
If given a trigonometric equation$\sqrt 3 \tan \theta = 3\sin \theta $, find the value of ${\sin ^2}\theta - {\cos ^2}\theta $
Answer
624k+ views
Hint: - Use the trigonometric identities and Pythagoras theorem.
Given:$\sqrt 3 \tan \theta = 3\sin \theta $
$
\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }}\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \sqrt 3 \sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta }} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent{\text{ }}side}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{B}{H} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
$
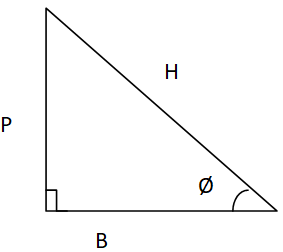
From the above figure for the Right angled triangle by using Pythagoras Theorem,
$
{H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2} \\
{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)^2} = {P^2} + {1^2} \\
{P^2} = 3 - 1 \\
{P^2} = 2 \\
P = \sqrt 2 \\
$
Now, ${\sin ^2}\theta - {\cos ^2}\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{P}{H}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{B}{H}} \right)^2}$
$
= {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} \\
= \dfrac{2}{3} - \dfrac{1}{3} \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \\
$
Note: The above question can be solved by using trigonometric identities, but here it is done by visualizing the terms in the form of sides of the right angled triangle, thus making the problem easier to solve.
Given:$\sqrt 3 \tan \theta = 3\sin \theta $
$
\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }}\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \sqrt 3 \sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta }} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent{\text{ }}side}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{B}{H} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
$

From the above figure for the Right angled triangle by using Pythagoras Theorem,
$
{H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2} \\
{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)^2} = {P^2} + {1^2} \\
{P^2} = 3 - 1 \\
{P^2} = 2 \\
P = \sqrt 2 \\
$
Now, ${\sin ^2}\theta - {\cos ^2}\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{P}{H}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{B}{H}} \right)^2}$
$
= {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} \\
= \dfrac{2}{3} - \dfrac{1}{3} \\
= \dfrac{1}{3} \\
$
Note: The above question can be solved by using trigonometric identities, but here it is done by visualizing the terms in the form of sides of the right angled triangle, thus making the problem easier to solve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




