
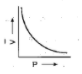
Graphs representing Boyle’s law is (are):
A:
B:

C:

D:




Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Boyle’s law states that pressure of a given substance varies inversely with its volume at constant temperature. According to this law $PV = k$ where $P$ is pressure, $V$ is volume and $k$ is a constant. According to this equation the product of pressure and volume is constant.
Complete step by step answer:
We know Boyle's law states that the product of pressure and volume is constant at a given temperature. Now we have to find the option in which graph represents product of pressure and volume constant or we can also say that the option in which pressure varies inversely with volume $\left( {P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}} \right)$ . We know that the graph is exponential if we have quantities that vary inversely with each other. There is only one option which represents an exponential graph and that option is option A. This means correct option is option A that is:
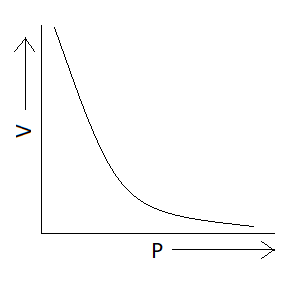
Additional information: Charles’s law tells that for an ideal gas when pressure is constant volume is directly proportional to the temperature. According to this law $PV = nRT$
Where,$P$ is pressure, $V$ is volume, $n$ is number of moles, $R$ is gas constant and $T$ is temperature of gas (in Kelvin).
According to Gay-Lussac’s law at constant volume pressure is directly proportional to the temperature of gas. According to this law $P \propto T$
Where,$P$ is pressure and $T$ is temperature.
Note:
The ideal gas model tends to fail at lower temperatures or higher pressures, when intermolecular forces and molecular size becomes important. It also fails for most heavy gases, such as many refrigerants and for gases with strong intermolecular forces, notably water vapour.
Complete step by step answer:
We know Boyle's law states that the product of pressure and volume is constant at a given temperature. Now we have to find the option in which graph represents product of pressure and volume constant or we can also say that the option in which pressure varies inversely with volume $\left( {P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}} \right)$ . We know that the graph is exponential if we have quantities that vary inversely with each other. There is only one option which represents an exponential graph and that option is option A. This means correct option is option A that is:

Additional information: Charles’s law tells that for an ideal gas when pressure is constant volume is directly proportional to the temperature. According to this law $PV = nRT$
Where,$P$ is pressure, $V$ is volume, $n$ is number of moles, $R$ is gas constant and $T$ is temperature of gas (in Kelvin).
According to Gay-Lussac’s law at constant volume pressure is directly proportional to the temperature of gas. According to this law $P \propto T$
Where,$P$ is pressure and $T$ is temperature.
Note:
The ideal gas model tends to fail at lower temperatures or higher pressures, when intermolecular forces and molecular size becomes important. It also fails for most heavy gases, such as many refrigerants and for gases with strong intermolecular forces, notably water vapour.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




