
(i) Define real image of an object.
(ii) Name the mirror that
(a) can give real as well as virtual images of an object.
(b) will always give a virtual image of the same size as an object.
(c) will always give a virtual and diminished image of an object.
(d) is used by a doctor in examining teeth.
(iii) With the help of a ray diagram explain the use of concave mirrors as solar concentrators.
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Real images can be generated by concave mirrors and converging lenses only if the object is located further apart from the mirror than the focal point, and this real picture is inverted. As the object reaches the focal point, the image reaches infinity, and when the object moves to the focal point, the image displays virtual and is not inverted. The distance is not equal to the object to the lenses.
Complete step-by-step solution:
(i) If refracted or reflected rays meet genuinely, the intersection point is called an object's actual or real image. An image is described as collecting focus points of light rays arising from an object. An actual image is the combination of focus points formed by converging rays, while a virtual image is the combination of focus points made by expansions of diverging rays. It is an image located in the plane of convergence for the light rays originating from a given object. Examples of real images compose an image on a cinema screen, the image displayed on a detector in the back of a camera, and the image displayed on an eyeball retina.
Complete, solid lines always represent the real light rays; perceived or extrapolated dashed lines represent light rays. An actual image happens where rays concentrate, whereas a virtual image happens where rays only appear to deviate.
(ii) (a) concave mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) convex mirror
(d) concave
iii) A solar concentrator uses lenses, which use a significant area of sunlight and focus it towards a particular spot by bending the light rays and concentrating them.
Similarly, in the concave mirror, all light rays moving parallel to the principal axis concentrate on a single point called the mirror's focus.
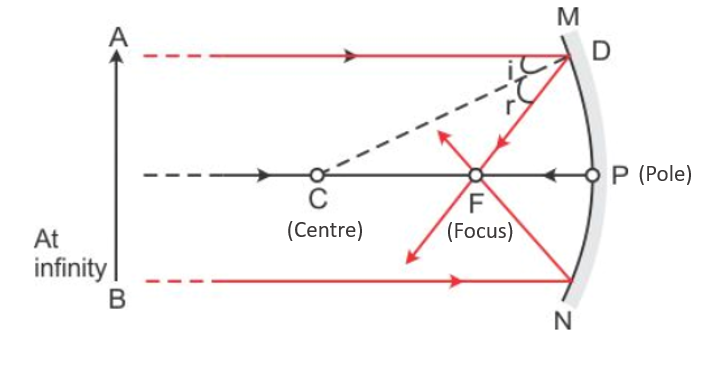
Hence when concave mirrors are utilized as solar concentrators, the concave mirror is located such that the sun rays converge at a single point, are parallel to the principal axis, and the object to be heated is located at this point.
Note: A second lens may also examine real images. This is the device used by binoculars, telescopes, and light microscopes. The objective lens converges the light from the object and extends an actual image within the composition of the optical instrument. A second lens, the eyepiece, then predicts a second actual image onto the eye's retina.
Complete step-by-step solution:
(i) If refracted or reflected rays meet genuinely, the intersection point is called an object's actual or real image. An image is described as collecting focus points of light rays arising from an object. An actual image is the combination of focus points formed by converging rays, while a virtual image is the combination of focus points made by expansions of diverging rays. It is an image located in the plane of convergence for the light rays originating from a given object. Examples of real images compose an image on a cinema screen, the image displayed on a detector in the back of a camera, and the image displayed on an eyeball retina.
Complete, solid lines always represent the real light rays; perceived or extrapolated dashed lines represent light rays. An actual image happens where rays concentrate, whereas a virtual image happens where rays only appear to deviate.
(ii) (a) concave mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) convex mirror
(d) concave
iii) A solar concentrator uses lenses, which use a significant area of sunlight and focus it towards a particular spot by bending the light rays and concentrating them.
Similarly, in the concave mirror, all light rays moving parallel to the principal axis concentrate on a single point called the mirror's focus.

Hence when concave mirrors are utilized as solar concentrators, the concave mirror is located such that the sun rays converge at a single point, are parallel to the principal axis, and the object to be heated is located at this point.
Note: A second lens may also examine real images. This is the device used by binoculars, telescopes, and light microscopes. The objective lens converges the light from the object and extends an actual image within the composition of the optical instrument. A second lens, the eyepiece, then predicts a second actual image onto the eye's retina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




