
Identify all the chiral centres in each molecule and determine the absolute configuration as R or S:
(A)
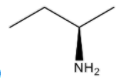
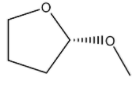
(B)
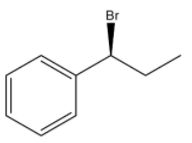
(C)
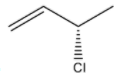
(D)
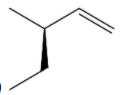
(E)





Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: a chiral centre of a molecule is an atom that has four different groups directly attached to it in such a manner that it has a non-superimposable mirror image.
Complete step by step solution:
Absolute Configuration or most commonly referred to as the R and S system are used to label chiral centres. To determine the absolute configuration, we need to first locate the carbon(s) with four different groups (atoms) connected to it. These are called chirality centers or chiral centers.
Firstly, we examine at the atoms directly attached to the chiral centre of the compound. A substituent with a greater atomic number takes precedence over a substituent with a smaller atomic number.
-While dealing with isotopes, the atom with the higher atomic mass gets higher priority.
-While imagining/visualizing the molecule, the lowest priority substituent should always point away from the viewer (which is indicated by a dashed line).
-Then we draw an arrow from the highest priority atom to the 2nd priority atom to the 3rd priority atom. As the 4th priority atom is placed in the back, the arrow should appear like it is moving round. If it is going clockwise, then it is an R-enantiomer and if it is going counterclockwise, it is an S-enantiomer.
The chiral center is marked by an asterix/star.
(A)
 R configuration.
R configuration.
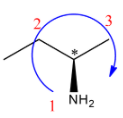
(B)
 S configuration.
S configuration.
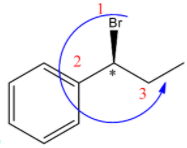
(C)
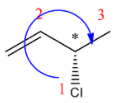 S configuration.
S configuration.
(D)
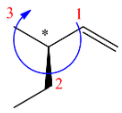 R configuration.
R configuration.
(E)
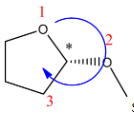 S configuration.
S configuration.
Additional information:
If two or more of the atoms which are bonded directly to the chiral center are the same, then these groups are prioritized based on the next set of atoms (atoms adjacent to the directly bonded atoms). And if two atoms have substituents of the same priority, then higher priority is given to the atom with more of these substituents.
Note: please remember that all the chirality centers in enantiomers are inverted which means every R is S, every S is R in the enantiomer. And also the lowest priority must point away from the viewer.
Complete step by step solution:
Absolute Configuration or most commonly referred to as the R and S system are used to label chiral centres. To determine the absolute configuration, we need to first locate the carbon(s) with four different groups (atoms) connected to it. These are called chirality centers or chiral centers.
Firstly, we examine at the atoms directly attached to the chiral centre of the compound. A substituent with a greater atomic number takes precedence over a substituent with a smaller atomic number.
-While dealing with isotopes, the atom with the higher atomic mass gets higher priority.
-While imagining/visualizing the molecule, the lowest priority substituent should always point away from the viewer (which is indicated by a dashed line).
-Then we draw an arrow from the highest priority atom to the 2nd priority atom to the 3rd priority atom. As the 4th priority atom is placed in the back, the arrow should appear like it is moving round. If it is going clockwise, then it is an R-enantiomer and if it is going counterclockwise, it is an S-enantiomer.
The chiral center is marked by an asterix/star.
(A)

(B)

(C)

(D)

(E)

Additional information:
If two or more of the atoms which are bonded directly to the chiral center are the same, then these groups are prioritized based on the next set of atoms (atoms adjacent to the directly bonded atoms). And if two atoms have substituents of the same priority, then higher priority is given to the atom with more of these substituents.
Note: please remember that all the chirality centers in enantiomers are inverted which means every R is S, every S is R in the enantiomer. And also the lowest priority must point away from the viewer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




