
If \[12{{\cot }^{2}}\theta -31\cos ec+32=0\], then value of \[\sin \theta \] is,
(a) \[\dfrac{3}{5}\]or 1
(b) \[\dfrac{2}{3}\]or \[\dfrac{-2}{3}\]
(c) \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]or \[\dfrac{3}{4}\]
(d) \[\pm \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Answer
621k+ views
Hint: Substitute the trigonometric formula for \[{{\cot }^{2}}\theta \]. The entire equation becomes in terms of \[\cos ec\theta \]. Solve the equation formed and find the roots. \[\sin \theta \] is the inverse of \[\cos ec\theta \]. Find the root and inverse it to get the value of \[\sin \theta \].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given the expression, \[12{{\cot }^{2}}\theta -31\cos ec+32=0-(1)\]
We know the trigonometric expression,
\[\begin{align}
& \cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -{{\cot }^{2}}\theta =1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cot }^{2}}\theta =\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -1 \\
\end{align}\]
Substitute the value of \[{{\cot }^{2}}\theta \]in equation (1),
\[\begin{align}
& 12{{\cot }^{2}}\theta -31\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta +32=0 \\
& 12\left( \cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -1 \right)-31\cos ec\theta +32=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Opening the bracket and simplifying it,
\[\begin{align}
& 12\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -12-31\cos ec\theta +32=0 \\
& 12\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -31\cos ec\theta +20=0-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equation (2) is in the form of a quadratic equation. We know a general quadratic equation is of the form \[a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\]. Comparing both the general equation (1) and equation (2), we get,
\[a=12,b=-31,c=20\]
Now substitute these values in the quadratic form \[\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\]to get the roots.
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{-\left( -31 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -31 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 12\times 20}}{2\times 12} \\
& =\dfrac{31\pm \sqrt{961-960}}{24}=\dfrac{31\pm \sqrt{1}}{24} \\
& =\dfrac{31\pm 1}{24} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]We get the roots as \[\left( \dfrac{31+1}{24} \right)\]and \[\left( \dfrac{31-1}{24} \right)\]\[=\dfrac{32}{24}\]and \[\dfrac{30}{24}\].
\[\therefore \]The roots are \[\dfrac{4}{3}\]and \[\dfrac{5}{4}\].
\[\therefore \]\[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]and \[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{5}{4}\].
We know, \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\]
\[\therefore \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{3}}\]or \[\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{5}{4}}\].
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Note: We got the value of \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Hence, we can find the value of \[\cos \theta \] and \[\tan \theta \].
\[\sin \theta \] = opposite side/ Hypotenuse.
By Pythagoras theorem,
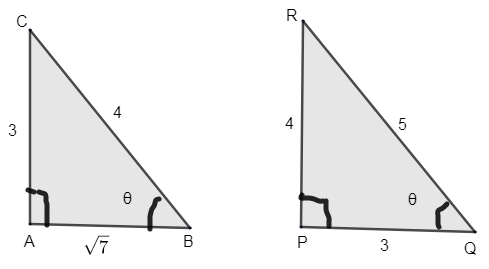
\[A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{B{{C}^{2}}-A{{C}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}}\]
\[AB=\sqrt{16-9}=\sqrt{7}\]
\[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{Q{{R}^{2}}-R{{P}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}-{{4}^{2}}}\]
\[PQ=\sqrt{25-16}=3\]
\[\tan \theta \]= opposite side/ adjacent side \[=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{3}\].
\[\cos \theta \]= adjacent side/ hypotenuse\[=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{3}{5}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given the expression, \[12{{\cot }^{2}}\theta -31\cos ec+32=0-(1)\]
We know the trigonometric expression,
\[\begin{align}
& \cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -{{\cot }^{2}}\theta =1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cot }^{2}}\theta =\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -1 \\
\end{align}\]
Substitute the value of \[{{\cot }^{2}}\theta \]in equation (1),
\[\begin{align}
& 12{{\cot }^{2}}\theta -31\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta +32=0 \\
& 12\left( \cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -1 \right)-31\cos ec\theta +32=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Opening the bracket and simplifying it,
\[\begin{align}
& 12\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -12-31\cos ec\theta +32=0 \\
& 12\cos e{{c}^{2}}\theta -31\cos ec\theta +20=0-(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equation (2) is in the form of a quadratic equation. We know a general quadratic equation is of the form \[a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\]. Comparing both the general equation (1) and equation (2), we get,
\[a=12,b=-31,c=20\]
Now substitute these values in the quadratic form \[\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\]to get the roots.
\[\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{-\left( -31 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -31 \right)}^{2}}-4\times 12\times 20}}{2\times 12} \\
& =\dfrac{31\pm \sqrt{961-960}}{24}=\dfrac{31\pm \sqrt{1}}{24} \\
& =\dfrac{31\pm 1}{24} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \]We get the roots as \[\left( \dfrac{31+1}{24} \right)\]and \[\left( \dfrac{31-1}{24} \right)\]\[=\dfrac{32}{24}\]and \[\dfrac{30}{24}\].
\[\therefore \]The roots are \[\dfrac{4}{3}\]and \[\dfrac{5}{4}\].
\[\therefore \]\[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]and \[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{5}{4}\].
We know, \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos ec\theta }\]
\[\therefore \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{3}}\]or \[\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{5}{4}}\].
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Note: We got the value of \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Hence, we can find the value of \[\cos \theta \] and \[\tan \theta \].
\[\sin \theta \] = opposite side/ Hypotenuse.
By Pythagoras theorem,

\[A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{B{{C}^{2}}-A{{C}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}}\]
\[AB=\sqrt{16-9}=\sqrt{7}\]
\[P{{Q}^{2}}+P{{R}^{2}}\Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{Q{{R}^{2}}-R{{P}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}-{{4}^{2}}}\]
\[PQ=\sqrt{25-16}=3\]
\[\tan \theta \]= opposite side/ adjacent side \[=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\]or \[\dfrac{4}{3}\].
\[\cos \theta \]= adjacent side/ hypotenuse\[=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\]or \[\dfrac{3}{5}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




