
Identify the stage when homologous chromosome are separated but sister chromatids remain associated
(a) Metaphase I
(b) Anaphase I
(c) Metaphase II
(d) Anaphase II
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: In this stage of meiosis, the attachment of the spindle fibers is completed and the homologous chromosomes are pulled apart and move towards opposite ends of the cell. We shouldn’t confuse this with the pulling apart of sister chromatids. This is the point when 23 chromosomes move to each pole and reduce to its half in each cell.
Complete step by step answer:
A set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pairs up with each other inside a cell during fertilization is called a set of homologous chromosomes. Before separating during meiosis, a pair of chromosomes align correctly with each other because homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along each chromosome which enable. The identical copies (chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere are called sister chromatids or it can be said as a 'one-half' of the duplicated chromosome.
The pairs of homologous chromosomes, also known as bivalents or tetrads, line up in a random order along with the metaphase plate in metaphase I of meiosis I. Meiotic spindles emanating from opposite spindle poles are attached to each of the homologs at the kinetochore.
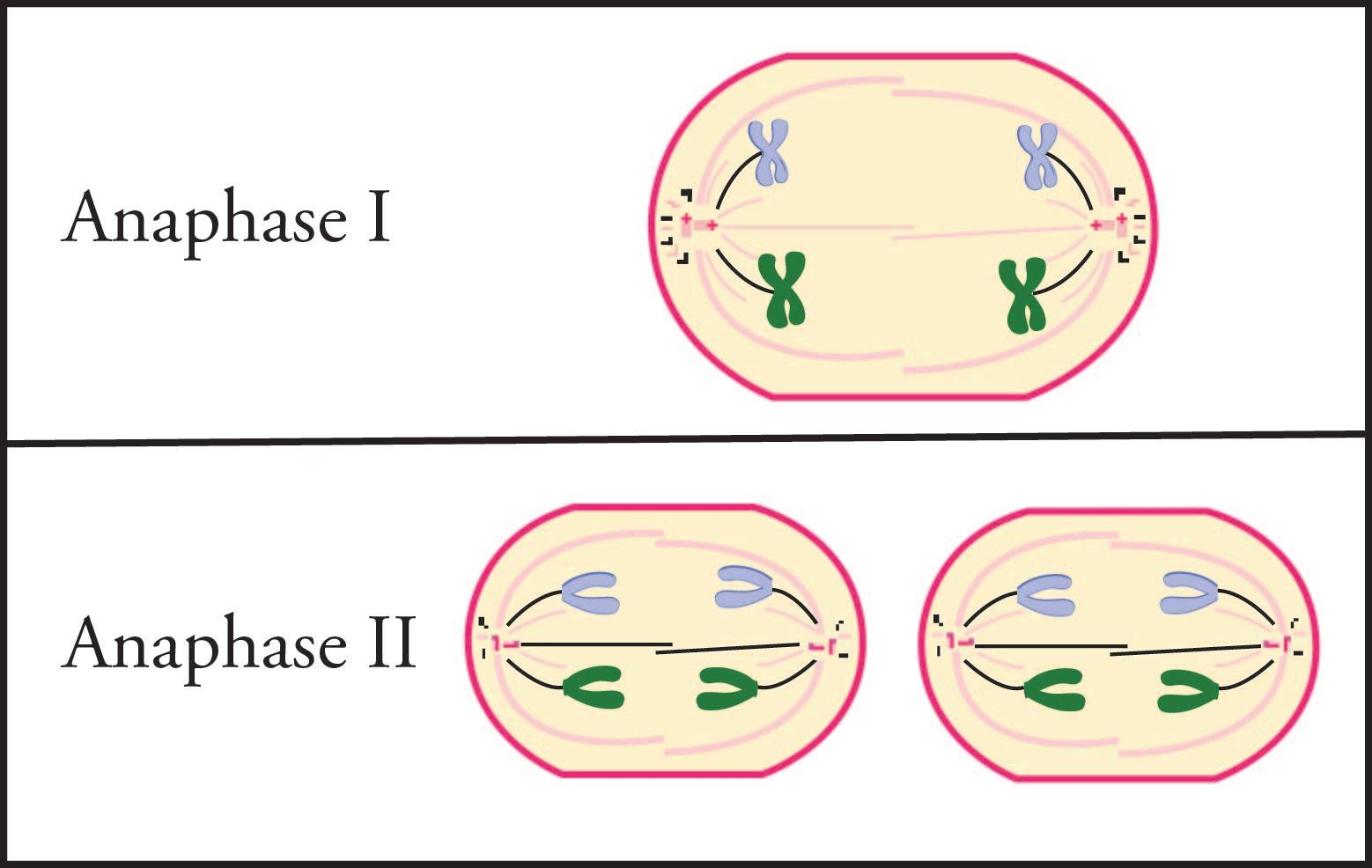
The homologous chromosomes are pulled apart from each other in anaphase I of meiosis I. The enzyme separase cleaves the homologs to release the cohesin that held the homologous chromosome arms together. As a result, homologs move to opposite poles of the cell and then randomly segregated into two daughter cells that will undergo meiosis II to produce four haploid daughter germ cells. In anaphase II the centromeres separate, and the two chromatids of each chromosome move to opposite poles on the spindle.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Anaphase I’.
Additional information:
1) The chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell replicate to produce double the amount of chromosomal material before meiosis. Chromosomes separate into sister chromatids after replication which is known as interphase. The meiotic cycle has the following phases: Growth (G) , and Synthesis (S) . Proteins and enzymes necessary for growth are synthesized during the growth phase, while during the S phase chromosomal material is doubled.
2) We know that meiosis I begin with one diploid parent cell and ends with two haploid daughter cells, halving the number of chromosomes in each cell, while meiosis II starts the division with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.
3) A scientist named Oskar Hertwig described the fusion of egg and sperm in the transparent sea urchin egg in 1876.
Note: When chromosomes do not segregate properly severe repercussions can occur and which can lead to fertility problems, embryo death, birth defects, and cancer. The mechanisms for pairing and adhering homologous chromosomes vary among organisms, but it must function properly for the final genetic material to be sorted correctly. It is very crucial that the homologous chromosome separate properly in meiosis I for sister chromatid separation in meiosis II. If they failed to separate properly is known as nondisjunction which is of 2 types that are trisomy and monosomy.
Complete step by step answer:
A set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pairs up with each other inside a cell during fertilization is called a set of homologous chromosomes. Before separating during meiosis, a pair of chromosomes align correctly with each other because homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along each chromosome which enable. The identical copies (chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere are called sister chromatids or it can be said as a 'one-half' of the duplicated chromosome.
The pairs of homologous chromosomes, also known as bivalents or tetrads, line up in a random order along with the metaphase plate in metaphase I of meiosis I. Meiotic spindles emanating from opposite spindle poles are attached to each of the homologs at the kinetochore.

The homologous chromosomes are pulled apart from each other in anaphase I of meiosis I. The enzyme separase cleaves the homologs to release the cohesin that held the homologous chromosome arms together. As a result, homologs move to opposite poles of the cell and then randomly segregated into two daughter cells that will undergo meiosis II to produce four haploid daughter germ cells. In anaphase II the centromeres separate, and the two chromatids of each chromosome move to opposite poles on the spindle.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Anaphase I’.
Additional information:
1) The chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell replicate to produce double the amount of chromosomal material before meiosis. Chromosomes separate into sister chromatids after replication which is known as interphase. The meiotic cycle has the following phases: Growth (G) , and Synthesis (S) . Proteins and enzymes necessary for growth are synthesized during the growth phase, while during the S phase chromosomal material is doubled.
2) We know that meiosis I begin with one diploid parent cell and ends with two haploid daughter cells, halving the number of chromosomes in each cell, while meiosis II starts the division with two haploid parent cells and ends with four haploid daughter cells, maintaining the number of chromosomes in each cell.
3) A scientist named Oskar Hertwig described the fusion of egg and sperm in the transparent sea urchin egg in 1876.
Note: When chromosomes do not segregate properly severe repercussions can occur and which can lead to fertility problems, embryo death, birth defects, and cancer. The mechanisms for pairing and adhering homologous chromosomes vary among organisms, but it must function properly for the final genetic material to be sorted correctly. It is very crucial that the homologous chromosome separate properly in meiosis I for sister chromatid separation in meiosis II. If they failed to separate properly is known as nondisjunction which is of 2 types that are trisomy and monosomy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




