
Identify the labels A, B, C and D in the given structure of t RNA and select the correct option:
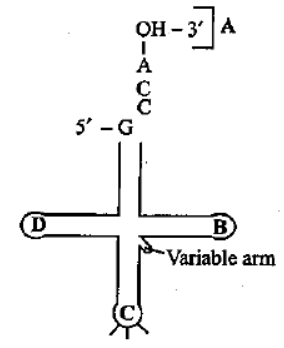
A. anticodon loop, T psi C loop, AA binding site, DHU loop
B. AA binding site, T psi C loop, anticodon loop, DHU loop
C. AA binding site, DHU loop, anticodon loop, T psi C loop
D. AA binding site, DHU loop, T psi C loop, anticodon loop

Answer
376.5k+ views
Hint: A form of RNA molecule called transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) aids in the translation of a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence into a protein. Translation, which creates a protein from an mRNA molecule, uses tRNAs at particular locations on the ribosome.
Complete step by step solution:
An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence that is complementary to a matching codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence and is found at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. The ribosome's initial docking location is where the tRNA is found. The initiation codon of the mRNA, where translation begins, is complementary to the anticodon of this tRNA.
The amino acid that goes with that codon is carried by the tRNA. In the opposite docking site of the ribosome, the next mRNA codon is now visible. Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) is predominantly produced from the tRNA gene by transcription by RNA polymerase, and it undergoes a number of processes before reaching its mature state, including processing, splicing, CCA addition, and posttranscriptional modification.
The T psi C loop in tRNA contains ribothymidine and pseudouridine. The loop serves as the location for ribosome attachment. Dihydrouridine is a component of another loop, the DHU loop. It serves as the aminoacyl synthetase enzyme's binding site. The 3 end of tRNA molecules has an unpaired (single-stranded) CCAOH sequence. Because the amino acid attaches covalently to adenylic acid, or A, of the CCA sequence during polypeptide synthesis, this region is known as an amino acid binding site. Three nitrogen bases make up the anticodon loop, which recognizes and binds to the mRNA codon.
So, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Transfer RNA, often known as tRNA, is a tiny RNA molecule that is essential for the production of proteins. Between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the expanding chain of amino acids that make up a protein, transfer RNA acts as a link (or adapter).
Complete step by step solution:
An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence that is complementary to a matching codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence and is found at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. The ribosome's initial docking location is where the tRNA is found. The initiation codon of the mRNA, where translation begins, is complementary to the anticodon of this tRNA.
The amino acid that goes with that codon is carried by the tRNA. In the opposite docking site of the ribosome, the next mRNA codon is now visible. Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) is predominantly produced from the tRNA gene by transcription by RNA polymerase, and it undergoes a number of processes before reaching its mature state, including processing, splicing, CCA addition, and posttranscriptional modification.
The T psi C loop in tRNA contains ribothymidine and pseudouridine. The loop serves as the location for ribosome attachment. Dihydrouridine is a component of another loop, the DHU loop. It serves as the aminoacyl synthetase enzyme's binding site. The 3 end of tRNA molecules has an unpaired (single-stranded) CCAOH sequence. Because the amino acid attaches covalently to adenylic acid, or A, of the CCA sequence during polypeptide synthesis, this region is known as an amino acid binding site. Three nitrogen bases make up the anticodon loop, which recognizes and binds to the mRNA codon.
So, option (B) is correct.
Note:
Transfer RNA, often known as tRNA, is a tiny RNA molecule that is essential for the production of proteins. Between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the expanding chain of amino acids that make up a protein, transfer RNA acts as a link (or adapter).
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




