
How do you find the values of all six trigonometric functions of a right triangle $ABC$ where $C$ is the right angle, given $a=20$, $b=21$, $c=29$?
Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have to calculate the values of six trigonometric ratios for a given right angled triangle. First, we will draw a diagram of the given right angled triangle with all the data we have. We need to represent all the data like side lengths, angels we have in the given problem. Now we will consider the two vertices other than the right angled vertex and we will write the adjacent, opposite ide to the respective vertex. Now we will use the basic definitions of the trigonometric ratios and calculate the values of the trigonometric ratios for both the vertices in the triangle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that, $ABC$ is a right-angle triangle with right angle at $C$. Hence the triangle $ABC$ is represented as
Now we have the values of side lengths of the above triangle as $a=20$, $b=21$, $c=29$. Now the above triangle is represented as
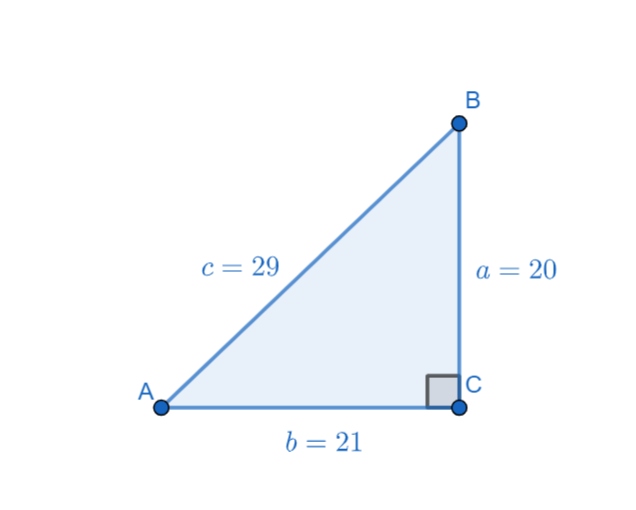
In the above triangle the hypotenuse is $AB=c=29$
Now considering the angle $\angle BAC$ in the above triangle. Adjacent side to the angle $\angle BAC$ is $AC=b=21$, Opposite side to the angle $\angle BAC$ is $BC=a=20$.
From the basic definitions of the trigonometric ratios, we have the values of all trigonometric ratios as
$\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{20}{29}$,
$\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{21}{29}$,
$\tan A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{20}{21}$,
$\cot A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{21}{20}$,
$\sec A=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{29}{21}$,
$\csc A=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{29}{20}$.
Now considering the angle $\angle ABC$ in the above triangle. Adjacent side to the angle $\angle ABC$ is $BC=a=20$, Opposite side to the angle $\angle ABC$ is $AC=b=21$.
From the basic definitions of the trigonometric ratios, we have the values of all trigonometric ratios as
$\sin B=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{21}{29}$,
$\cos B=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{20}{29}$,
$\tan B=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{21}{20}$,
$\cot B=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{20}{21}$,
$\sec B=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{29}{20}$,
$\csc B=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{29}{21}$.
Note: In this problem we have a lot of data related to triangles. So, it is easy to solve when we have the diagrammatic representation of the given data. Without representing the given triangle, it will be very hard to solve the problem.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that, $ABC$ is a right-angle triangle with right angle at $C$. Hence the triangle $ABC$ is represented as

Now we have the values of side lengths of the above triangle as $a=20$, $b=21$, $c=29$. Now the above triangle is represented as

In the above triangle the hypotenuse is $AB=c=29$
Now considering the angle $\angle BAC$ in the above triangle. Adjacent side to the angle $\angle BAC$ is $AC=b=21$, Opposite side to the angle $\angle BAC$ is $BC=a=20$.
From the basic definitions of the trigonometric ratios, we have the values of all trigonometric ratios as
$\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{20}{29}$,
$\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{21}{29}$,
$\tan A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{20}{21}$,
$\cot A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{21}{20}$,
$\sec A=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{29}{21}$,
$\csc A=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{29}{20}$.
Now considering the angle $\angle ABC$ in the above triangle. Adjacent side to the angle $\angle ABC$ is $BC=a=20$, Opposite side to the angle $\angle ABC$ is $AC=b=21$.
From the basic definitions of the trigonometric ratios, we have the values of all trigonometric ratios as
$\sin B=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{21}{29}$,
$\cos B=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}=\dfrac{20}{29}$,
$\tan B=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{21}{20}$,
$\cot B=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{20}{21}$,
$\sec B=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Adjacent side}\left( a \right)}=\dfrac{29}{20}$,
$\csc B=\dfrac{\text{Hypotenuse}\left( c \right)}{\text{Opposite side}\left( b \right)}=\dfrac{29}{21}$.
Note: In this problem we have a lot of data related to triangles. So, it is easy to solve when we have the diagrammatic representation of the given data. Without representing the given triangle, it will be very hard to solve the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




