
If length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 20cm, 15cm and 10cm respectively, then find :
(a) Area of the base.
(b) Surface area of its vertical faces.
(c) Volume.
Answer
619.5k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this problem, we must use formulas of surface area and volume of Cuboid along with proper understanding of length, breadth and height of cuboid to get the required result.
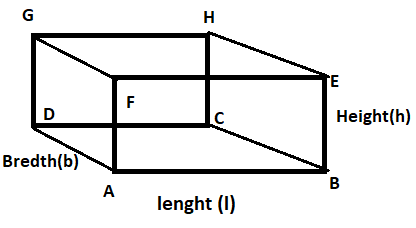
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question it is given the length(l) = 20cm, breadth(b) =15cm, height(h)=10cm of cuboid.
(A) Area of base ABCD = length(l) × breadth(b)
So on putting the values of length(l) & breadth(b)
=20×15
=300${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$.
(B) Surface area of its vertical faces
Here it is total 4 vertical surfaces, ABEF, BEHC, HCDG, AFGD
By observing the given figure, we can say that Surface area of its vertical faces ABEF, HCDG will be equal and will be the length(l) × height(h)
So Surface area of its vertical faces ABEF, HCDG = 2 (length(l) × height(h))
Similarly, by observing the given figure, we can say that Surface area of its vertical faces BEHC, AFGD will be equal and will be the breadth(b) × height(h)
So Surface area of its vertical faces BEHC, AFGD = 2 (breadth(b) × height(h))
So Total Surface area of its vertical faces =
2 (length(l) × height(h)) + 2 (breadth(b) × height(h))
=2(lh+bh)
So on putting all the values
= 2(20×10+15×10)
=2×350
=700 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$.
(C) we know that the Volume of cuboid is equal to length(l) × breadth(b) × height(h)
So on putting all the value
=20×15×10
=300×10
=3000 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$.
Note: Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept we have to remember is that always remember the formula of Surface area and volume of Cuboid which are stated above, then using those formulas calculate, whatever is asked in question.

Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question it is given the length(l) = 20cm, breadth(b) =15cm, height(h)=10cm of cuboid.
(A) Area of base ABCD = length(l) × breadth(b)
So on putting the values of length(l) & breadth(b)
=20×15
=300${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$.
(B) Surface area of its vertical faces
Here it is total 4 vertical surfaces, ABEF, BEHC, HCDG, AFGD
By observing the given figure, we can say that Surface area of its vertical faces ABEF, HCDG will be equal and will be the length(l) × height(h)
So Surface area of its vertical faces ABEF, HCDG = 2 (length(l) × height(h))
Similarly, by observing the given figure, we can say that Surface area of its vertical faces BEHC, AFGD will be equal and will be the breadth(b) × height(h)
So Surface area of its vertical faces BEHC, AFGD = 2 (breadth(b) × height(h))
So Total Surface area of its vertical faces =
2 (length(l) × height(h)) + 2 (breadth(b) × height(h))
=2(lh+bh)
So on putting all the values
= 2(20×10+15×10)
=2×350
=700 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$.
(C) we know that the Volume of cuboid is equal to length(l) × breadth(b) × height(h)
So on putting all the value
=20×15×10
=300×10
=3000 ${\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^3}$.
Note: Whenever we face such types of problems the key concept we have to remember is that always remember the formula of Surface area and volume of Cuboid which are stated above, then using those formulas calculate, whatever is asked in question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




