
Give the name of the cell division type at A, B, C and D.
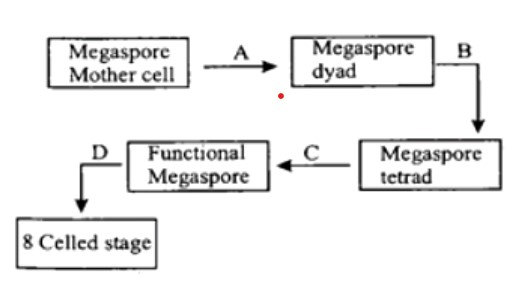
A) A-Meiosis-I, B-Mitosis, C-Mitosis, D-Meiosis
B) A-Meiosis-I, B-Meiosis-II, C-No division, D-Mitosis
C) A-Mitosis, B-No 'division, C-Meiosis-II, D-Meiosis-I
D) A-Mitosis, B-Mitosis, C-Meiosis-I, D-Meiosis-I

Answer
355.5k+ views
Hint: After meiosis I and II, the megaspore tetrad is formed, in which three of the four cells die as a result, leaving only one functioning megaspore, and in which three mitotic divisions result in eight cells stages.
Step by step solution:
The megaspore mother cell divides through mitosis to create two nuclei, which travel to opposing polar regions to form a two-nucleate embryo sac. 4 nucleate and then 8 nucleate stages of the embryo sac are produced by further mitosis. The cell wall is established and the typical embryo sac forms after the eighth nucleate stage.
Megasporogenesis is the process by which a megaspore develops from its mother cell. In the micropylar area of the nucellus, ovules typically differentiate a single mother cell that produces megaspores. This mother cell goes through meiosis, producing a linear tetrad of four mesaspores. The four megaspores near the micropylar end typically have one functional megaspore and three degenerating ones. The female gametophyte only develops from the functional megaspore (embryo sac). The functioning megaspore's nucleus divides during mitosis to produce two nuclei, which migrate to opposing poles to form a 2-nucleate embryo sac. The creation of the 4 nuclei and subsequent 8-nucleate stage of the embryo sac is the consequence of two further consecutive mitotic nuclear divisions.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Note that the functional megaspore grows and develops into eggs. Microsporogenesis is the process by which tetrads, whether tetrahedral, decussate, or isobilateral, are formed. The spores that make up the male gametophyte are known as microspores. The egg is fertilised with this male gametophyte to create a zygote.
Step by step solution:
The megaspore mother cell divides through mitosis to create two nuclei, which travel to opposing polar regions to form a two-nucleate embryo sac. 4 nucleate and then 8 nucleate stages of the embryo sac are produced by further mitosis. The cell wall is established and the typical embryo sac forms after the eighth nucleate stage.
Megasporogenesis is the process by which a megaspore develops from its mother cell. In the micropylar area of the nucellus, ovules typically differentiate a single mother cell that produces megaspores. This mother cell goes through meiosis, producing a linear tetrad of four mesaspores. The four megaspores near the micropylar end typically have one functional megaspore and three degenerating ones. The female gametophyte only develops from the functional megaspore (embryo sac). The functioning megaspore's nucleus divides during mitosis to produce two nuclei, which migrate to opposing poles to form a 2-nucleate embryo sac. The creation of the 4 nuclei and subsequent 8-nucleate stage of the embryo sac is the consequence of two further consecutive mitotic nuclear divisions.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Note that the functional megaspore grows and develops into eggs. Microsporogenesis is the process by which tetrads, whether tetrahedral, decussate, or isobilateral, are formed. The spores that make up the male gametophyte are known as microspores. The egg is fertilised with this male gametophyte to create a zygote.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




