
If two lenses of power 3D and -1D are kept in contact, what is the focal length and nature of the combined lens? Note that D implies dioptre.
A. 50 cm, convex
B. 50 cm, concave
C. 200 cm, convex
D. 200 cm, concave
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: When two or more lenses are kept in contact with each other, the resultant power of the combined lens is equal to the algebraic sum of the individual powers.
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + ..$
Formula Used:
$P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + ..$
Complete step by step answer:
When the 2 lenses are kept in contact together, the resultant power,
$P = {P_1} + {P_2}$
Substituting, we get –
$
P = 3D + ( - 1D) \\
P = 3 - 1 = 2D \\
$
Power is defined at the inverse of the focal length, $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Hence, the focal length is given by, $f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
Substituting the value of P, we get –
$
f = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
f = 0.5m \\
f = 50cm \\
$
For a convex lens, the focal length is positive and for a concave lens, the focal length is negative. Since, the focal length is +50cm, the combination lens is of convex nature.
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:
Note:
1. The convex lens is called convergent because the ray of light passing parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after passing through the convex lens, converges towards the centre to a point called focal length. Since the focus is along the direction of the incident light, the focal length is positive.
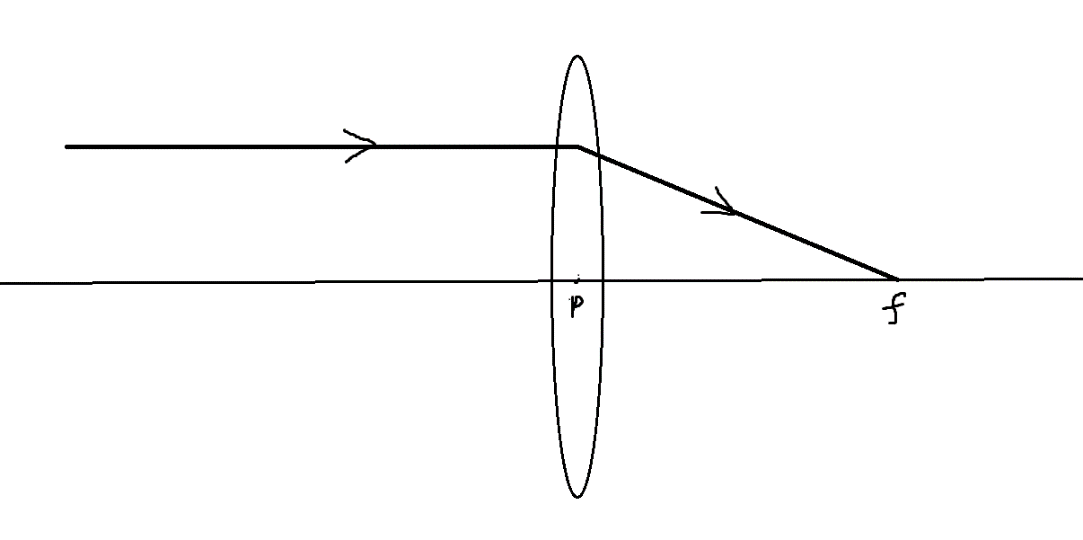
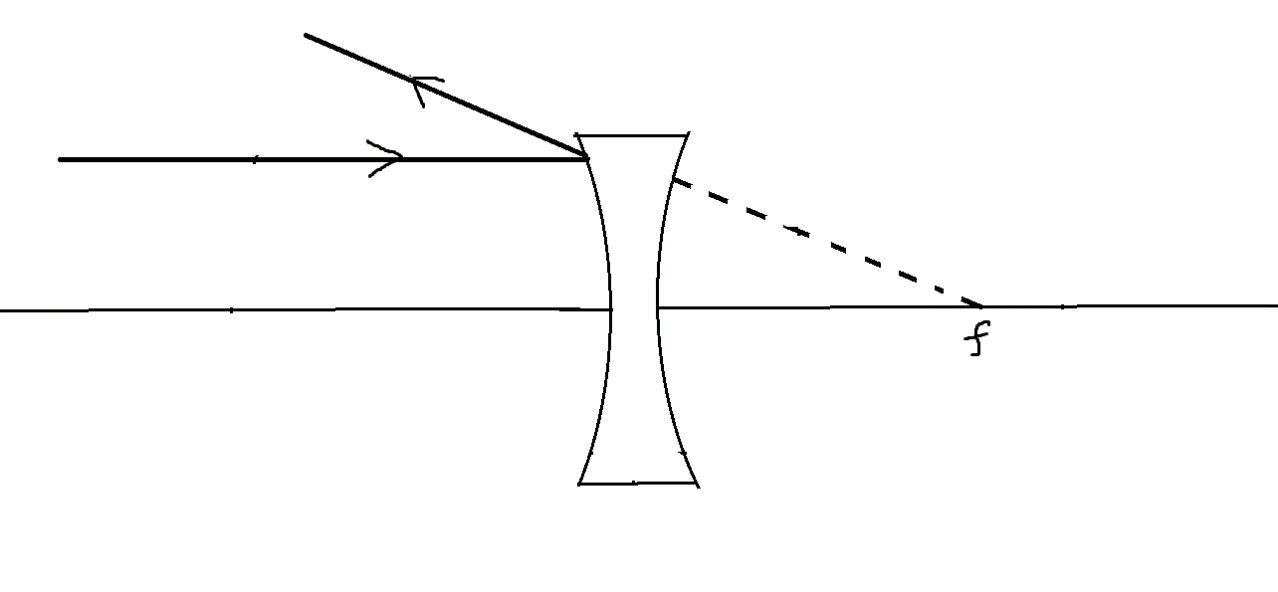
2. The concave lens is called divergent because the ray of light passing parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after passing through the convex lens, diverges away from the lens and it appears to be emerging away from an imaginary point called focus. Since the focus is in the reverse direction of the incident light, the focal length is negative.
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + ..$
Formula Used:
$P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + ..$
Complete step by step answer:
When the 2 lenses are kept in contact together, the resultant power,
$P = {P_1} + {P_2}$
Substituting, we get –
$
P = 3D + ( - 1D) \\
P = 3 - 1 = 2D \\
$
Power is defined at the inverse of the focal length, $P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Hence, the focal length is given by, $f = \dfrac{1}{P}$
Substituting the value of P, we get –
$
f = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
f = 0.5m \\
f = 50cm \\
$
For a convex lens, the focal length is positive and for a concave lens, the focal length is negative. Since, the focal length is +50cm, the combination lens is of convex nature.
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note:
Note:
1. The convex lens is called convergent because the ray of light passing parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after passing through the convex lens, converges towards the centre to a point called focal length. Since the focus is along the direction of the incident light, the focal length is positive.

2. The concave lens is called divergent because the ray of light passing parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after passing through the convex lens, diverges away from the lens and it appears to be emerging away from an imaginary point called focus. Since the focus is in the reverse direction of the incident light, the focal length is negative.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




