
How do you find the turning points of a cubic function?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: The gradient of the turning point of a curve is found by calculating the gradient of the tangent of that point. These tangents have positive and negative gradients. The horizontal tangents have zero gradient. The point which is at zero gradient is called the turning point.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we will take an example, we will solve an equation to know how to find the turning point of a cubic function. The equation is \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\].
First, we have to differentiate the given cubic equation. This will give us the derivative. The derivative is the rate of change of function at a point equivalent to the tangent drawn.
Each term of the cubic equation is in the form of \[y = a{x^n}\]. So, to differentiate, we need to apply the differentiating method,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = na{x^{n - 1}}\]
Applying this rule to the terms in the cubic equations, which is differentiating the first term of the equation \[2{x^3}\]gives us,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 6{x^2}\]
On differentiating the second term of the equation we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 10x\]
On differentiating the third term of the equation we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1\]
Finally, differentiating the last term of the equation, we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 0\]
The turning point of the gradient is \[0\]. So, equate the differentiated equation to \[0\].
\[ \Rightarrow 6{x^2} + 10x - 1 = 0\]
This is a quadratic equation. To solve this quadratic equation, we will use the formula for the quadratic equation which is,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}\], \[where\,a,b\,and\,c\,\]are constants.
Now comparing both the quadratic equations we get that \[a = 6,\,b = 10,\,c = - 1\]
Putting the values of \[a,b\,and\,c\]in the quadratic formula we get,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - 10 \pm \sqrt {{{10}^2} - (4 \cdot 6 \cdot ( - 1))} }}{{2 \cdot 6}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 10 \pm \sqrt {100 + 24} }}{{12}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 10 + \sqrt {124} }}{{12}}\] and \[x = \dfrac{{ - 10 - \sqrt {124} }}{{12}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 0.09642\] and \[x = - 1.76129\]
When we put the value of \[x = 0.09642\] into the equation \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\] and we get:
\[y = - 6.048\]
This gives us the first value of the turning point:
Turning point = \[(0.095, - 6.048)\] = \[(0.10, - 6.05)\] to two decimal places.
Then we need to substitute the second value of \[x = - 1.76129\] we get in the equation \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\] and we get: \[y = 0.344\]
So, now turning point = \[( - 1.761,0.344) = ( - 1.76,0.34)\]
Now, we will graph the points in the graph paper and see what kind of curve we get.
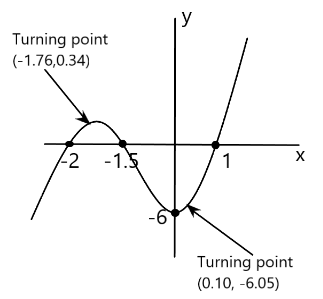
So, this is how we find the turning points of a cubic function and make the graph.
Note: The above method is easy to solve. But there is another method. It is called the Hit and Trial Method in which we take our desired values and put that in the equation and try to solve. Generally the values which we take should be the values which are more prone to be correct.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we will take an example, we will solve an equation to know how to find the turning point of a cubic function. The equation is \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\].
First, we have to differentiate the given cubic equation. This will give us the derivative. The derivative is the rate of change of function at a point equivalent to the tangent drawn.
Each term of the cubic equation is in the form of \[y = a{x^n}\]. So, to differentiate, we need to apply the differentiating method,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = na{x^{n - 1}}\]
Applying this rule to the terms in the cubic equations, which is differentiating the first term of the equation \[2{x^3}\]gives us,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 6{x^2}\]
On differentiating the second term of the equation we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 10x\]
On differentiating the third term of the equation we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1\]
Finally, differentiating the last term of the equation, we get,
\[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 0\]
The turning point of the gradient is \[0\]. So, equate the differentiated equation to \[0\].
\[ \Rightarrow 6{x^2} + 10x - 1 = 0\]
This is a quadratic equation. To solve this quadratic equation, we will use the formula for the quadratic equation which is,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}\], \[where\,a,b\,and\,c\,\]are constants.
Now comparing both the quadratic equations we get that \[a = 6,\,b = 10,\,c = - 1\]
Putting the values of \[a,b\,and\,c\]in the quadratic formula we get,
\[x = \dfrac{{ - 10 \pm \sqrt {{{10}^2} - (4 \cdot 6 \cdot ( - 1))} }}{{2 \cdot 6}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 10 \pm \sqrt {100 + 24} }}{{12}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{ - 10 + \sqrt {124} }}{{12}}\] and \[x = \dfrac{{ - 10 - \sqrt {124} }}{{12}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 0.09642\] and \[x = - 1.76129\]
When we put the value of \[x = 0.09642\] into the equation \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\] and we get:
\[y = - 6.048\]
This gives us the first value of the turning point:
Turning point = \[(0.095, - 6.048)\] = \[(0.10, - 6.05)\] to two decimal places.
Then we need to substitute the second value of \[x = - 1.76129\] we get in the equation \[2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - 6\] and we get: \[y = 0.344\]
So, now turning point = \[( - 1.761,0.344) = ( - 1.76,0.34)\]
Now, we will graph the points in the graph paper and see what kind of curve we get.

So, this is how we find the turning points of a cubic function and make the graph.
Note: The above method is easy to solve. But there is another method. It is called the Hit and Trial Method in which we take our desired values and put that in the equation and try to solve. Generally the values which we take should be the values which are more prone to be correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




