
If C is the midpoint of AB and P is any point outside AB then,
(a) $\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=\overrightarrow{PC}$
(b) $\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC}$
(c) $\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}+\overrightarrow{PC}=0$
(d) $\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}+2\overrightarrow{PC}=0$
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this problem, we need to carefully draw the vector diagram. From the vector diagram, we need to find the relation of the $\overrightarrow{PA}$ and $\overrightarrow{PB}$ separately, and then by adding them we will get the answer.
Complete ste-by-step solution:
In this question, we are given that the point C is the midpoint of line AB.
Let there be the point P outside the line AB.
Let's draw and understand the figure better.
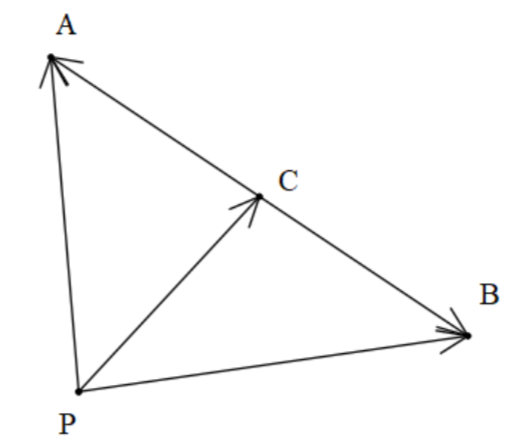
As we can see that point C is the midpoint of line AB.
The vector can be expressed as starting from the tail to the tip.
For example, for vector $\overrightarrow{PA}$ means the vector starts from the P and ends on the A.
In the triangle, ACP, we can write as follows,
$\overrightarrow{PA}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}...................(i)$
We can say this as we can go from P to A directly from P to A vector or we can go to C and then from C to A.
Similarly, in triangle PCB, we can write as follows,
$\overrightarrow{PB}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CB}...................(ii)$
We can say this as we can go from P to B directly from P to B vector or we can go to C and then from C to B.
Adding two equation we get,
$\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CB}$
Solving this we can say that,
$\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}$
The vector $\overrightarrow{CA}$ is equal to the vector $\overrightarrow{CB}$ but in opposite in direction. Because the point C is the midpoint of line AB.
Hence, the distance from point C to A and from C to B is the same.
So, we can write as,
$\overrightarrow{CA}=-\overrightarrow{CB}$
Substituting we get,
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC}-\overrightarrow{CB}+\overrightarrow{CB} \\
& \overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note:In this question, the direction of the vector is very important. From which point we consider the tail and from which we consider the tail is important. For a hint, we can check what all vectors are present from the option given below. Also, we need to be careful while adding the two vectors with the tail of the first vector, and the head of the second vector can be added together, and the resultant of these vectors from the head of the first vector to the tail of the second vector.
Complete ste-by-step solution:
In this question, we are given that the point C is the midpoint of line AB.
Let there be the point P outside the line AB.
Let's draw and understand the figure better.

As we can see that point C is the midpoint of line AB.
The vector can be expressed as starting from the tail to the tip.
For example, for vector $\overrightarrow{PA}$ means the vector starts from the P and ends on the A.
In the triangle, ACP, we can write as follows,
$\overrightarrow{PA}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}...................(i)$
We can say this as we can go from P to A directly from P to A vector or we can go to C and then from C to A.
Similarly, in triangle PCB, we can write as follows,
$\overrightarrow{PB}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CB}...................(ii)$
We can say this as we can go from P to B directly from P to B vector or we can go to C and then from C to B.
Adding two equation we get,
$\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CB}$
Solving this we can say that,
$\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC}+\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}$
The vector $\overrightarrow{CA}$ is equal to the vector $\overrightarrow{CB}$ but in opposite in direction. Because the point C is the midpoint of line AB.
Hence, the distance from point C to A and from C to B is the same.
So, we can write as,
$\overrightarrow{CA}=-\overrightarrow{CB}$
Substituting we get,
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC}-\overrightarrow{CB}+\overrightarrow{CB} \\
& \overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{PB}=2\overrightarrow{PC} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note:In this question, the direction of the vector is very important. From which point we consider the tail and from which we consider the tail is important. For a hint, we can check what all vectors are present from the option given below. Also, we need to be careful while adding the two vectors with the tail of the first vector, and the head of the second vector can be added together, and the resultant of these vectors from the head of the first vector to the tail of the second vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




