
If\[\sqrt 3 \sin \theta = \cos \theta \], find the value of \[\dfrac{{\sin \theta \tan \theta \left( {1 + \cos \theta } \right)}}{{\sin \theta + {\text{cos}}\theta }}\]
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: Write the value of the trigonometric functions. The trigonometric function is the function that relates the ratio of the length of two sides with the angles of the right-angled triangle widely used in navigation, oceanography, the theory of periodic functions, and projectiles.
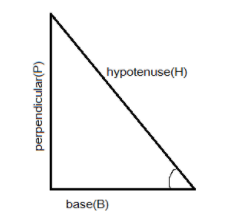
Commonly used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent, whereas the cosecant, the secant, the cotangent are their reciprocal, respectively. The value of these functions can be determined by the relation of the sides of a right-angled triangle where sine function is the ratio of perpendicular (P) and hypotenuses (H) of the triangle \[\sin \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuses}}}}\]. Cosine is the ratio of the base (B) and hypotenuses (H) of the triangle \[\cos \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuses}}}}\]; the tangent is the ratio of the perpendicular (P) and base (B) of the triangle \[\tan \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\] , whereas ${\text{cosec}}\theta $, \[\sec \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are their inverse respectively. The given value determines the value of these functions.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given relation\[\sqrt 3 \sin \theta = \cos \theta \] we can write it as
\[
\sqrt 3 \sin \theta = \cos \theta \\
\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\][Since\[\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \tan \theta \]]
Hence the value \[\theta \] of will be equal to
\[
\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right) \\
\theta = {30^ \circ } \\
\]
Now use the value \[\theta = {30^ \circ }\] to find the value of the given expression
\[
\dfrac{{\sin \theta \tan \theta \left( {1 + \cos \theta } \right)}}{{\sin \theta + {\text{cos}}\theta }} = \dfrac{{\sin {{30}^ \circ }\tan {{30}^ \circ }\left( {1 + \cos {{30}^ \circ }} \right)}}{{\sin {{30}^ \circ } + \cos {{30}^ \circ }}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\left( {1 + \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2 + \sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{1 + \sqrt 3 }}{2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{4\sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{2\sqrt 3 \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}} \\
\]
Hence the value of the given equation by using the values of trigonometric functions from the above given table will be equal to \[\dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{2\sqrt 3 \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}\]
Note: Write the value of the function in the relation for the given respective angles in cases of \[{\text{cosec}}\theta \] \[\sec \theta \], \[\cot \theta \]either inverse them or write their values, respectively. Alternatively, the given trigonometric function can be reduced to a smaller expression by carrying out general algebraic and trigonometric identities and at last put the values of the trigonometric functions for the respective values of$\theta $.

Commonly used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent, whereas the cosecant, the secant, the cotangent are their reciprocal, respectively. The value of these functions can be determined by the relation of the sides of a right-angled triangle where sine function is the ratio of perpendicular (P) and hypotenuses (H) of the triangle \[\sin \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuses}}}}\]. Cosine is the ratio of the base (B) and hypotenuses (H) of the triangle \[\cos \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuses}}}}\]; the tangent is the ratio of the perpendicular (P) and base (B) of the triangle \[\tan \theta {\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}}\] , whereas ${\text{cosec}}\theta $, \[\sec \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are their inverse respectively. The given value determines the value of these functions.
Complete step by step solution:
| Function | $\sin \theta $ | $\cos \theta $ | $\tan \theta $ |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ${30^0}$ | $\dfrac{1}{2}$ | $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ | $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ |
| ${45^0}$ | $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ | $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ | 1 |
| ${60^0}$ | $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ | $\dfrac{1}{2}$ | $\sqrt 3 $ |
| ${90^0}$ | 1 | 0 | Indeterminate |
From the given relation\[\sqrt 3 \sin \theta = \cos \theta \] we can write it as
\[
\sqrt 3 \sin \theta = \cos \theta \\
\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\][Since\[\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \tan \theta \]]
Hence the value \[\theta \] of will be equal to
\[
\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right) \\
\theta = {30^ \circ } \\
\]
Now use the value \[\theta = {30^ \circ }\] to find the value of the given expression
\[
\dfrac{{\sin \theta \tan \theta \left( {1 + \cos \theta } \right)}}{{\sin \theta + {\text{cos}}\theta }} = \dfrac{{\sin {{30}^ \circ }\tan {{30}^ \circ }\left( {1 + \cos {{30}^ \circ }} \right)}}{{\sin {{30}^ \circ } + \cos {{30}^ \circ }}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\left( {1 + \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{2\sqrt 3 }}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2 + \sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{1 + \sqrt 3 }}{2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{4\sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{2}{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{2\sqrt 3 \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}} \\
\]
Hence the value of the given equation by using the values of trigonometric functions from the above given table will be equal to \[\dfrac{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{{2\sqrt 3 \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}\]
Note: Write the value of the function in the relation for the given respective angles in cases of \[{\text{cosec}}\theta \] \[\sec \theta \], \[\cot \theta \]either inverse them or write their values, respectively. Alternatively, the given trigonometric function can be reduced to a smaller expression by carrying out general algebraic and trigonometric identities and at last put the values of the trigonometric functions for the respective values of$\theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




