
In a cell cycle crossing over occurs at
(a) Single strand stage
(b) Two strand stage
(c) Four strand stage
(d) Eight strand stage
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Crossing over is the mutual exchange and reciprocal recombination of chromatid segments, DNA fragments, or block of genes between the non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs during prophase I of meiosis before tetrads are aligned along the equator in metaphase I. Only two of the four chromatids are involved in Crossing over.
Complete answer:
In a cell cycle, crossing over occurs at the four-strand stage. Crossing over involves the symmetrical breakage of chromatids, and the reciprocal exchange and crosswise reunion of segments between non-sister chromatids, often breaking linkage. This results in the recombination of genes. Crossing over occurs at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis I.
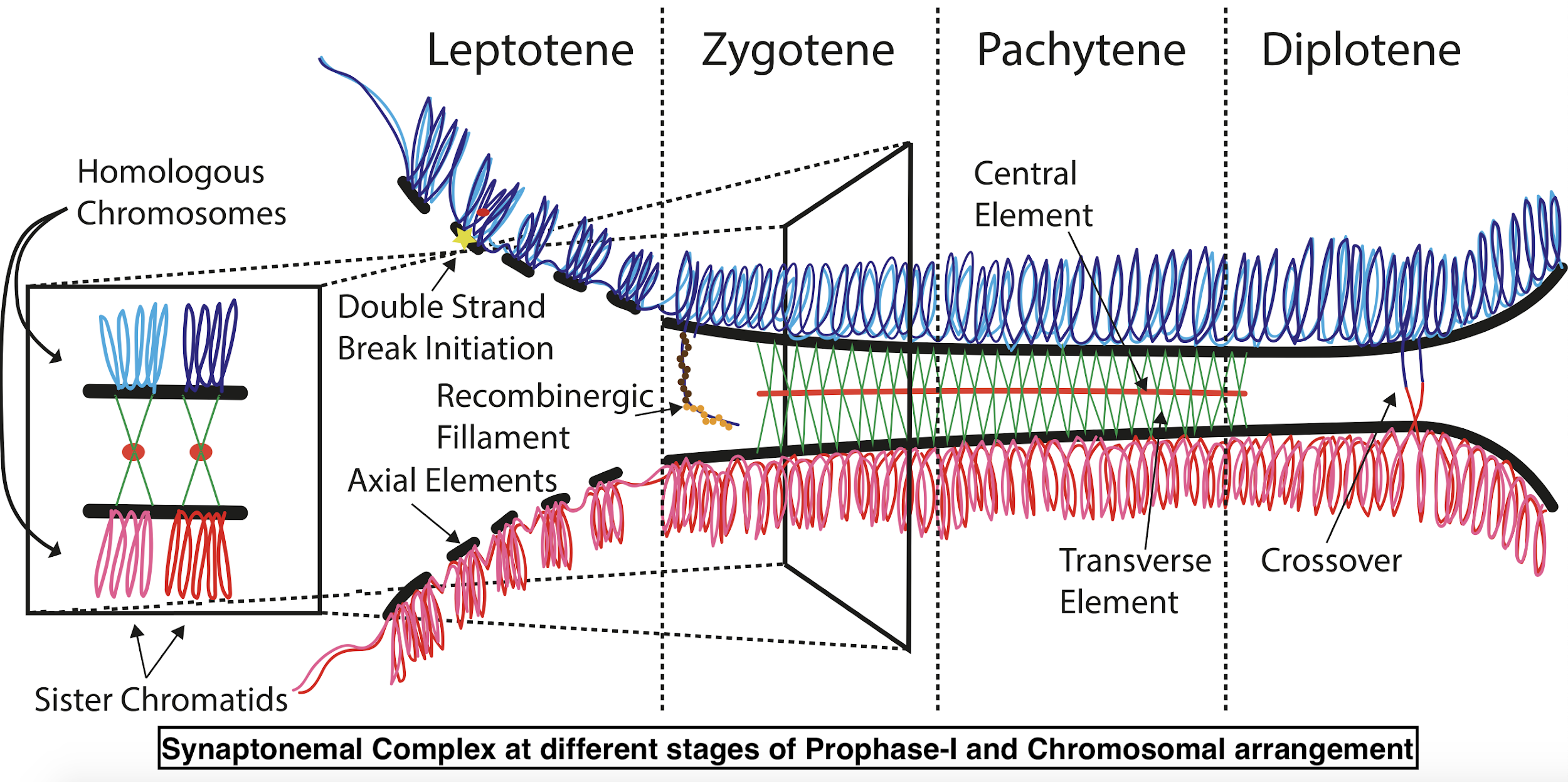
During the pachytene, stage one chromatid of each homologue overlaps or crosses over a corresponding non-sister chromatid of the other homologue at one or more points. These crossing points are called chiasma. At this point, the non-sister chromatids divide transversely with the help of endonuclease. The broken segments are then mutually exchanged by them. Each exchanged segment fuses with a corresponding portion of non-sister chromatids with the help of ligases. The whole process which involves the breakage, mutual exchange, and reciprocal reunion of chromosome segments is called crossing over.
Additional Information:
- Crossing over and the independent assortment of alleles are the major mechanisms for producing new, non-parental gene combinations and genetic variations.
- Natural selection acts upon these recombinant genotypes and genetic variations and thereby enhances the fitness, survival value, and evolutionary potentiality of organisms.
- In eukaryotes, crossing over may be mitotic or meiotic. Mitotic crossing over occurs in somatic cells and finial cells.
So, the correct answer is the '(c) four-strand stage’.
Note:
- Mitotic crossing over involves five major events; synapsis of homologous chromosomes and tetrad formation, crossing over of non-sister chromatids and chiasma formation, symmetrical breakage of non-sister chromatids, reciprocal recombination through the mutual exchange and crosswise reunion of broken segments, dissociation of the homologues by the decriminalization of chiasma.
- Synapsis is the close pairing of homologous chromosomes during the zygotene stage of the first meiotic division.
- Double-crossing over is the crossing over which involves two chiasma, two, three, or four chromatids.
Complete answer:
In a cell cycle, crossing over occurs at the four-strand stage. Crossing over involves the symmetrical breakage of chromatids, and the reciprocal exchange and crosswise reunion of segments between non-sister chromatids, often breaking linkage. This results in the recombination of genes. Crossing over occurs at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis I.

During the pachytene, stage one chromatid of each homologue overlaps or crosses over a corresponding non-sister chromatid of the other homologue at one or more points. These crossing points are called chiasma. At this point, the non-sister chromatids divide transversely with the help of endonuclease. The broken segments are then mutually exchanged by them. Each exchanged segment fuses with a corresponding portion of non-sister chromatids with the help of ligases. The whole process which involves the breakage, mutual exchange, and reciprocal reunion of chromosome segments is called crossing over.
Additional Information:
- Crossing over and the independent assortment of alleles are the major mechanisms for producing new, non-parental gene combinations and genetic variations.
- Natural selection acts upon these recombinant genotypes and genetic variations and thereby enhances the fitness, survival value, and evolutionary potentiality of organisms.
- In eukaryotes, crossing over may be mitotic or meiotic. Mitotic crossing over occurs in somatic cells and finial cells.
So, the correct answer is the '(c) four-strand stage’.
Note:
- Mitotic crossing over involves five major events; synapsis of homologous chromosomes and tetrad formation, crossing over of non-sister chromatids and chiasma formation, symmetrical breakage of non-sister chromatids, reciprocal recombination through the mutual exchange and crosswise reunion of broken segments, dissociation of the homologues by the decriminalization of chiasma.
- Synapsis is the close pairing of homologous chromosomes during the zygotene stage of the first meiotic division.
- Double-crossing over is the crossing over which involves two chiasma, two, three, or four chromatids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




