
Give the structure of ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ .
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: Phosphorous acid undergoes polymerization reaction in the presence of acetic anhydride and generates two types of polymers. They are chain-like polymers and ring like polymers contain repeated units of phosphorous acid.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that write the structure of ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ .
- The name of ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ is phosphorous acid.
- Generally phosphorus acid undergoes polymerization and forms the ring type polymers in a major amount.
- The structure of the metaphosphoric acid ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is as follows.
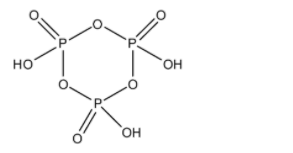
- It contains a ring-like structure in which oxygen and phosphorus atoms are arranged in alternate positions in the ring.
- Later each phosphorus atom is attached to another oxygen atom through a double bond and each phosphorus atom carries a –OH group with it.
- There are three phosphorus atoms and contain three –OH groups.
- ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is called Trimetaphosphoric acid.
- In the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ there is no P-P bond means the number of P-P bonds in the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is zero.
- At the same time there is a bond between two oxygen atoms. Means there is no O-O bond in the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ .
Note: Once the polymerized product is formed from the phosphorus acid monomers it is very stable and won’t undergo any cleavage with the external reagents. Means polymerization structures of the phosphorous acid are more stable than the normal simple structures. If ‘n’ molecules of phosphorous acid undergo polymerization then it forms a chain like structure.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that write the structure of ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ .
- The name of ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ is phosphorous acid.
- Generally phosphorus acid undergoes polymerization and forms the ring type polymers in a major amount.
- The structure of the metaphosphoric acid ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is as follows.

- It contains a ring-like structure in which oxygen and phosphorus atoms are arranged in alternate positions in the ring.
- Later each phosphorus atom is attached to another oxygen atom through a double bond and each phosphorus atom carries a –OH group with it.
- There are three phosphorus atoms and contain three –OH groups.
- ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is called Trimetaphosphoric acid.
- In the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ there is no P-P bond means the number of P-P bonds in the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ is zero.
- At the same time there is a bond between two oxygen atoms. Means there is no O-O bond in the structure of the ${{\left( HP{{O}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}$ .
Note: Once the polymerized product is formed from the phosphorus acid monomers it is very stable and won’t undergo any cleavage with the external reagents. Means polymerization structures of the phosphorous acid are more stable than the normal simple structures. If ‘n’ molecules of phosphorous acid undergo polymerization then it forms a chain like structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




