
If an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC = 6cm is inscribed in a circle of radius 9cm, find the area of the triangle.
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In this question we will use the basic properties of the circle and Pythagoras theorem. Here we will make an isosceles triangle inside a circle of given radius and then by using properties of the circle and Pythagoras theorem we will find out the area of that triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
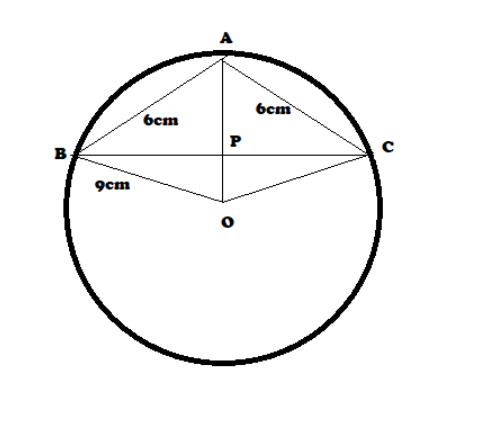
Given that,
In $\vartriangle ABC$, AB = AC = 6cm and it is inscribed in a circle having radius 9cm.
Let O be the centre of the circle and P be the midpoint of side BC, then $OP \bot BC$
Since $\vartriangle ABC$ is isosceles and p is the mid-point of BC.
Therefore,
$AP \bot BC$ as the median from the vertex in an isosceles triangle is perpendicular to the base.
Let AP = x and PB = CP = y.
Now, applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle APB$, we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BP} \right)^2} + {\left( {AP} \right)^2}$ …………(i)
Put AB = 6cm, AP = x and BP = y in equation (i), we will get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 6 \right)^2} = {\left( y \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 36 = {x^2} + {y^2}$ ………. (ii)
Similarly, we will apply Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle OPB$, we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {OB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BP} \right)^2} + {\left( {OP} \right)^2}$ …….. (iii)
Now, put OB =9cm, OP = 9 – x, BP = y in equation (iii), we get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 9 \right)^2} = {\left( y \right)^2} + {\left( {9 - x} \right)^2}$,
Solving this by using the identity, ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$, we will get
$ \Rightarrow 81 = {y^2} + {x^2} + 81 - 18x$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = 18x$ ………. (iv)
Putting equation (iv) in equation (ii), we will get
$ \Rightarrow 18x = 36$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{36}}{{18}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2$
Here we will put this value of x in equation (iv), we get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 2 \right)^2} + {y^2} = 18 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 36 - 4$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 32$
Taking square root on both sides, we will get
$ \Rightarrow y = 4\sqrt 2 $
Hence, we get x = 2 and $y = 4\sqrt 2 $
So, AP = x = 2cm and BC = BP + PC = y + y = $8\sqrt 2 $
We know that,
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {base} \right)\left( {height} \right)$
So, the area of triangle ABC = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AP} \right)$
Area of triangle ABC = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8\sqrt 2 } \right)\left( 2 \right)$
Area of triangle ABC = $8\sqrt 2 c{m^2}$
Hence, area of triangle ABC is $8\sqrt 2 c{m^2}$
Note: In this type of question, first we have to make the proper figure regarding the statements given in the question and then we will take some values like x and y as assumptions. Then we will use the Pythagoras theorem to find those values and then using those values we will find the area of the given triangle by using the formula of area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {base} \right)\left( {height} \right)$,
then we will get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given that,
In $\vartriangle ABC$, AB = AC = 6cm and it is inscribed in a circle having radius 9cm.
Let O be the centre of the circle and P be the midpoint of side BC, then $OP \bot BC$
Since $\vartriangle ABC$ is isosceles and p is the mid-point of BC.
Therefore,
$AP \bot BC$ as the median from the vertex in an isosceles triangle is perpendicular to the base.
Let AP = x and PB = CP = y.
Now, applying Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle APB$, we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BP} \right)^2} + {\left( {AP} \right)^2}$ …………(i)
Put AB = 6cm, AP = x and BP = y in equation (i), we will get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 6 \right)^2} = {\left( y \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 36 = {x^2} + {y^2}$ ………. (ii)
Similarly, we will apply Pythagoras theorem in $\vartriangle OPB$, we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {OB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BP} \right)^2} + {\left( {OP} \right)^2}$ …….. (iii)
Now, put OB =9cm, OP = 9 – x, BP = y in equation (iii), we get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 9 \right)^2} = {\left( y \right)^2} + {\left( {9 - x} \right)^2}$,
Solving this by using the identity, ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$, we will get
$ \Rightarrow 81 = {y^2} + {x^2} + 81 - 18x$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = 18x$ ………. (iv)
Putting equation (iv) in equation (ii), we will get
$ \Rightarrow 18x = 36$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{36}}{{18}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2$
Here we will put this value of x in equation (iv), we get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( 2 \right)^2} + {y^2} = 18 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 36 - 4$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 32$
Taking square root on both sides, we will get
$ \Rightarrow y = 4\sqrt 2 $
Hence, we get x = 2 and $y = 4\sqrt 2 $
So, AP = x = 2cm and BC = BP + PC = y + y = $8\sqrt 2 $
We know that,
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {base} \right)\left( {height} \right)$
So, the area of triangle ABC = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AP} \right)$
Area of triangle ABC = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8\sqrt 2 } \right)\left( 2 \right)$
Area of triangle ABC = $8\sqrt 2 c{m^2}$
Hence, area of triangle ABC is $8\sqrt 2 c{m^2}$
Note: In this type of question, first we have to make the proper figure regarding the statements given in the question and then we will take some values like x and y as assumptions. Then we will use the Pythagoras theorem to find those values and then using those values we will find the area of the given triangle by using the formula of area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {base} \right)\left( {height} \right)$,
then we will get the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




