the mid-19th century, Gregor Johann Mendel was the first person who discovered the basic principles of heredity. Therefore he is regarded as the “Father of Modern Genetics.” Involving two characters, Mendel performed crosses known as Dihybrid Cross. The dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment between the two organisms for two traits. Therefore, a cross between two organisms for two specific traits is known as dihybrid cross. In their genotypes in a dihybrid cross, the breeding of two-parent organisms possessing different allele pairs is carried out. Here a pea plant with round yellow seeds is crossed with another pea plant having wrinkled green seeds. To get the F2 generation, the F1 generation is then self-Fertilised. The phenotype ratio (yellow round: yellow wrinkled: green round: green wrinkled) is 9:3:3:1.
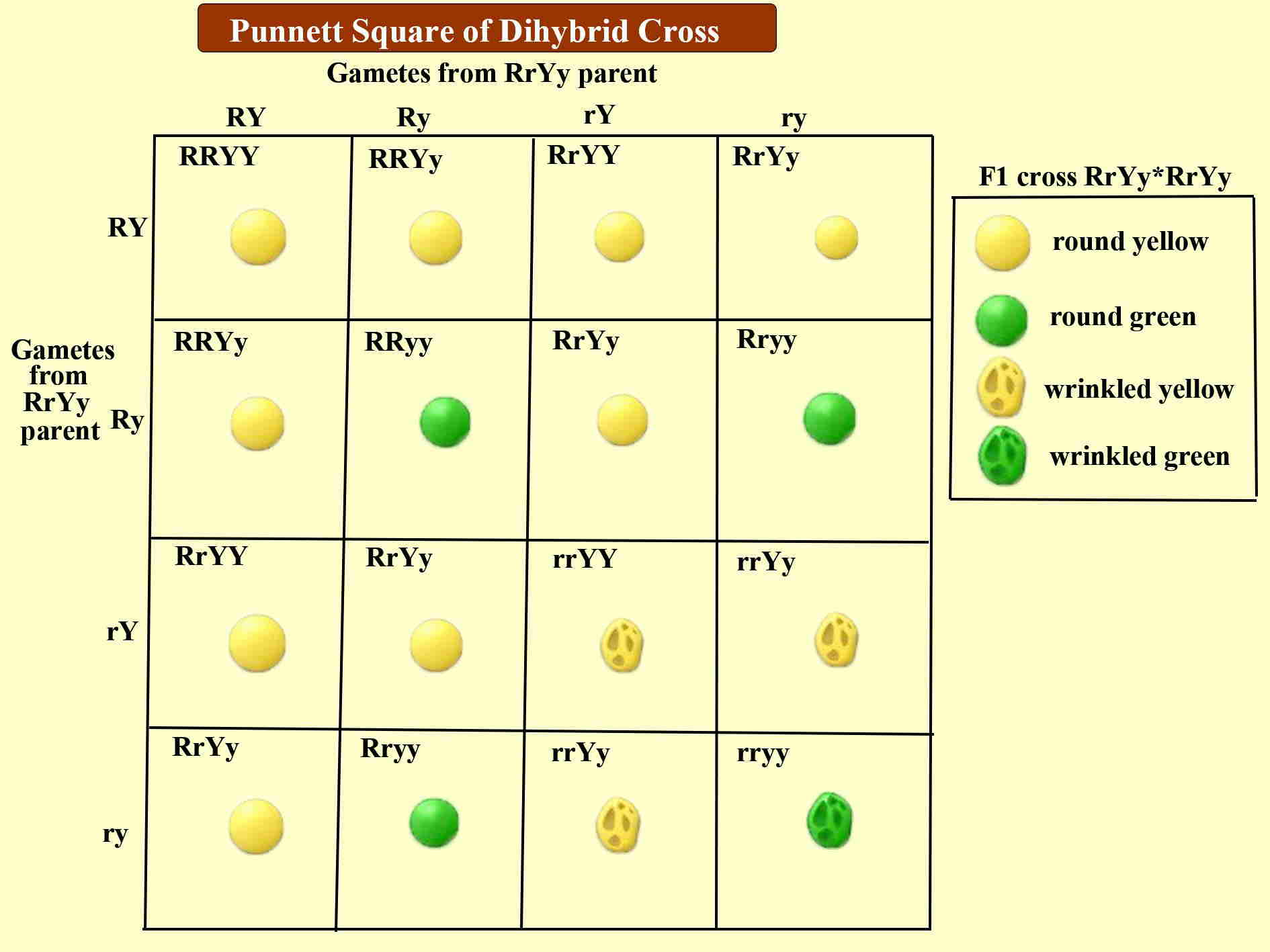
Image: Diagram showing Punnett Square of Dihybrid Cross.
Therefore, the recombination frequency is less than 50% in a dihybrid cross. Option B is correct.
Note: By DNA segments, these traits are determined and are known as genes. The parent carries various pairs of alleles in a dihybrid cross for every single trait.
Complete Step-By-Step Answer :
During the mid-19th century, Gregor Johann Mendel was the first person who discovered the basic principles of heredity. Therefore he is regarded as the “Father of Modern Genetics.” Involving two characters, Mendel performed crosses known as Dihybrid Cross. The dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment between the two organisms for two traits. Therefore, a cross between two organisms for two specific traits is known as dihybrid cross. In their genotypes in a dihybrid cross, the breeding of two-parent organisms possessing different allele pairs is carried out. Here a pea plant with round yellow seeds is crossed with another pea plant having wrinkled green seeds. To get the F2 generation, the F1 generation is then self-Fertilised. The phenotype ratio (yellow round: yellow wrinkled: green round: green wrinkled) is 9:3:3:1.

Image: Diagram showing Punnett Square of Dihybrid Cross.
Therefore, the recombination frequency is less than 50% in a dihybrid cross. Option B is correct.
Note: By DNA segments, these traits are determined and are known as genes. The parent carries various pairs of alleles in a dihybrid cross for every single trait.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




