
How do amino acids bond together?
Answer
348.3k+ views
Hint: Amino acids are the basic building blocks that form proteins. Each amino acid is made of carboxylic acid, side chain, and amino functional groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amino acids are organic compounds that makeup proteins. Various elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, and selenium are found in amino acids. These molecules are bound to each other by peptide bonds.
It is a type of amide bond formed between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amino group of the second amino acid. This reaction results in the release of a water molecule. This is an example of a dehydration synthesis reaction. The formation of peptide bonds requires energy in the form of ATP.
Peptide bonds help in stabilising the structure of proteins. The proteins formed are used in varied roles like physical support, identification of various molecules, and as catalysts for reactions.
Enzymes called peptidyl transferases aid in the growth of the polypeptide chain by the addition of amino acid residues.
Amide bonds refer to the bonds in short simple molecules, whereas peptide bonds refer to the bonds present in long peptide chains.
Peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain show partial double bond character because of resonance. These bonds are kinetically stable, strong, and require high activation energy for the bond to be broken. Exposure to a strong base or acid at an increased temperature causes it to break. The action of digestive enzymes can also cause the bond to be cleaved.
Peptide bonds are planar and rigid. Both N-H and C=O bonds lie on the same plane restricting the rotation of the bond. This gives the molecules a trans or cis configuration or stereochemistry, which further stabilizes the structure of the protein.
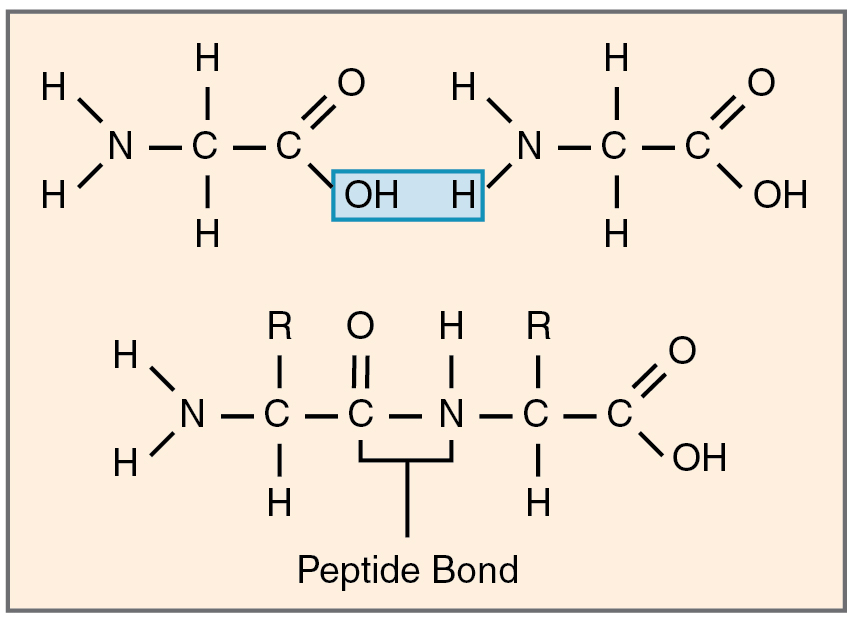
Image: Peptide bond formation between two amino acids
Note: Different regions of the peptide bond form hydrogen bonding. This is because the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are partially positive and negative respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amino acids are organic compounds that makeup proteins. Various elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, and selenium are found in amino acids. These molecules are bound to each other by peptide bonds.
It is a type of amide bond formed between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amino group of the second amino acid. This reaction results in the release of a water molecule. This is an example of a dehydration synthesis reaction. The formation of peptide bonds requires energy in the form of ATP.
Peptide bonds help in stabilising the structure of proteins. The proteins formed are used in varied roles like physical support, identification of various molecules, and as catalysts for reactions.
Enzymes called peptidyl transferases aid in the growth of the polypeptide chain by the addition of amino acid residues.
Amide bonds refer to the bonds in short simple molecules, whereas peptide bonds refer to the bonds present in long peptide chains.
Peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain show partial double bond character because of resonance. These bonds are kinetically stable, strong, and require high activation energy for the bond to be broken. Exposure to a strong base or acid at an increased temperature causes it to break. The action of digestive enzymes can also cause the bond to be cleaved.
Peptide bonds are planar and rigid. Both N-H and C=O bonds lie on the same plane restricting the rotation of the bond. This gives the molecules a trans or cis configuration or stereochemistry, which further stabilizes the structure of the protein.

Image: Peptide bond formation between two amino acids
Note: Different regions of the peptide bond form hydrogen bonding. This is because the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are partially positive and negative respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




