
How many geometric isomers exist for the molecule \[C{H_3} - CH = CH - CH = CH - C{H_3}\] ?
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: Geometric isomers are the ones which have the same atoms or groups bonded in a different spatial arrangement. The atoms of groups are bonded to a rigid structure like a double bond or a ring which makes the molecules differ in structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Geometric isomers are a pair of compounds or more than two compounds which have the same bonded atoms and groups to a rigid structure but only differ in the molecular geometry. As a result such compounds appear as a different structure.
The most common of the geometric isomers are the cis and trans isomerism which are arise due to restricted rotation around a double bond. The cis isomer is the one which has the same atoms or groups in same side and the trans isomer is the one which has the same atoms or groups on opposite side.
As for example cis-\[2\]-butene and trans-\[2\]-butene exhibit cis-trans isomerism or geometric isomerism as follows:
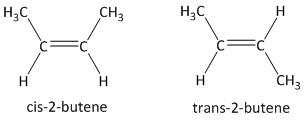
From the structures, it is evident that in cis-\[2\]-butene both the methyl groups are on same side but in trans-\[2\]-butene both the methyl groups are on opposite side. The cis-\[2\]-butene is also referred as \[Z\]-alkene and the trans-\[2\]-butene is referred as \[E\]-alkene.
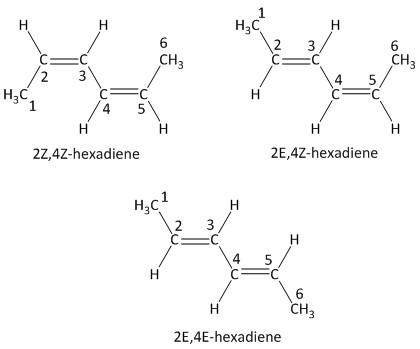
The given molecule is hexa-\[2,4\]-diene. It is a conjugated diene as the two double bonds are positioned on the \[C - 2\] carbon and \[C - 4\] carbon atoms. The presence of two double bonds indicates that four geometric isomers are possible. These are labeled as \[\left( {Z,Z} \right)\], \[\left( {Z,E} \right)\], \[\left( {E,Z} \right)\] and \[\left( {E,E} \right)\].
Out of these four isomers two isomers are similar which are \[\left( {Z,E} \right)\] and \[\left( {E,Z} \right)\]). Hence the number of geometric isomers exists for the molecule is three.
The structures can be drawn as
Note: Geometrical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism. The compounds exhibiting stereoisomers are optically active in nature. The compounds are said as chiral compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Geometric isomers are a pair of compounds or more than two compounds which have the same bonded atoms and groups to a rigid structure but only differ in the molecular geometry. As a result such compounds appear as a different structure.
The most common of the geometric isomers are the cis and trans isomerism which are arise due to restricted rotation around a double bond. The cis isomer is the one which has the same atoms or groups in same side and the trans isomer is the one which has the same atoms or groups on opposite side.
As for example cis-\[2\]-butene and trans-\[2\]-butene exhibit cis-trans isomerism or geometric isomerism as follows:

From the structures, it is evident that in cis-\[2\]-butene both the methyl groups are on same side but in trans-\[2\]-butene both the methyl groups are on opposite side. The cis-\[2\]-butene is also referred as \[Z\]-alkene and the trans-\[2\]-butene is referred as \[E\]-alkene.
The given molecule is hexa-\[2,4\]-diene. It is a conjugated diene as the two double bonds are positioned on the \[C - 2\] carbon and \[C - 4\] carbon atoms. The presence of two double bonds indicates that four geometric isomers are possible. These are labeled as \[\left( {Z,Z} \right)\], \[\left( {Z,E} \right)\], \[\left( {E,Z} \right)\] and \[\left( {E,E} \right)\].
Out of these four isomers two isomers are similar which are \[\left( {Z,E} \right)\] and \[\left( {E,Z} \right)\]). Hence the number of geometric isomers exists for the molecule is three.
The structures can be drawn as

Note: Geometrical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism. The compounds exhibiting stereoisomers are optically active in nature. The compounds are said as chiral compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




