
What is the function of kidneys in excretion? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Kidneys are two dark red, bean shaped organs situated at the back of the abdomen, one on either side of the vertebral column. The right kidney is lying slightly lower than the left. It mainly takes part in elimination of body wastes and to regulate the composition of body fluids and tissues.
Complete answer:
The human excretory system comprises a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. The main route by which the body eliminates substances is through the kidneys. The primary function of the kidney is the elimination of waste from the bloodstream by production of urine. Kidneys also perform several homeostatic functions such as:-
Maintaining volume of extracellular fluid
Maintaining ionic balance in extracellular fluid
Maintaining pH and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid.
Excreting toxic metabolic by-products such as ammonia, urea, and uric acid.
The structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each kidney comprises about one million (ten lakhs) of nephrons. Each nephron consists of Malpighian corpuscle and renal tubule. Malpighian corpuscle or renal corpuscle comprises glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule that take part in filtration of blood. Renal tubule consists of proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule that take part in selective reabsorption and tubular secretion. Once all these processes are completed, the needed materials go back into the bloodstream, and unneeded materials become urine and are gotten rid of.
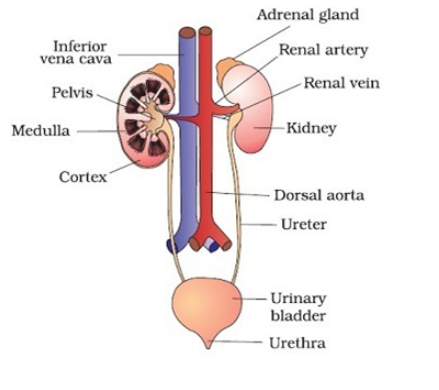
Note: The kidneys are considered as the most vital organs of the human body. The kidneys produce urine by eliminating toxic wastes and excess water from the body. Urine formed in each kidney passes through the ureter, flows into the bladder before finally being excreted through the urethra.
Complete answer:
The human excretory system comprises a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. The main route by which the body eliminates substances is through the kidneys. The primary function of the kidney is the elimination of waste from the bloodstream by production of urine. Kidneys also perform several homeostatic functions such as:-
Maintaining volume of extracellular fluid
Maintaining ionic balance in extracellular fluid
Maintaining pH and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid.
Excreting toxic metabolic by-products such as ammonia, urea, and uric acid.
The structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each kidney comprises about one million (ten lakhs) of nephrons. Each nephron consists of Malpighian corpuscle and renal tubule. Malpighian corpuscle or renal corpuscle comprises glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule that take part in filtration of blood. Renal tubule consists of proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule that take part in selective reabsorption and tubular secretion. Once all these processes are completed, the needed materials go back into the bloodstream, and unneeded materials become urine and are gotten rid of.

Note: The kidneys are considered as the most vital organs of the human body. The kidneys produce urine by eliminating toxic wastes and excess water from the body. Urine formed in each kidney passes through the ureter, flows into the bladder before finally being excreted through the urethra.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




