
Hybridisation and shape of $ Xe{F_4} $ is:
(A) $ s{p^3}d $, Trigonal bipyramidal
(B) $ s{p^3} $, Tetrahedral
(C) $ s{p^3}{d^2} $, Square planar
(D) $ s{p^3}{d^2} $, Hexagonal
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: To determine the shape and the geometry of the molecule, we use VSEPR theory. According to VSEPR theory, the force of repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons on the central atom should be minimal. This is to stabilize the molecule.
Complete answer:
Let’s solve this question using VSEPR theory and the valence shell of the xenon, $ Xe $ .
Since, we know that our central atom is xenon, $ Xe $ and it has $ 8 $ valence electron in the valence shell, and out of these $ 8 $ electrons, $ 6 $ electrons are in the $ 5p $ orbital and the $ 2 $ electrons are in the $ 5s $ orbital.
Also, the $ 5d $ and the $ 5f $ orbitals of the xenon are empty. So during the formation of $ Xe{F_4} $ , the two excited electrons of the $ 5p $ orbital move to the empty $ 5d $ orbital. As a result, there are $ 4 $ unpaired electrons, $ 2 $ in the $ 5p $ orbital and $ 2 $ in the $ 5d $ orbital.
This all over arrangement of electrons in the s,p,d orbitals gives $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ hybridisation of the molecule.
Let’s look at the structure too carefully for better understanding.
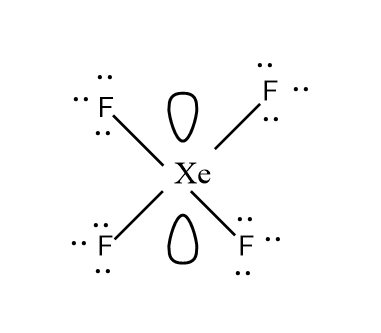
And according to the VSEPR theory, the molecule with $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ hybridisation has square planar geometry.
So, based on the above discussion, the correct option is (C). Therefore, Hybridisation and shape of $ Xe{F_4} $ is $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ and square planar respectively.
Note:
The four fluorine atoms pairs with the four half-filled orbitals (i.e. $ 5p $ and the $ 5d $ orbital) and they lie at the corners of the central atom to minimise the repulsion. Also, the two lone pairs of electrons of the central atom i.e. xenon lie perpendicular to the plane to make the molecule overall stable. Hence, this gives the molecule its square planar shape.
Complete answer:
Let’s solve this question using VSEPR theory and the valence shell of the xenon, $ Xe $ .
Since, we know that our central atom is xenon, $ Xe $ and it has $ 8 $ valence electron in the valence shell, and out of these $ 8 $ electrons, $ 6 $ electrons are in the $ 5p $ orbital and the $ 2 $ electrons are in the $ 5s $ orbital.
Also, the $ 5d $ and the $ 5f $ orbitals of the xenon are empty. So during the formation of $ Xe{F_4} $ , the two excited electrons of the $ 5p $ orbital move to the empty $ 5d $ orbital. As a result, there are $ 4 $ unpaired electrons, $ 2 $ in the $ 5p $ orbital and $ 2 $ in the $ 5d $ orbital.
This all over arrangement of electrons in the s,p,d orbitals gives $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ hybridisation of the molecule.
Let’s look at the structure too carefully for better understanding.

And according to the VSEPR theory, the molecule with $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ hybridisation has square planar geometry.
So, based on the above discussion, the correct option is (C). Therefore, Hybridisation and shape of $ Xe{F_4} $ is $ s{p^3}{d^2} $ and square planar respectively.
Note:
The four fluorine atoms pairs with the four half-filled orbitals (i.e. $ 5p $ and the $ 5d $ orbital) and they lie at the corners of the central atom to minimise the repulsion. Also, the two lone pairs of electrons of the central atom i.e. xenon lie perpendicular to the plane to make the molecule overall stable. Hence, this gives the molecule its square planar shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




