
Gem dihalide on hydrolysis gives:
a.) vicinal diol
b.) geminal diol
c.) carbonyl compound
d.) carboxylic acid
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: Geminal dihalide hydrolysis is an organic reaction in which the gem-halide reacts with water or undergo hydrolysis in an alkaline medium. There are two products which can be formed.
Complete step by step solution: Geminal dihalides are dihalogen compounds in which both the halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom.
For example, Ethylidene dichloride
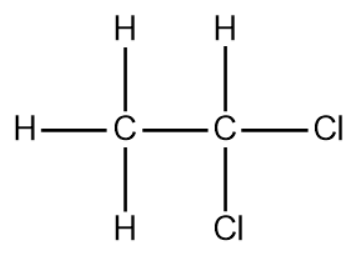
Suppose, there is a geminal dihalide \[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(Cl)}_{2}}\] is present, the hydrolysis of gem-halides takes place in alkaline medium. So, we will hydrolyse it in the presence of aqueous NaOH/KOH.
On hydrolysis, both of the chlorine group will be replaced by hydroxyl group (OH),
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(OH)}_{2}}\] will be formed.
As both the hydroxyl groups are present on the same carbon, this compound is not stable. So, water acts as a leaving group i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\] will be removed.
Thus, forming an aldehyde group \[C{{H}_{3}}CHO\], this compound is called acetaldehyde. But this is the case when gem-dihalide is present at the terminal position.
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(Cl)}_{2}}\xrightarrow[aq]{KOH}C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(OH)}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{3}}COH+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Now, let's take a compound \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(Cl)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\], on hydrolysis the chlorine groups will be replaced by hydroxyl groups, \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(OH)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\]will be obtained.
Similarly, as the previous example, this compound will also be unstable, thus water will act as a leaving group.
Thus, forming a keto or carbonyl group \[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\], this compound is called acetone.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(Cl)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[aq]{KOH}C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}+2KCl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Therefore, from the above statements we can conclude that the correct option is (c).
Note: Geminal dihalides are prepared by reacting a non-enolizable aldehyde and/or ketone with phosgene or thionyl chloride in the presence of an organic-phosphorus compound.
Complete step by step solution: Geminal dihalides are dihalogen compounds in which both the halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom.
For example, Ethylidene dichloride

Suppose, there is a geminal dihalide \[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(Cl)}_{2}}\] is present, the hydrolysis of gem-halides takes place in alkaline medium. So, we will hydrolyse it in the presence of aqueous NaOH/KOH.
On hydrolysis, both of the chlorine group will be replaced by hydroxyl group (OH),
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(OH)}_{2}}\] will be formed.
As both the hydroxyl groups are present on the same carbon, this compound is not stable. So, water acts as a leaving group i.e. \[{{H}_{2}}O\] will be removed.
Thus, forming an aldehyde group \[C{{H}_{3}}CHO\], this compound is called acetaldehyde. But this is the case when gem-dihalide is present at the terminal position.
\[C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(Cl)}_{2}}\xrightarrow[aq]{KOH}C{{H}_{3}}CH{{(OH)}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{3}}COH+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Now, let's take a compound \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(Cl)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\], on hydrolysis the chlorine groups will be replaced by hydroxyl groups, \[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(OH)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\]will be obtained.
Similarly, as the previous example, this compound will also be unstable, thus water will act as a leaving group.
Thus, forming a keto or carbonyl group \[C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}\], this compound is called acetone.
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{(Cl)}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[aq]{KOH}C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}+2KCl+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Therefore, from the above statements we can conclude that the correct option is (c).
Note: Geminal dihalides are prepared by reacting a non-enolizable aldehyde and/or ketone with phosgene or thionyl chloride in the presence of an organic-phosphorus compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




