
Hydroboration-oxidation of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ produces:
A. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$
B. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
C. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(OH)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$
D. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we should know the reactant and reagent used in the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. We should also familiar about the working of reagent.as the name of the reaction indicates the hydroboration is done by hydride of boron that is ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ followed by oxidation which is done by water. The product of the reaction is alcohol which is formed by syn addition of boron hydride. The product also follows the anti-markovnikov rule.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hydroboration followed by oxidation is used for the formation of alcohols. The reagent used for hydroboration-oxidation is ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$.
The reaction of propene with${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{THF/}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ is as follows:
The whole reaction takes place in two parts. In the first part, the boron hydride gets attached with alkene. The boron gets attached at terminal carbon of the alkene. Boron has three hydrogen so it can bind with three alkene molecules.
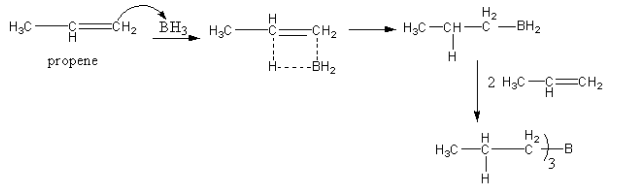
The second part of the reaction is hydrolysis. The hydrolysis of the trimer of boron alkyl gives the alcohol. The hydrolysis is done by ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$.
The hydrolysis is shown as follows:
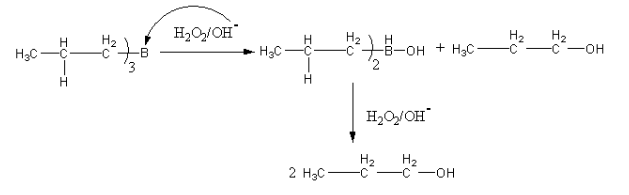
Hydroboration-oxidation of propene ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ produces propanol${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$.
Therefore, option (A) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$is correct.
Note: The alcohol formed by hydroboration-oxidation is primary alcohol. The reagent of hydroboration-oxidation, boron hydride, gives syn addition. As both the hydrogen ${\text{H}}$and ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ get attached from the same side or face forming a cyclic structure so, the addition is known as syn addition. According to the anti-markovnikov rule the hydrogen get attached at the carbon of the double bond having less number of hydrogen. So, the formation of propanol follows is anti-markovnikov because hydrogen gets attached to the carbon having less number of hydrogens.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hydroboration followed by oxidation is used for the formation of alcohols. The reagent used for hydroboration-oxidation is ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$.
The reaction of propene with${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - {\text{THF/}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ is as follows:
The whole reaction takes place in two parts. In the first part, the boron hydride gets attached with alkene. The boron gets attached at terminal carbon of the alkene. Boron has three hydrogen so it can bind with three alkene molecules.

The second part of the reaction is hydrolysis. The hydrolysis of the trimer of boron alkyl gives the alcohol. The hydrolysis is done by ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$.
The hydrolysis is shown as follows:

Hydroboration-oxidation of propene ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ produces propanol${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$.
Therefore, option (A) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$is correct.
Note: The alcohol formed by hydroboration-oxidation is primary alcohol. The reagent of hydroboration-oxidation, boron hydride, gives syn addition. As both the hydrogen ${\text{H}}$and ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ get attached from the same side or face forming a cyclic structure so, the addition is known as syn addition. According to the anti-markovnikov rule the hydrogen get attached at the carbon of the double bond having less number of hydrogen. So, the formation of propanol follows is anti-markovnikov because hydrogen gets attached to the carbon having less number of hydrogens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




