
Give the major product the following reaction?
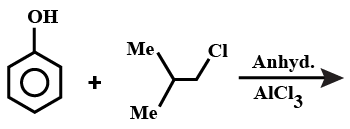
A.
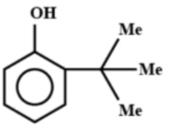
B.
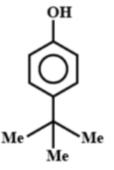
C.
D.None of these




Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: The reaction given in the question is an example of Friedel-Crafts alkylation. Friedel–Crafts alkylation involves the alkylation of an aromatic ring with an alkyl halide using a strong lewis acid. Now, you should use this to reach the correct answer.
Complete answer:
To solve this question first we need to identify the type of reaction. Here we can see an aromatic ring (phenol) reacting with an alkyl halide in the presence of $AlCl_{ 3 }$, which is a lewis acid and works as a catalyst. Hence, we can categorize it under Friedel–Crafts alkylation.
It is the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring with the help of a carbocation.
A Lewis acid catalyst such as $AlCl_{ 3 }$ is employed in this reaction to form a carbocation by facilitating the removal of the halide. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Now, let’s move to the question. We have phenol or we can say benzene with -OH group attached to it. This -OH has two lone pairs that it will donate one to the empty orbitals of $AlCl_{ 3 }$, meaning phenol will work as a base and will form a complex salt. This salt will not undergo any further reaction.
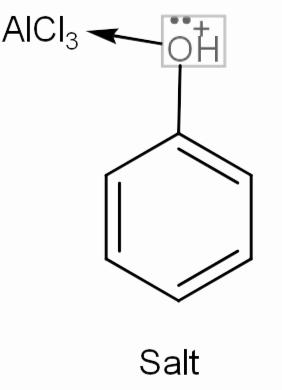
Hence we can say that we will not get a desired Friedel-crafts alkylation product.
Therefore the correct answer to this question would be option D.
Note: If this reaction somehow makes its way through Friedel-crafts reaction, then you can think that options A and B could be major products. But, no, they aren't. This reaction in question can only make para alkylated products, that too in negligible amounts because of the steric hindrance on the ortho position. Hence, only B will be formed, but not as a major product.
Complete answer:
To solve this question first we need to identify the type of reaction. Here we can see an aromatic ring (phenol) reacting with an alkyl halide in the presence of $AlCl_{ 3 }$, which is a lewis acid and works as a catalyst. Hence, we can categorize it under Friedel–Crafts alkylation.
It is the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring with the help of a carbocation.
A Lewis acid catalyst such as $AlCl_{ 3 }$ is employed in this reaction to form a carbocation by facilitating the removal of the halide. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Now, let’s move to the question. We have phenol or we can say benzene with -OH group attached to it. This -OH has two lone pairs that it will donate one to the empty orbitals of $AlCl_{ 3 }$, meaning phenol will work as a base and will form a complex salt. This salt will not undergo any further reaction.

Hence we can say that we will not get a desired Friedel-crafts alkylation product.
Therefore the correct answer to this question would be option D.
Note: If this reaction somehow makes its way through Friedel-crafts reaction, then you can think that options A and B could be major products. But, no, they aren't. This reaction in question can only make para alkylated products, that too in negligible amounts because of the steric hindrance on the ortho position. Hence, only B will be formed, but not as a major product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




