
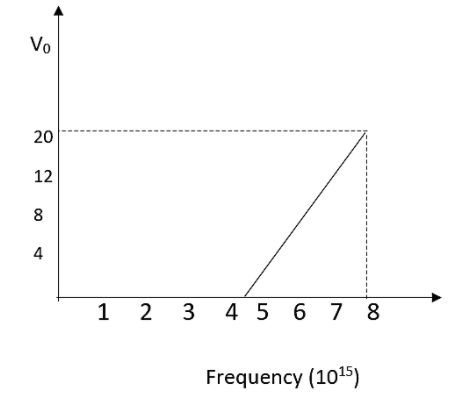
For photoelectric effect taking place in a metal, the graph of the stopping potential ${{V}_{0}}$ (in volt) versus frequency $\nu $ (in hertz) of the incident radiation is shown in figure. The work function of the metal (in eV) is
$\begin{align}
& A. 12.5 \\
& B. 14.5 \\
& C. 16.5 \\
& D. 18.5 \\
\end{align}$

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: first of all check the graph thoroughly in which the x intercept is the point up to which photoelectric effect will take place. Below this point there will be no photo electric effect taking place. The equation for the work function is also helpful in solving this question.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, let us take a look at what actually the photoelectric effect means. Photoelectric effect is defined as a phenomenon in which electrically charged particles are ejected from or within a substance when it is absorbing electromagnetic radiation. The effect is sometimes explained as the ejection of electrons from a metal plate when light shines on it.
The x-intercept in the graph given is being the last point up to which only the photoelectric effect is non zero. Below this point there is no photo electric effect.
Therefore the work function of the material is given by the equation,
$W=h{{\nu }_{0}}$
Where $h$ is the Planck’s constant, ${{\nu }_{0}}$ is the threshold frequency.
From the graph we got an information that,
${{\nu }_{0}}=4\times {{10}^{15}}Hz$
$h=6.63\times {{10}^{-34}}Js$
Substituting this values in the equation,
$\begin{align}
& W=6.63\times {{10}^{-34}}\times 4\times {{10}^{15}} \\
& W=26.52\times {{10}^{-19}}J \\
\end{align}$
Now we have to convert this into electron volt
$\begin{align}
& W=\dfrac{26.52\times {{10}^{-19}}}{1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}} \\
& W=16.5eV \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The phenomenon has been fundamentally peculiar in the progression of modern physics. The photoelectric effect stays important in the research areas from materials science to astrophysics and also produces the basis for a variety of useful equipment. The device using this effect is having a fast response time.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, let us take a look at what actually the photoelectric effect means. Photoelectric effect is defined as a phenomenon in which electrically charged particles are ejected from or within a substance when it is absorbing electromagnetic radiation. The effect is sometimes explained as the ejection of electrons from a metal plate when light shines on it.

The x-intercept in the graph given is being the last point up to which only the photoelectric effect is non zero. Below this point there is no photo electric effect.
Therefore the work function of the material is given by the equation,
$W=h{{\nu }_{0}}$
Where $h$ is the Planck’s constant, ${{\nu }_{0}}$ is the threshold frequency.
From the graph we got an information that,
${{\nu }_{0}}=4\times {{10}^{15}}Hz$
$h=6.63\times {{10}^{-34}}Js$
Substituting this values in the equation,
$\begin{align}
& W=6.63\times {{10}^{-34}}\times 4\times {{10}^{15}} \\
& W=26.52\times {{10}^{-19}}J \\
\end{align}$
Now we have to convert this into electron volt
$\begin{align}
& W=\dfrac{26.52\times {{10}^{-19}}}{1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}} \\
& W=16.5eV \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The phenomenon has been fundamentally peculiar in the progression of modern physics. The photoelectric effect stays important in the research areas from materials science to astrophysics and also produces the basis for a variety of useful equipment. The device using this effect is having a fast response time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




