
Give and account of prophase – 1 of Meiosis.
Answer
561.9k+ views
Hint: Meiosis takes place in special cells at specific times. Meiosis occurs in cells called meiocytes which are oocytes, spermatocytes and sporacytes. Two successive divisions produce four daughter cells. The term meiosis was introduced by J.B. Farmer and Moore in 1905.
Complete answer:
By Meiosis a parent cell produces four daughter cells, having half the number of chromosomes and half of the nuclear DNA to that of the parent cell. Thus, it is also known as reduction division. Two divisions of Meiosis- Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II.
Meiosis-I is known as heterotypic division. In this division, the two homologous chromosomes of each pair separate from each other and go to separate daughter cells. Thus, the number of chromosomes from diploid to haploid condition. There are four phases of Meiosis-I which are-prophase-I, metaphase-I, anaphase-I and telophase-I.
Brief description of Prophase-1:
It lasts for a long time. It has five sub – phases:
i. Leptotene
ii. Zygotene
iii. Pachytene
iv. Diplotene
v. Diakinesis
i. Leptotene-Characteristics of leptotene are:
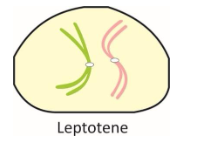
Beaded, long chromosomes.
Chromosomes show bouquet arrangement.
ii. Zygotene –
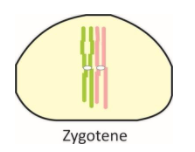
Chromosomes become shorter and thicker.
Bivalents or tetrads (paired homologous chromosomes) are seen.
Synapsis occurs
Bivalents form synaptonemal complexes.
iii. Pachytene –
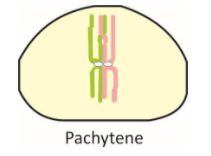
It is the longest stage, where tetrads clearly appear as spirally arranged chromosomes of homologous pairs.
Crossing over occurs in this stage.
iv. Diplotene –
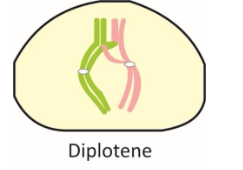
In this stage bivalents repel each other.
Chiasmata appears.
In oocytes of vertebrates it lasts for months or years.
v. Diakinesis –
Nuclear membrane disappears, centrioles migrate to poles and spindle fibres begin to form.
Note: In diplotene, the chromosomes may unfold and start transcription of mRNA and rRNA build up food reserve in the cytoplasm. Example: In primary oocytes of amphibians, reptiles and birds. In some species chromosomes enlarge greatly, like lampbrush form.
Complete answer:
By Meiosis a parent cell produces four daughter cells, having half the number of chromosomes and half of the nuclear DNA to that of the parent cell. Thus, it is also known as reduction division. Two divisions of Meiosis- Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II.
Meiosis-I is known as heterotypic division. In this division, the two homologous chromosomes of each pair separate from each other and go to separate daughter cells. Thus, the number of chromosomes from diploid to haploid condition. There are four phases of Meiosis-I which are-prophase-I, metaphase-I, anaphase-I and telophase-I.
Brief description of Prophase-1:
It lasts for a long time. It has five sub – phases:
i. Leptotene
ii. Zygotene
iii. Pachytene
iv. Diplotene
v. Diakinesis
i. Leptotene-Characteristics of leptotene are:

Beaded, long chromosomes.
Chromosomes show bouquet arrangement.
ii. Zygotene –

Chromosomes become shorter and thicker.
Bivalents or tetrads (paired homologous chromosomes) are seen.
Synapsis occurs
Bivalents form synaptonemal complexes.
iii. Pachytene –

It is the longest stage, where tetrads clearly appear as spirally arranged chromosomes of homologous pairs.
Crossing over occurs in this stage.
iv. Diplotene –

In this stage bivalents repel each other.
Chiasmata appears.
In oocytes of vertebrates it lasts for months or years.
v. Diakinesis –

Nuclear membrane disappears, centrioles migrate to poles and spindle fibres begin to form.
Note: In diplotene, the chromosomes may unfold and start transcription of mRNA and rRNA build up food reserve in the cytoplasm. Example: In primary oocytes of amphibians, reptiles and birds. In some species chromosomes enlarge greatly, like lampbrush form.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




