
What happens when vegetable oils are hydrogenated? Name catalyst used.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Vegetable oils are basically polyunsaturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids are converted into saturated fatty acids by the hydrogenation process. Unsaturated fatty acids are liquids while saturated fatty acids are solids. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils is carried out by passing out hydrogen gas (${H_2}$) into the heated oil in the presence of a catalyst that does reduction.
Complete Solution :
- Hydrogenation is a process that reduces unsaturated fatty acids of triglycerides by attaching hydrogen atoms at the point of unsaturation in the presence of a catalyst. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils is carried out by passing out hydrogen gas (${H_2}$) into the heated oil in the presence of ‘powdered nickel as catalyst’. After hydrogenation vegetable oil is heated and the catalyst is recovered by filtration. The hydrogenation reaction of vegetable oil or unsaturated fatty acids can be shown as:
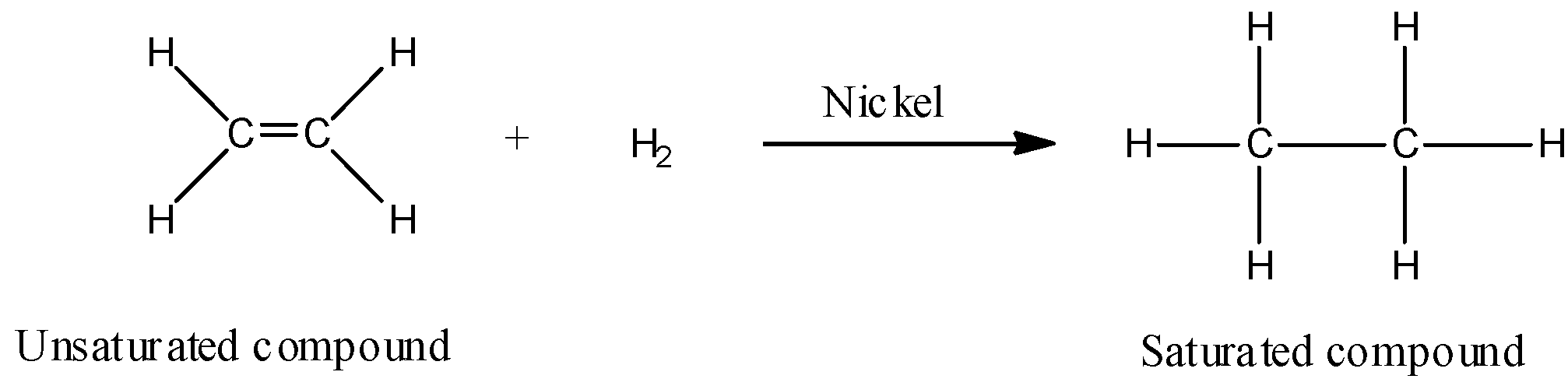
- Thus when vegetable oils which are polyunsaturated fatty acids are hydrogenated, double bonds get converted to single bonds or we get saturated compounds like vegetable ghee.
- Hydrogenation of vegetable oils (example: cotton seed oil, corn oil, or soybean oil) convert these liquids into solids having consistency comparable to that of butter. This process is also known as hardening of oil.
Also, hydrogenation of oil slows down the development of rancidity by decreasing the number of double bonds.
Hence, this is the required answer.
Note: In nearly all the naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids, the double bonds are in cis-configuration. Trans fatty acids are produced by the partial hydrogenation of oils. Trans fatty acids are the result of side chain reaction with the catalyst of hydrogenation reaction.
Complete Solution :
- Hydrogenation is a process that reduces unsaturated fatty acids of triglycerides by attaching hydrogen atoms at the point of unsaturation in the presence of a catalyst. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils is carried out by passing out hydrogen gas (${H_2}$) into the heated oil in the presence of ‘powdered nickel as catalyst’. After hydrogenation vegetable oil is heated and the catalyst is recovered by filtration. The hydrogenation reaction of vegetable oil or unsaturated fatty acids can be shown as:

- Thus when vegetable oils which are polyunsaturated fatty acids are hydrogenated, double bonds get converted to single bonds or we get saturated compounds like vegetable ghee.
- Hydrogenation of vegetable oils (example: cotton seed oil, corn oil, or soybean oil) convert these liquids into solids having consistency comparable to that of butter. This process is also known as hardening of oil.
Also, hydrogenation of oil slows down the development of rancidity by decreasing the number of double bonds.
Hence, this is the required answer.
Note: In nearly all the naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids, the double bonds are in cis-configuration. Trans fatty acids are produced by the partial hydrogenation of oils. Trans fatty acids are the result of side chain reaction with the catalyst of hydrogenation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




