
If \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + \sin A}}{{1 - \sin A}}} = \sec A + \tan A\], then, the quadrant in which the angle A lies are.
A. I, II
B. II, III
C. I, IV
D. III, V
Answer
592.8k+ views
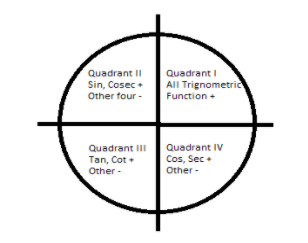
Hint: When two lines, one real axis and the other imaginary axis passes perpendicular through a circle, the circle is divided into four quadrants. Into quadrant I, where both x and y-axis are positive, Quadrant II, here x-axis is negative, and the y-axis is positive, Quadrant III here both the x-axis and y-axis are negative, and in Quadrant IV x-axis is positive, and the y-axis is negative.
In the case of the trigonometric functions in quadrant I, all the functions are positive, in Quadrant II, Sin and Cosec functions are positive, and other functions are negative, in Quadrant III, tan and cot functions are positive and other are negative, and in the case of Quadrant IV, Cos and Sec functions are positive and other being negative.
Complete step by step solution: \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + \sin A}}{{1 - \sin A}}} = \sec A + \tan A\]
One of the methods to remove the square root is the rationalization where the numerator and the denominator are multiplied by the same rational number; hence we will rationalize the LHS of the given function:
\[
\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + \sin A}}{{1 - \sin A}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left( {1 - \sin A} \right)\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}^2}}}{{\left( {1 - {{\sin }^2}A} \right)}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\sqrt {\left( {{{\cos }^2}A} \right)} }}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {{\sin }^2}A + {{\cos }^2}A = 1} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} \\
\]
Hence, we have got the LHS as: \[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}}\]
We know\[\sqrt {\left( {{{\cos }^2}A} \right)} = \left| {\cos A} \right| = \pm \cos A\], hence we put the value \[ + \cos A\]and \[ - \cos A\]to check the function:
\[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} = \dfrac{1}{{ + \cos A}} + \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{ + \cos A}} = \sec A + \tan A - - - - (i)\]
\[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - \cos A}} + \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{ - \cos A}} = - \sec A - \tan A - - - - (ii)\]
Hence we can see in equation (i) \[ + \cos A\] satisfy the given equation, \[\cos A\] is positive only in quadrant I and quadrant IV.
Option C is correct.
Note: The co-function identities show the relationship between the sin, cos, tan, cosine, sec, and cot function. The value of the trigonometric function for an angle is equal to the value of the cofunction of the complement.
In the case of the trigonometric functions in quadrant I, all the functions are positive, in Quadrant II, Sin and Cosec functions are positive, and other functions are negative, in Quadrant III, tan and cot functions are positive and other are negative, and in the case of Quadrant IV, Cos and Sec functions are positive and other being negative.

Complete step by step solution: \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + \sin A}}{{1 - \sin A}}} = \sec A + \tan A\]
One of the methods to remove the square root is the rationalization where the numerator and the denominator are multiplied by the same rational number; hence we will rationalize the LHS of the given function:
\[
\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + \sin A}}{{1 - \sin A}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left( {1 - \sin A} \right)\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}^2}}}{{\left( {1 - {{\sin }^2}A} \right)}}} \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\sqrt {\left( {{{\cos }^2}A} \right)} }}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {{\sin }^2}A + {{\cos }^2}A = 1} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} \\
\]
Hence, we have got the LHS as: \[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}}\]
We know\[\sqrt {\left( {{{\cos }^2}A} \right)} = \left| {\cos A} \right| = \pm \cos A\], hence we put the value \[ + \cos A\]and \[ - \cos A\]to check the function:
\[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} = \dfrac{1}{{ + \cos A}} + \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{ + \cos A}} = \sec A + \tan A - - - - (i)\]
\[\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sin A} \right)}}{{\left| {\cos A} \right|}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - \cos A}} + \dfrac{{\sin A}}{{ - \cos A}} = - \sec A - \tan A - - - - (ii)\]
Hence we can see in equation (i) \[ + \cos A\] satisfy the given equation, \[\cos A\] is positive only in quadrant I and quadrant IV.
Option C is correct.
Note: The co-function identities show the relationship between the sin, cos, tan, cosine, sec, and cot function. The value of the trigonometric function for an angle is equal to the value of the cofunction of the complement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




