
How to identify epimers and anomers in carbohydrates (sugar)?
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: Isomerism is an important phenomenon for compounds. The phenomena in which different compounds having the same chemical formula but different structures are known as isomerism and the compounds exhibiting isomerism are known as isomers.
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of different types. Broadly they are divided into structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers are further divided into chain isomers, position isomers and functional isomers. Whereas stereoisomers are of two types namely enantiomers and diastereomers.
Enantiomers are non-superimposable chiral centers mirror type whereas diastereomers are non-superimposable chiral centers but are not mirror image to each other.
Epimers and Anomers are both diastereomers, but epimer is a stereoisomer that differs in configuration at any single stereogenic center, while anomers is actually an epimer that differs in configuration at the acetal/hemiacetal carbon.
Epimer at stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each.
Anomer is an epimer differing from each other in the configuration \[C - 1\] if they are aldoses or in configuration at \[C - 2\] if they are ketoses. The epimer carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Epimers differ in the configuration of a single carbon atom. Examples are \[D - galactose\] and \[D - mannose\] which are epimers of \[D - glucose\]. \[D - galactose\] differ only at \[C - 4\] from D-glucose, whereas \[D - mannose\] differ only at the \[C - 2\] configuration.
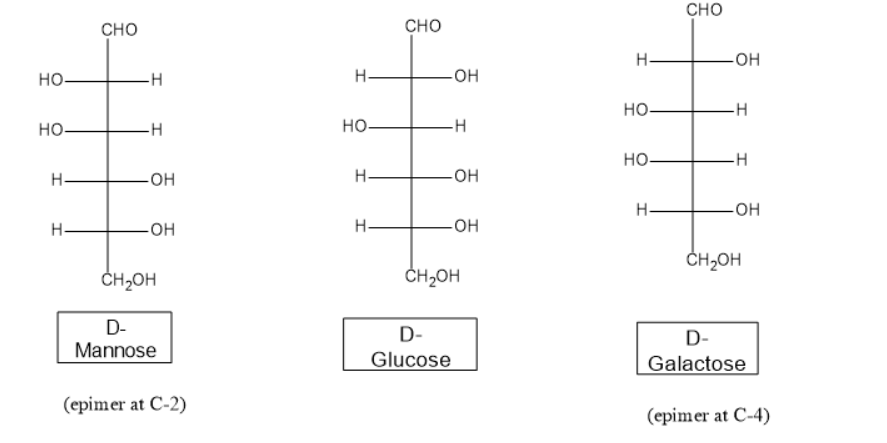
Anomers differ in a configuration only at the anomeric carbon.
For example, \[\alpha - D - glucose\] and \[\beta - D - glucose\] are anomers. The \[\alpha \] form has anomeric \[OH\] at \[C - 1\] on the opposite side of the ring from \[C{H_2}OH\] group at \[C - 5\] whereas the \[\beta \] form has anomeric \[OH\] group at \[C{H_2}OH\]
Note:
Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or in the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Complete answer:
Isomerism is of different types. Broadly they are divided into structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers are further divided into chain isomers, position isomers and functional isomers. Whereas stereoisomers are of two types namely enantiomers and diastereomers.
Enantiomers are non-superimposable chiral centers mirror type whereas diastereomers are non-superimposable chiral centers but are not mirror image to each other.
Epimers and Anomers are both diastereomers, but epimer is a stereoisomer that differs in configuration at any single stereogenic center, while anomers is actually an epimer that differs in configuration at the acetal/hemiacetal carbon.
Epimer at stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each.
Anomer is an epimer differing from each other in the configuration \[C - 1\] if they are aldoses or in configuration at \[C - 2\] if they are ketoses. The epimer carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Epimers differ in the configuration of a single carbon atom. Examples are \[D - galactose\] and \[D - mannose\] which are epimers of \[D - glucose\]. \[D - galactose\] differ only at \[C - 4\] from D-glucose, whereas \[D - mannose\] differ only at the \[C - 2\] configuration.

Anomers differ in a configuration only at the anomeric carbon.
For example, \[\alpha - D - glucose\] and \[\beta - D - glucose\] are anomers. The \[\alpha \] form has anomeric \[OH\] at \[C - 1\] on the opposite side of the ring from \[C{H_2}OH\] group at \[C - 5\] whereas the \[\beta \] form has anomeric \[OH\] group at \[C{H_2}OH\]
Note:
Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses or in the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




