
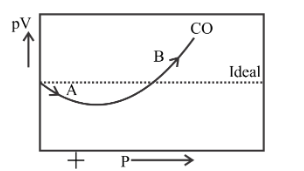
For $CO$, isotherm is of the type as shown. Near the point compressibility factor $Z$ is?
1.$\left( {1 + \dfrac{b}{V}} \right)$
2.$\left( {1 - \dfrac{b}{V}} \right)$
3.$\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{{RTV}}} \right)$
4.$\left( {1 - \dfrac{a}{{RTV}}} \right)$

Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: This question gives the knowledge about the compressibility factor and van der Waals gas equation. Compressibility factor is the factor which is used for transforming the ideal gas law to justify the behavior of real gases. It is also known as the gas deviation factor.
Formula used: The formula used to determine the compressibility factor for van der Waals gas equation is as follows:
$\left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)\left( {V - b} \right) = RT$
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$is the volume, $R$is the gas constants, $T$ is the temperature, $a$ and $b$ are van der Waals gas constants.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Van der Waals gas equation is the equation which corrects for the two properties of real gases: attractive forces between the gas molecules and the excluded volume
of gas particles.
Consider the van der Waals gas equation as follows:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)\left( {V - b} \right) = RT$
At very low pressure $P$ , volume $V$is very high.
$V - b \approx V$
Substitute $V - b$ as $V$ in the van der Waals gas equation.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)V = RT$
On simplifying the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow PV + \dfrac{a}{V} = RT$
On further simplifying, we have
$ \Rightarrow PV = RT - \dfrac{a}{V}$
Divide the above equation with $RT$,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}} = \dfrac{{RT}}{{RT}} - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
On further simplifying, we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}} = 1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
Consider this as equation $1$.
As we know,
Compressibility factor is the factor which is used for transforming the ideal gas law to justify the behavior of real gases. It is also known as the gas deviation factor. It is generally represented by $Z$.
$Z = \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}}$
Now, substitute $\dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}}$ as $Z$ in equation $1$ as follows:
$ \Rightarrow Z = 1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
Therefore, the compressibility factor $Z$ is $1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$.
Hence, option $4$ is correct.
Note: Van der Waals gas equation results in the correction of the two properties of real gases, one of which is attractive forces between the gas molecules and the second is the excluded volume of gaseous particles.
Formula used: The formula used to determine the compressibility factor for van der Waals gas equation is as follows:
$\left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)\left( {V - b} \right) = RT$
Where $P$ is the pressure, $V$is the volume, $R$is the gas constants, $T$ is the temperature, $a$ and $b$ are van der Waals gas constants.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Van der Waals gas equation is the equation which corrects for the two properties of real gases: attractive forces between the gas molecules and the excluded volume
of gas particles.
Consider the van der Waals gas equation as follows:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)\left( {V - b} \right) = RT$
At very low pressure $P$ , volume $V$is very high.
$V - b \approx V$
Substitute $V - b$ as $V$ in the van der Waals gas equation.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {P + \dfrac{a}{{{V^2}}}} \right)V = RT$
On simplifying the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow PV + \dfrac{a}{V} = RT$
On further simplifying, we have
$ \Rightarrow PV = RT - \dfrac{a}{V}$
Divide the above equation with $RT$,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}} = \dfrac{{RT}}{{RT}} - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
On further simplifying, we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}} = 1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
Consider this as equation $1$.
As we know,
Compressibility factor is the factor which is used for transforming the ideal gas law to justify the behavior of real gases. It is also known as the gas deviation factor. It is generally represented by $Z$.
$Z = \dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}}$
Now, substitute $\dfrac{{PV}}{{RT}}$ as $Z$ in equation $1$ as follows:
$ \Rightarrow Z = 1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$
Therefore, the compressibility factor $Z$ is $1 - \dfrac{a}{{VRT}}$.
Hence, option $4$ is correct.
Note: Van der Waals gas equation results in the correction of the two properties of real gases, one of which is attractive forces between the gas molecules and the second is the excluded volume of gaseous particles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




