
Gauss law in magnetism concludes that
a. Mono-pole does not exist
b. Magnetic flux can be determined
c. $\nabla \times B = 0$
d. $\nabla \cdot B = 0$
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Gauss’ law in magnetism states that the divergence of any magnetic field is zero. Divergence of a field is related with the outward or inward flow of any field but since magnetic field is a type of curl field, there is no outward or inward flow in it and hence the divergence is zero.
Gauss law in magnetism also suggests that magnetic monopoles do not exist.
Complete step by step answer:
Gauss law of magnetic field is a formal way of saying that magnetic monopoles do not exist.
Let us understand this by an example,
Let a circular loop in which $I$ current is flowing. The current is in anticlockwise sense as seen from our eye as shown in the figure.
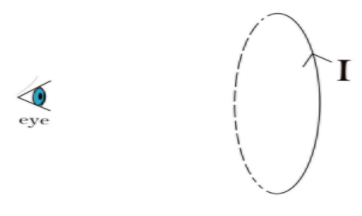
In general, we define poles by determining the sense of rotation of current. Anticlockwise current refers to a north pole and clockwise current refers to a south pole.
But when we cannot separate these two poles because they are described by the sense of motion of charge. Further we can say that the north and south pole in a loop emerges from the same thing (current) but are distinguished by the sense of rotation. They never meant to be separated.
That’s why magnetic monopoles do not exist.
According to Gauss law of magnetic field, net magnetic field through any closed gaussian surface is zero.
${\phi _B} = \oint \vec B \cdot {\text{d}}A = 0$
The magnetic flux associated with the magnetic field is defined in a way similar to electric flux. The unit of magnetic flux is $T{m^2} = Wb$ weber.
It also states that the divergence of the magnetic flux density is zero.
$\nabla \cdot B = 0$
Option a) and d) are correct
Additional information:
DIVERGENCE: in physical terms, the divergence of a vector field is the extent to which the vector field flux behaves like a source at a given point. If the divergence of a field is high it means that the outgoingness of the field is high. If the divergence of a field is low it means that the point is behaving less like a source or the outgoingness of the field is low.
Note: Divergence is calculated by the dot product of del ($\Delta $) operator and the given vector field.
Del operator is given by
$\Delta =\dfrac{d}{dx}\cdot i+\dfrac{d}{dy}\cdot j=\dfrac{d}{dz}\cdot k$
Gauss law in magnetism also suggests that magnetic monopoles do not exist.
Complete step by step answer:
Gauss law of magnetic field is a formal way of saying that magnetic monopoles do not exist.
Let us understand this by an example,
Let a circular loop in which $I$ current is flowing. The current is in anticlockwise sense as seen from our eye as shown in the figure.

In general, we define poles by determining the sense of rotation of current. Anticlockwise current refers to a north pole and clockwise current refers to a south pole.
But when we cannot separate these two poles because they are described by the sense of motion of charge. Further we can say that the north and south pole in a loop emerges from the same thing (current) but are distinguished by the sense of rotation. They never meant to be separated.
That’s why magnetic monopoles do not exist.
According to Gauss law of magnetic field, net magnetic field through any closed gaussian surface is zero.
${\phi _B} = \oint \vec B \cdot {\text{d}}A = 0$
The magnetic flux associated with the magnetic field is defined in a way similar to electric flux. The unit of magnetic flux is $T{m^2} = Wb$ weber.
It also states that the divergence of the magnetic flux density is zero.
$\nabla \cdot B = 0$
Option a) and d) are correct
Additional information:
DIVERGENCE: in physical terms, the divergence of a vector field is the extent to which the vector field flux behaves like a source at a given point. If the divergence of a field is high it means that the outgoingness of the field is high. If the divergence of a field is low it means that the point is behaving less like a source or the outgoingness of the field is low.
Note: Divergence is calculated by the dot product of del ($\Delta $) operator and the given vector field.
Del operator is given by
$\Delta =\dfrac{d}{dx}\cdot i+\dfrac{d}{dy}\cdot j=\dfrac{d}{dz}\cdot k$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




