
Give the structure of alkene 2 methyl buta - 1,3 - diene?
Answer
494.1k+ views
Hint: An alkene is a hydrocarbon with a carbon–carbon double bond in chemistry. Alkene is frequently used interchangeably with olefin, which refers to any hydrocarbon with one or more double bonds. Mono Alkenes are divided into two categories: terminal and internal.
Complete answer:
A diene is a covalent molecule in organic chemistry that includes two double bonds, generally between carbon atoms. They have two alkene units and the usual systematic naming prefix di. Dienes are found in both natural and manufactured compounds and are utilised in organic synthesis as a component of larger molecules. In the polymer industry, conjugated dienes are commonly employed as monomers. Nutritionists are interested in polyunsaturated fats.
The compound's stem/root name, 'buta,' denotes that the longest C-chain in its structure has four carbon atoms.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
The suffix name '-1-3-diene' indicates the existence of two $C=C$ bonds between $1-2$ and $3-$ 4 carbon atoms.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
The presence of a methyl group ($\left(C H_{3}-\right)$) at position -2 is indicated by the prefix term '2-methyl'.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
So, once H-atoms fulfil residual valency, the structural formula looks like this.
$\stackrel{1}{C} H_{2}=\stackrel{2}{C}\left(C H_{3}\right)-\stackrel{3}{C H}=\stackrel{4}{C} H_{2}$
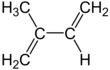
Isoprene is generated and exhaled by a wide range of tree species (major producers are oaks, poplars, eucalyptus, and some legumes). Isoprene emissions by vegetation are estimated to be approximately 600 million metric tonnes per year, with half coming from tropical broadleaf trees and the rest largely from shrubs. This amounts to nearly one-third of all hydrocarbons emitted into the atmosphere, roughly comparable to methane emissions. Isoprene accounts for around 80% of hydrocarbon emissions in deciduous woods. Algae, both microscopic and macroscopic, generate isoprene, but in modest amounts compared to trees.
Note:
Trees appear to employ isoprene emission as a defence strategy against abiotic stressors. Isoprene, in particular, has been proven to protect against mild heat stress (about 40 degrees Celsius). It may also protect plants against significant temperature swings in the leaves. In reaction to heat stress, isoprene is incorporated into cell membranes and helps to stabilise them. Resistance to reactive oxygen species is another advantage of isoprene. Leaf mass, leaf area, light (especially photosynthetic photon flux density, or PPFD), and leaf temperature all influence the quantity of isoprene emitted by isoprene-emitting plants.
Complete answer:
A diene is a covalent molecule in organic chemistry that includes two double bonds, generally between carbon atoms. They have two alkene units and the usual systematic naming prefix di. Dienes are found in both natural and manufactured compounds and are utilised in organic synthesis as a component of larger molecules. In the polymer industry, conjugated dienes are commonly employed as monomers. Nutritionists are interested in polyunsaturated fats.
The compound's stem/root name, 'buta,' denotes that the longest C-chain in its structure has four carbon atoms.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
The suffix name '-1-3-diene' indicates the existence of two $C=C$ bonds between $1-2$ and $3-$ 4 carbon atoms.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
The presence of a methyl group ($\left(C H_{3}-\right)$) at position -2 is indicated by the prefix term '2-methyl'.
$-\overset{1}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{2}{\mathop{C}}\,\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-\overset{3}{\mathop{C}}\,=\overset{4}{\mathop{C}}\,-$
So, once H-atoms fulfil residual valency, the structural formula looks like this.
$\stackrel{1}{C} H_{2}=\stackrel{2}{C}\left(C H_{3}\right)-\stackrel{3}{C H}=\stackrel{4}{C} H_{2}$

Isoprene is generated and exhaled by a wide range of tree species (major producers are oaks, poplars, eucalyptus, and some legumes). Isoprene emissions by vegetation are estimated to be approximately 600 million metric tonnes per year, with half coming from tropical broadleaf trees and the rest largely from shrubs. This amounts to nearly one-third of all hydrocarbons emitted into the atmosphere, roughly comparable to methane emissions. Isoprene accounts for around 80% of hydrocarbon emissions in deciduous woods. Algae, both microscopic and macroscopic, generate isoprene, but in modest amounts compared to trees.
Note:
Trees appear to employ isoprene emission as a defence strategy against abiotic stressors. Isoprene, in particular, has been proven to protect against mild heat stress (about 40 degrees Celsius). It may also protect plants against significant temperature swings in the leaves. In reaction to heat stress, isoprene is incorporated into cell membranes and helps to stabilise them. Resistance to reactive oxygen species is another advantage of isoprene. Leaf mass, leaf area, light (especially photosynthetic photon flux density, or PPFD), and leaf temperature all influence the quantity of isoprene emitted by isoprene-emitting plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




