
If events A and B are independent and $P\left( A \right)=0.15,\,\,P\left( A\cup B \right)=0.45$, then $P\left( B \right)$ is:
(a) $\dfrac{6}{13}$
(b) $\dfrac{6}{17}$
(c) $\dfrac{6}{19}$
(d) $\dfrac{6}{23}$
Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: Use the given condition to find the value of intersection of events A, B. Now draw Venn diagrams of two events X, Y. Then derive a formula for their union. Try to relate union, intersection and the two events themselves for this formula. Now substitute all the values you have. Then you will be left with a single variable $P\left( B \right)$. Now keep this $P\left( B \right)$ variable term on the left-hand side and send all other constants on to the right-hand side. By this, after all simplification the values on the right hand side will be our required result that is the value of $P\left( B \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Venn Diagram: A Venn diagram is a diagram that shows all possible logical relations between a collection of different sets. These diagrams depict elements as points in a space, and as set as regions inside a closed curve generally circles. Each circle represents a set. The overlapping region represents the common points between sets.
Intersection of sets: In mathematics, intersection of 2 sets A, B is the set consisting of all elements common in both A, B denoted by $A\cap B$.
Union of sets: In mathematics, union of 2 sets A, B is the set consisting of all elements belonging to A, B denoted by $A\cup B$.
Let us take any two random events X, Y.
Let us assume the probability of events X is P(X).
Let us assume the probability of event y is P(Y).
Let us assume intersection of events as $P\left( X\cap Y \right)$
Let us assume union of events as $P\left( X\cup Y \right)$
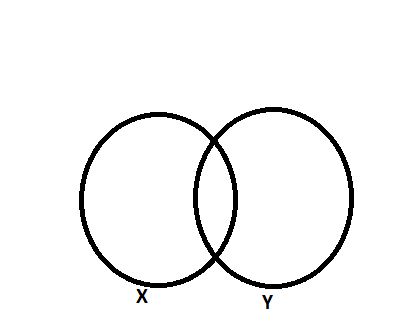
First Venn diagram is representation of X and the second Venn diagram is representation of the event y.
By the diagram, when we combine both X and Y events, we count the intersection part twice. So, we need to subtract the intersection term once to get the union. So, we can write it as:
$P\left( X\cup Y \right)=P\left( X \right)+P\left( Y \right)-P\left( X\cap Y \right)$
It is given in the question they are independent, so, we say:
$P\left( A\cap B \right)=P\left( A \right)\times P\left( B \right)$
Given in the question the values of few terms, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=0.45,P\left( A \right)=0.15$
By substituting events A, B into union formula, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)-P\left( A\cap B \right)$
By substituting the value of $P\left( A\cap B \right)$ in the equation, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)-P\left( A \right)\times P\left( B \right)$
By substituting the values, you know, we get it as:
$0.45=0.15+P\left( B \right)-0.15P\left( B \right)$
So, simplifying, we get $P\left( B \right)$ value, as below:
$P\left( B \right)=\dfrac{30}{25}=\dfrac{6}{17}$
Therefore option (b) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note: Generally, students confuse and take $P\left( A\cap B \right)=0$ when they are all independent but it is a wrong method. You must always take $P\left( A\cap B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)$. While substituting don’t forget the term $P\left( B \right)$ generated by intersection probability. Students forget that term and solve where they get the wrong result. So, solve it carefully.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Venn Diagram: A Venn diagram is a diagram that shows all possible logical relations between a collection of different sets. These diagrams depict elements as points in a space, and as set as regions inside a closed curve generally circles. Each circle represents a set. The overlapping region represents the common points between sets.
Intersection of sets: In mathematics, intersection of 2 sets A, B is the set consisting of all elements common in both A, B denoted by $A\cap B$.
Union of sets: In mathematics, union of 2 sets A, B is the set consisting of all elements belonging to A, B denoted by $A\cup B$.
Let us take any two random events X, Y.
Let us assume the probability of events X is P(X).
Let us assume the probability of event y is P(Y).
Let us assume intersection of events as $P\left( X\cap Y \right)$
Let us assume union of events as $P\left( X\cup Y \right)$
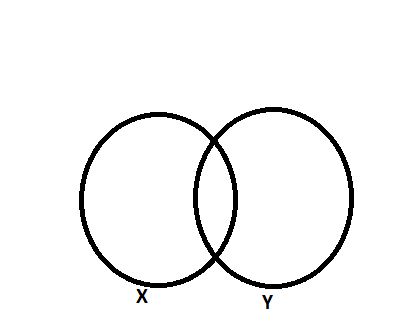
First Venn diagram is representation of X and the second Venn diagram is representation of the event y.
By the diagram, when we combine both X and Y events, we count the intersection part twice. So, we need to subtract the intersection term once to get the union. So, we can write it as:
$P\left( X\cup Y \right)=P\left( X \right)+P\left( Y \right)-P\left( X\cap Y \right)$
It is given in the question they are independent, so, we say:
$P\left( A\cap B \right)=P\left( A \right)\times P\left( B \right)$
Given in the question the values of few terms, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=0.45,P\left( A \right)=0.15$
By substituting events A, B into union formula, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)-P\left( A\cap B \right)$
By substituting the value of $P\left( A\cap B \right)$ in the equation, we get:
$P\left( A\cup B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)-P\left( A \right)\times P\left( B \right)$
By substituting the values, you know, we get it as:
$0.45=0.15+P\left( B \right)-0.15P\left( B \right)$
So, simplifying, we get $P\left( B \right)$ value, as below:
$P\left( B \right)=\dfrac{30}{25}=\dfrac{6}{17}$
Therefore option (b) is the correct answer for the given question.
Note: Generally, students confuse and take $P\left( A\cap B \right)=0$ when they are all independent but it is a wrong method. You must always take $P\left( A\cap B \right)=P\left( A \right)+P\left( B \right)$. While substituting don’t forget the term $P\left( B \right)$ generated by intersection probability. Students forget that term and solve where they get the wrong result. So, solve it carefully.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

What are the advantages of vegetative propagation class 12 biology CBSE

Suicide bags of cells are aEndoplasmic reticulum bLysosome class 12 biology CBSE

What is the Full Form of PVC, PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP and PS ?




