
If $z$ and $\overline z $ represent adjacent vertices of a regular polygon of $n$ sides with centre at origin and if $\dfrac{{\operatorname{Im} z}}{{\operatorname{Re} z}} = \sqrt 2 - 1$, then the value of $n$ is equal to
A) $2$
B) $4$
C) $6$
D) $8$
Answer
520.2k+ views
Hint: First of all we should know that a regular polygon is a polygon that has equal sides and equal angles. In this question we should know that we have complex numbers. We can assume that ${z_1} = x + iy$, then the value of $\overline {{z_1}} $ will be $x - iy$. We know that the angle between two corresponding vertices is $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume that ${z_1}$ be the first vertex of the polygon in the first quadrant i.e. ${z_1} = x + iy$, then the $\overline {{z_1}} $ be in the fourth quadrant i.e. $\overline {{z_1}} = x - iy$.
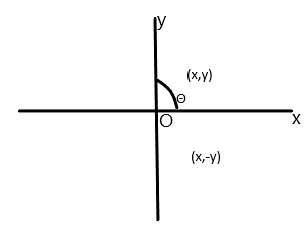
In the above figure we have points in the first quadrant as $(x,y)$ and in the fourth quadrant the coordinates are $(x, - y)$.
Now we have assumed that the angle at the centre in the first quadrant is $\theta $.
So we can write from the question that $\tan \theta = \sqrt 2 - 1$. We know that the angle between two corresponding vertices is $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n}$. From this we can write $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = 2\theta $, because $\dfrac{\pi }{n} = \theta $ from the above figure.
By multiplying with $\tan $ on both the sides, it gives us $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \tan 2\theta $. On simplifying this we can write $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \dfrac{{2\tan \theta }}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}\theta }}$.
By putting the value of $\tan \theta = \sqrt 2 - 1$in the right hand side of the equation, we have$\dfrac{{2(\sqrt 2 - 1)}}{{1 - {{(\sqrt 2 - 1)}^2}}}$.
We will solve it now: $\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}{{1 - 2 - 1 + 2\sqrt 2 }} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}$. It gives us the value $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = 1$.
Now we know that the value of $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}$ is $1$, so we can write it as $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{4} = 1$.
Therefore we can write by eliminating tan, $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$. It gives us the value of $n = 4 \times 2 = 8$.
Hence the required answer is (D) $8$.
Note:
We should know that we have used the trigonometric identity in the above question i.e. $\tan 2\theta = \dfrac{{2\tan \theta }}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}\theta }}$. We have also applied the algebraic identity of difference square formula which is ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$. Before solving this kind of question we should have a clear knowledge of the trigonometric identities and their functions.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume that ${z_1}$ be the first vertex of the polygon in the first quadrant i.e. ${z_1} = x + iy$, then the $\overline {{z_1}} $ be in the fourth quadrant i.e. $\overline {{z_1}} = x - iy$.

In the above figure we have points in the first quadrant as $(x,y)$ and in the fourth quadrant the coordinates are $(x, - y)$.
Now we have assumed that the angle at the centre in the first quadrant is $\theta $.
So we can write from the question that $\tan \theta = \sqrt 2 - 1$. We know that the angle between two corresponding vertices is $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n}$. From this we can write $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = 2\theta $, because $\dfrac{\pi }{n} = \theta $ from the above figure.
By multiplying with $\tan $ on both the sides, it gives us $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \tan 2\theta $. On simplifying this we can write $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \dfrac{{2\tan \theta }}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}\theta }}$.
By putting the value of $\tan \theta = \sqrt 2 - 1$in the right hand side of the equation, we have$\dfrac{{2(\sqrt 2 - 1)}}{{1 - {{(\sqrt 2 - 1)}^2}}}$.
We will solve it now: $\dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}{{1 - 2 - 1 + 2\sqrt 2 }} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}{{2\sqrt 2 - 2}}$. It gives us the value $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = 1$.
Now we know that the value of $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}$ is $1$, so we can write it as $\tan \dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \tan \dfrac{\pi }{4} = 1$.
Therefore we can write by eliminating tan, $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{n} = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$. It gives us the value of $n = 4 \times 2 = 8$.
Hence the required answer is (D) $8$.
Note:
We should know that we have used the trigonometric identity in the above question i.e. $\tan 2\theta = \dfrac{{2\tan \theta }}{{1 - {{\tan }^2}\theta }}$. We have also applied the algebraic identity of difference square formula which is ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$. Before solving this kind of question we should have a clear knowledge of the trigonometric identities and their functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




