
Give the structure of Z and E forms of Cinnamic acid.
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: E and Z notation is the representation to show absolute stereochemistry of alkene. E isomer is similar to trans stereochemistry and Z isomer is similar to cis stereochemistry of the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s know what is meant by E and Z notation.
- E and Z notation is used in order to describe the absolute stereochemistry of alkene.
- E stands for entgegen in german which means opposite and Z stands for zusammen in german which means together.
- So, in order to give the notation, the four groups attached to the alkene are given priority according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. So, if the groups with higher priority are on the same side of the double bonds, then it is called Z-alkene and if they are on other sides of alkene, then it is called E-alkene.
- We need to know that Cinnamic acid is a carboxylic acid compound containing a double bond. We can write cinnamic acid as ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}-CH=CH-COOH$. Let’s draw its E and Z structures.
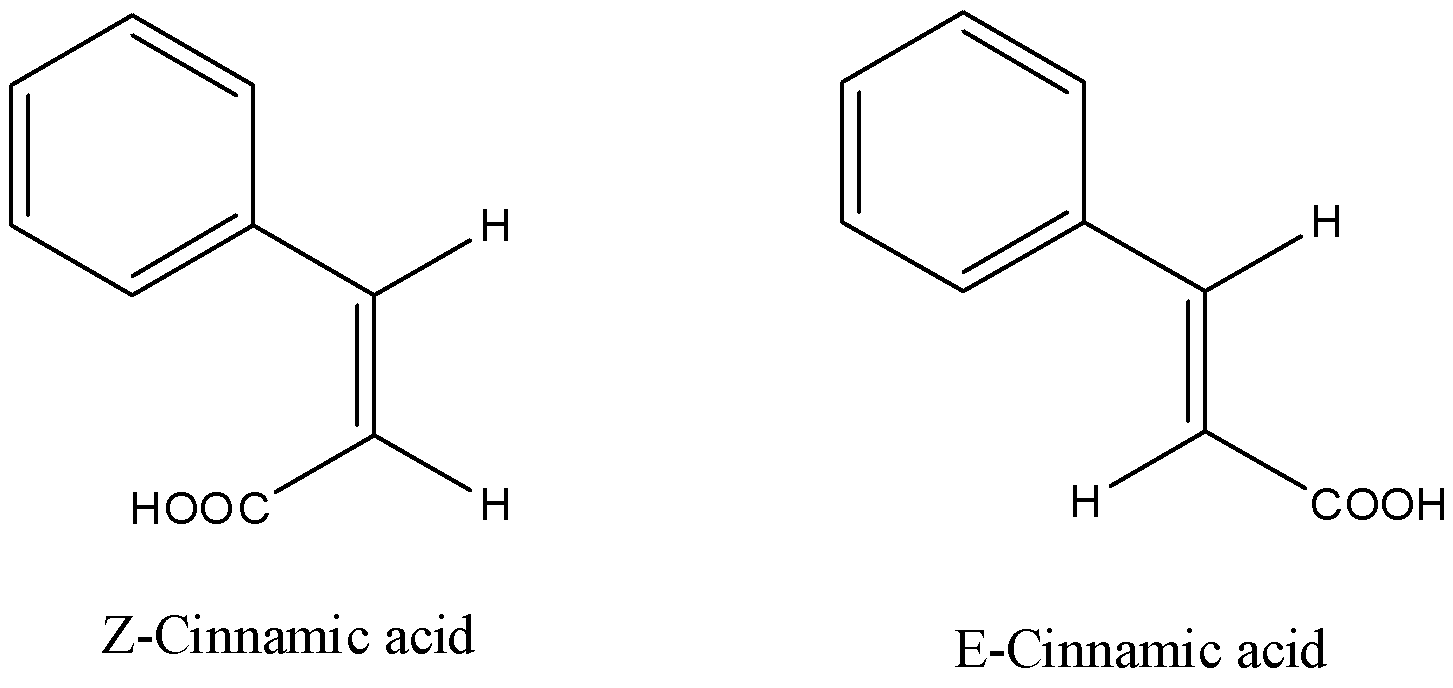
- Here, we can say that in Z-Cinnamic acid, the groups with higher priority will be phenyl group among it and hydrogen atom at carbon-3 and carboxylic acid group will have high priority among itself and hydrogen atom at carbon-2. So, we can see that both groups with high priority, phenyl and carboxylic acid groups are at the same side. So, it will be called Z-Cinnamic acid.
- In E-cinnamic acid, we can see that groups with higher priority, phenyl and carboxylic acid groups are at different sides of the double bond.
Note: The difference between E-Z notation and Cis-Trans notation is that E-Z notation shows absolute stereochemistry of the compound while Cis-trans stereochemistry is a relative representation.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s know what is meant by E and Z notation.
- E and Z notation is used in order to describe the absolute stereochemistry of alkene.
- E stands for entgegen in german which means opposite and Z stands for zusammen in german which means together.
- So, in order to give the notation, the four groups attached to the alkene are given priority according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. So, if the groups with higher priority are on the same side of the double bonds, then it is called Z-alkene and if they are on other sides of alkene, then it is called E-alkene.
- We need to know that Cinnamic acid is a carboxylic acid compound containing a double bond. We can write cinnamic acid as ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}-CH=CH-COOH$. Let’s draw its E and Z structures.

- Here, we can say that in Z-Cinnamic acid, the groups with higher priority will be phenyl group among it and hydrogen atom at carbon-3 and carboxylic acid group will have high priority among itself and hydrogen atom at carbon-2. So, we can see that both groups with high priority, phenyl and carboxylic acid groups are at the same side. So, it will be called Z-Cinnamic acid.
- In E-cinnamic acid, we can see that groups with higher priority, phenyl and carboxylic acid groups are at different sides of the double bond.
Note: The difference between E-Z notation and Cis-Trans notation is that E-Z notation shows absolute stereochemistry of the compound while Cis-trans stereochemistry is a relative representation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




