
If primary root continues to grow type of root system will be known as
A. Secondary root
B. Fibrous root
C. Tap root
D. Stilt root
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Root is the underground part of the plant. Roots originate by the elongation of the radicle of the embryo. There are different types of root found in plants like tap, fibrous, adventitious roots.
Complete step by step answer:
Roots originate by the elongation of the radicle of the embryo. Root gives support to the aerial part of the plant that is the stem. Also, the root absorbs minerals and water from the soil. Along with these functions root also performs various functions and modifies according to this. Roots are of different types in different plants. In monocot plants, the fibrous root is found and in dicot plants root is called tap root. The tap root is found in dicot angiosperms. At the time of embryonic development, the radicle elongates and forms the primary root. This primary root grows continuously downward and also gives rise to many branches during growth. These branches are secondary and tertiary roots. All secondary and tertiary branches are called lateral roots. This type of root is called a tap root system.
Fibrous roots are found in monocots. These are also called adventitious roots. The primary root that is developed from radicle destruction and new roots are developed from any other part of the plant-like basal part of the stem. This root has thick fibers and is called the fibrous root.
Stilt roots are modified adventitious roots that are found in mangrove plants.
Hence option C is correct.
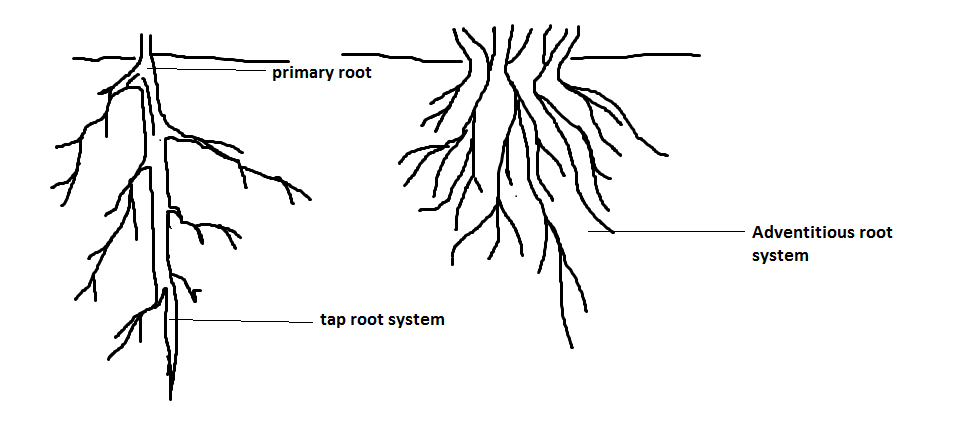
Note: The lateral roots and adventitious roots are endogenous in nature. In epiphytes and climbers, aerial roots are found. Plants that live in a saline water area called mangroves. These have pneumatophore roots. Sometimes root modifies food. For example- carrot, radish, beets, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Roots originate by the elongation of the radicle of the embryo. Root gives support to the aerial part of the plant that is the stem. Also, the root absorbs minerals and water from the soil. Along with these functions root also performs various functions and modifies according to this. Roots are of different types in different plants. In monocot plants, the fibrous root is found and in dicot plants root is called tap root. The tap root is found in dicot angiosperms. At the time of embryonic development, the radicle elongates and forms the primary root. This primary root grows continuously downward and also gives rise to many branches during growth. These branches are secondary and tertiary roots. All secondary and tertiary branches are called lateral roots. This type of root is called a tap root system.
Fibrous roots are found in monocots. These are also called adventitious roots. The primary root that is developed from radicle destruction and new roots are developed from any other part of the plant-like basal part of the stem. This root has thick fibers and is called the fibrous root.
Stilt roots are modified adventitious roots that are found in mangrove plants.
Hence option C is correct.

Note: The lateral roots and adventitious roots are endogenous in nature. In epiphytes and climbers, aerial roots are found. Plants that live in a saline water area called mangroves. These have pneumatophore roots. Sometimes root modifies food. For example- carrot, radish, beets, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




